System Reference Manual
Encyclopedia
Firmware
In electronic systems and computing, firmware is a term often used to denote the fixed, usually rather small, programs and/or data structures that internally control various electronic devices...
written by Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation was a major American company in the computer industry and a leading vendor of computer systems, software and peripherals from the 1960s to the 1990s...
(DEC) for computer systems based on the Alpha AXP microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
. The acronym SRM is derived from the phrase Alpha System Reference Manual, the publication detailing the Alpha AXP architecture and which specified various features of the SRM firmware.
The SRM console was initially designed to boot DEC's OSF/1 AXP (later called Digital UNIX and finally Tru64 UNIX) and OpenVMS
OpenVMS
OpenVMS , previously known as VAX-11/VMS, VAX/VMS or VMS, is a computer server operating system that runs on VAX, Alpha and Itanium-based families of computers. Contrary to what its name suggests, OpenVMS is not open source software; however, the source listings are available for purchase...
operating systems, although various other operating systems (such as Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
, NetBSD
NetBSD
NetBSD is a freely available open source version of the Berkeley Software Distribution Unix operating system. It was the second open source BSD descendant to be formally released, after 386BSD, and continues to be actively developed. The NetBSD project is primarily focused on high quality design,...
, OpenBSD
OpenBSD
OpenBSD is a Unix-like computer operating system descended from Berkeley Software Distribution , a Unix derivative developed at the University of California, Berkeley. It was forked from NetBSD by project leader Theo de Raadt in late 1995...
, and FreeBSD
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free Unix-like operating system descended from AT&T UNIX via BSD UNIX. Although for legal reasons FreeBSD cannot be called “UNIX”, as the direct descendant of BSD UNIX , FreeBSD’s internals and system APIs are UNIX-compliant...
, for example) were also written to boot from the SRM console. The third proprietary operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
published for the Alpha AXP architecture – Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
Windows NT
Windows NT
Windows NT is a family of operating systems produced by Microsoft, the first version of which was released in July 1993. It was a powerful high-level-language-based, processor-independent, multiprocessing, multiuser operating system with features comparable to Unix. It was intended to complement...
– did not boot from SRM; instead, Windows booted from the ARC
Advanced RISC Computing
Advanced RISC Computing is a specification promulgated by a defunct consortium of computer manufacturers , setting forth a standard MIPS RISC-based computer hardware and firmware environment....
boot firmware. (ARC is also known as AlphaBIOS.)
On many Alpha computer systems – for example, the Digital Personal Workstation
Digital Personal Workstation
The Digital Personal Workstation is a family of entry-level to mid-range workstation computers developed and manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation . These workstations are based on the DEC Alpha and Intel Pentium Pro or Pentium II microprocessors...
– both SRM and ARC could be loaded onto the EEPROM
EEPROM
EEPROM stands for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory and is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices to store small amounts of data that must be saved when power is removed, e.g., calibration...
which held the boot firmware. However, on some smaller systems (or large systems which were never intended to boot Windows), only one of the two boot firmwares could fit onto the EEPROM at one time. For example, the flash EEPROM of the DEC Multia
DEC Multia
The Multia, later re-branded the Universal Desktop Box, was a line of desktop computers introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation on 7 November 1994. The line is notable in that units were offered with either an Alpha AXP or Intel Pentium processor as the CPU, and most hardware other than the...
, which was a small, personal Alpha AXP workstation designed to run Windows NT, was only large enough to hold a single firmware.
The SRM console is capable of display on either a graphical adapter (such as a PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Conventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
VGA
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
card) or, if no graphical console and/or local keyboard is detected, on a serial connection to a VT100
VT100
The VT100 is a video terminal that was made by Digital Equipment Corporation . Its detailed attributes became the de facto standard for terminal emulators.-History:...
-compatible terminal. In this way the SRM console is similar to the Open Firmware
Open Firmware
Open Firmware, or OpenBoot in Sun Microsystems parlance, is a standard defining the interfaces of a computer firmware system, formerly endorsed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers . It originated at Sun, and has been used by Sun, Apple, IBM, and most other non-x86 PCI chipset...
used in SPARC
SPARC
SPARC is a RISC instruction set architecture developed by Sun Microsystems and introduced in mid-1987....
and Apple
Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs and markets consumer electronics, computer software, and personal computers. The company's best-known hardware products include the Macintosh line of computers, the iPod, the iPhone and the iPad...
PowerMac computers, for example.
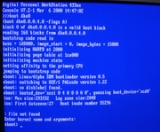
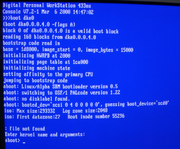
Upon system initialization, an Alpha AXP computer set to boot from the SRM console displays a short report of the software version of the firmware, and presents a prompt consisting of a series of brackets:
Digital Personal WorkStation 433u
Console V7.2-1 Mar 6 2000 14:47:02
>>>
Several commands are available by typing them at the prompt, and a list of possible commands is available by entering the command
help or man at the prompt. Various system variables for establishing automatic boot settings, parameter strings to be passed to an operating system and the like may also be set from the SRM prompt. The SRM firmware contains drivers for booting from boot media including SCSI hard disks and CD-ROM drives attached to a supported SCSI adapter, various IDE ATA and ATAPI devices, and network booting via BOOTPBOOTP
In computer networking, the Bootstrap Protocol, or BOOTP, is a network protocol used by a network client to obtain an IP address from a configuration server. The BOOTP protocol was originally defined in RFC 951....
or DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a network configuration protocol for hosts on Internet Protocol networks. Computers that are connected to IP networks must be configured before they can communicate with other hosts. The most essential information needed is an IP address, and a default...
is possible with supported network adapters.
When an appropriate disk boot device is available, the SRM console locates and loads the target primary bootstrap image using information written in the target disk boot block; in logical block zero. The boot block contains the disk location and block size of the target primary bootstrap image file, and SRM will load that into memory and will then transfer control to it.

