
Surface wave magnitude
Encyclopedia
The surface wave magnitude (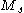 ) scale is one of the magnitude scales used in seismology
) scale is one of the magnitude scales used in seismology
to describe the size of an earthquake
. It is based on measurements in Rayleigh surface waves
that travel primarily along the uppermost layers of the earth. It is currently used in People's Republic of China
as a national standard (GB 17740-1999) for categorising earthquakes.
Surface wave magnitude was initially developed in 1950s by the same researchers who developed the local magnitude scale ML in order to improve resolution on larger earthquakes:
Recorded magnitudes of earthquakes during that time, commonly attributed to Richter
, could be either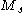 or
or 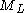 .
.
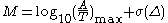
where A is the maximum particle displacement
in surface waves (vector sum of the two horizontal displacements) in μm
, T is the corresponding period in s
, Δ is the epicentral distance in °
, and
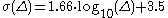
According to GB 17740-1999, the two horizontal displacements must be measured at the same time or within 1/8 of a period; if the two displacements have different periods, weighed sum must be used:
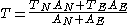
where AN is the north-south displacement in μm, AE is the east-west displacement in μm, TN is the period corresponding to AN in s, and TE is the period corresponding to AE in s.

Other formulas include three revised formulae proposed by CHEN Junjie et al.:

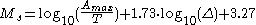
and

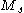 ) scale is one of the magnitude scales used in seismology
) scale is one of the magnitude scales used in seismologySeismology
Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. The field also includes studies of earthquake effects, such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, oceanic,...
to describe the size of an earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
. It is based on measurements in Rayleigh surface waves
Rayleigh wave
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travels on solids. They are produced on the Earth by earthquakes, in which case they are also known as "ground roll", or by other sources of seismic energy such as ocean waves an explosion or even a sledgehammer impact...
that travel primarily along the uppermost layers of the earth. It is currently used in People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
as a national standard (GB 17740-1999) for categorising earthquakes.
Surface wave magnitude was initially developed in 1950s by the same researchers who developed the local magnitude scale ML in order to improve resolution on larger earthquakes:
Recorded magnitudes of earthquakes during that time, commonly attributed to Richter
Richter magnitude scale
The expression Richter magnitude scale refers to a number of ways to assign a single number to quantify the energy contained in an earthquake....
, could be either
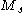 or
or 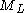 .
.Definition
The formula to calculate surface wave magnitude is: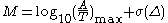
where A is the maximum particle displacement
Particle displacement
Particle displacement or particle amplitude is a measurement of distance of the movement of a particle from its equilibrium position in a medium as it transmits a wave....
in surface waves (vector sum of the two horizontal displacements) in μm
Micrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
, T is the corresponding period in s
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
, Δ is the epicentral distance in °
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
, and
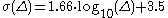
According to GB 17740-1999, the two horizontal displacements must be measured at the same time or within 1/8 of a period; if the two displacements have different periods, weighed sum must be used:
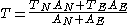
where AN is the north-south displacement in μm, AE is the east-west displacement in μm, TN is the period corresponding to AN in s, and TE is the period corresponding to AE in s.
Other studies
Vladimír Tobyáš and Reinhard Mittag proposed to relate surface wave magnitude to local magnitude scale ML, using
Other formulas include three revised formulae proposed by CHEN Junjie et al.:

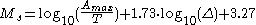
and

External links
- Visual Glossary - magnitude - USGSUnited States Geological SurveyThe United States Geological Survey is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization has four major science disciplines, concerning biology,...
- Earthquake Size

