Sum rule in quantum mechanics
Encyclopedia
In quantum mechanics
, a sum rule is a formula for transitions between energy levels, in which the sum of the transition strengths is expressed in a simple form. Sum rules are used to describe the properties of many physical systems, including solids, atoms, atomic nuclei, and nuclear constituents such as protons and neutrons.
The sum rules are derived from quite general principles, and are useful in situations where the behavior of individual energy levels is too complex to describe by a precise quantum-mechanical theory. In general, sum rules are derived by using Heisenberg's quantum-mechanical algebra to construct operator equalities, which are then applied to particles or the energy levels of a system.
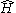 has a complete
has a complete
set of eigenfunctions with eigenvalues
with eigenvalues
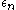 :
: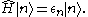
For the Hermitian operator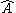 we define the
we define the
repeated commutator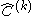 by:
by:
The operator is Hermitian since
is Hermitian since 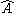
is defined to be Hermitian. The operator is
is
anti-Hermitian:
By induction one finds: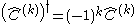
and also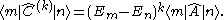
For a Hermitian operator we have
Using this relation we derive:
The result can be written as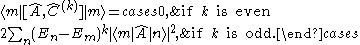
For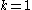 this gives:
this gives: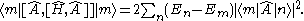
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, a sum rule is a formula for transitions between energy levels, in which the sum of the transition strengths is expressed in a simple form. Sum rules are used to describe the properties of many physical systems, including solids, atoms, atomic nuclei, and nuclear constituents such as protons and neutrons.
The sum rules are derived from quite general principles, and are useful in situations where the behavior of individual energy levels is too complex to describe by a precise quantum-mechanical theory. In general, sum rules are derived by using Heisenberg's quantum-mechanical algebra to construct operator equalities, which are then applied to particles or the energy levels of a system.
Derivation of sum rules
Assume that the HamiltonianHamiltonian (quantum mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, the Hamiltonian H, also Ȟ or Ĥ, is the operator corresponding to the total energy of the system. Its spectrum is the set of possible outcomes when one measures the total energy of a system...
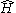 has a complete
has a completeset of eigenfunctions
 with eigenvalues
with eigenvalues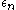 :
: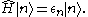
For the Hermitian operator
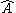 we define the
we define therepeated commutator
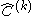 by:
by:
The operator
 is Hermitian since
is Hermitian since 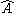
is defined to be Hermitian. The operator
 is
isanti-Hermitian:

By induction one finds:
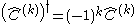
and also
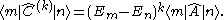
For a Hermitian operator we have

Using this relation we derive:

The result can be written as
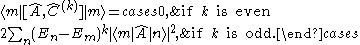
For
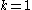 this gives:
this gives: