
Student's t-statistic
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the t-statistic is a ratio of the departure of an estimated parameter from its notional value and its standard error
. It is used in hypothesis testing
, for example in the Student's t-test
, in the augmented Dickey–Fuller test, and in bootstrapping
.
. Then a t-statistic for this parameter is any quantity of the form
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the t-statistic is a ratio of the departure of an estimated parameter from its notional value and its standard error
Standard error (statistics)
The standard error is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic. The term may also be used to refer to an estimate of that standard deviation, derived from a particular sample used to compute the estimate....
. It is used in hypothesis testing
Statistical hypothesis testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of making decisions using data, whether from a controlled experiment or an observational study . In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, according to a pre-determined threshold...
, for example in the Student's t-test
Student's t-test
A t-test is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's t distribution if the null hypothesis is supported. It is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution if the value of a scaling term in the test statistic were known...
, in the augmented Dickey–Fuller test, and in bootstrapping
Bootstrapping (statistics)
In statistics, bootstrapping is a computer-based method for assigning measures of accuracy to sample estimates . This technique allows estimation of the sample distribution of almost any statistic using only very simple methods...
.
Definition
Let be an estimator of parameter β in some statistical modelStatistical model
A statistical model is a formalization of relationships between variables in the form of mathematical equations. A statistical model describes how one or more random variables are related to one or more random variables. The model is statistical as the variables are not deterministically but...
. Then a t-statistic for this parameter is any quantity of the form
-

where β0 is a non-random, known constant, and is the standard errorStandard error (statistics)The standard error is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic. The term may also be used to refer to an estimate of that standard deviation, derived from a particular sample used to compute the estimate....
of the estimator . By default, statistical packages report t-statistic with (these t-statistics are used to test the significance of corresponding regressor). However, when t-statistic is needed to test the hypothesis of the form , then a non-zero β0 may be used.
If is an ordinary least squaresOrdinary least squaresIn statistics, ordinary least squares or linear least squares is a method for estimating the unknown parameters in a linear regression model. This method minimizes the sum of squared vertical distances between the observed responses in the dataset and the responses predicted by the linear...
estimator in the classical linear regression model (that is, with normally distributed and homoskedasticHomoscedasticityIn statistics, a sequence or a vector of random variables is homoscedastic if all random variables in the sequence or vector have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity...
error terms), and if the true value of parameter β is equal to β0, then the sampling distributionSampling distributionIn statistics, a sampling distribution or finite-sample distribution is the probability distribution of a given statistic based on a random sample. Sampling distributions are important in statistics because they provide a major simplification on the route to statistical inference...
of the t-statistic is the Student’s t-distribution with degrees of freedom, where n is the number of observations, and k is the number of regressors (including the intercept).
In the majority of models the estimator is consistent for β and distributed asymptotically normally. If the true value of parameter β is equal to β0 and the quantity correctly estimates the asymptotic variance of this estimator, then the t-statistic will have asymptotically the standard normal distribution.
In some models the distribution of t-statistic is different from normal, even asymptotically. For example, when a time seriesTime seriesIn statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
with unit rootUnit rootIn time series models in econometrics , a unit root is a feature of processes that evolve through time that can cause problems in statistical inference if it is not adequately dealt with....
is regressed in the augmented Dickey–Fuller test, the test t-statistic will asymptotically have one of the Dickey–Fuller distributions (depending on the test setting).
Use
Most frequently, t-statistics are used in Student's t-testStudent's t-testA t-test is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's t distribution if the null hypothesis is supported. It is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution if the value of a scaling term in the test statistic were known...
s, a form of statistical hypothesis testingStatistical hypothesis testingA statistical hypothesis test is a method of making decisions using data, whether from a controlled experiment or an observational study . In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, according to a pre-determined threshold...
, and in the computation of certain confidence intervalConfidence intervalIn statistics, a confidence interval is a particular kind of interval estimate of a population parameter and is used to indicate the reliability of an estimate. It is an observed interval , in principle different from sample to sample, that frequently includes the parameter of interest, if the...
s.
The key property of the t-statistic is that it is a pivotal quantityPivotal quantityIn statistics, a pivotal quantity or pivot is a function of observations and unobservable parameters whose probability distribution does not depend on unknown parameters....
– while defined in terms of the sample mean, its sampling distribution does not depend on the sample parameters, and thus it can be used regardless of what these may be.
One can also divide a residualErrors and residuals in statisticsIn statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
by the sample standard deviation: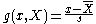
to compute an estimate for the number of standard deviations a given sample is from the mean, as a sample version of a z-score, the z-score requiring the population parameters.
Prediction
Given a normal distribution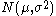 with unknown mean and variance, the t-statistic of a future observation
with unknown mean and variance, the t-statistic of a future observation  after one has made n observations, is an ancillary statisticAncillary statisticIn statistics, an ancillary statistic is a statistic whose sampling distribution does not depend on which of the probability distributions among those being considered is the distribution of the statistical population from which the data were taken...
after one has made n observations, is an ancillary statisticAncillary statisticIn statistics, an ancillary statistic is a statistic whose sampling distribution does not depend on which of the probability distributions among those being considered is the distribution of the statistical population from which the data were taken...
– a pivotal quantity (does not depend on the values of μ and σ2) that is a statistic (computed from observations). This allows one to compute a frequentist prediction intervalPrediction intervalIn statistical inference, specifically predictive inference, a prediction interval is an estimate of an interval in which future observations will fall, with a certain probability, given what has already been observed...
(a predictive confidence intervalConfidence intervalIn statistics, a confidence interval is a particular kind of interval estimate of a population parameter and is used to indicate the reliability of an estimate. It is an observed interval , in principle different from sample to sample, that frequently includes the parameter of interest, if the...
), via the following t-distribution:
Solving for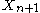 yields the prediction distribution
yields the prediction distribution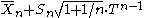
from which one may compute predictive confidence intervals – given a probability p, one may compute intervals such that 100p% of the time, the next observation will fall in that interval.
will fall in that interval.
History
The term "t-statistic" is abbreviated from "test statistic", while "Student" was the pen name of William Sealy GossetWilliam Sealy GossetWilliam Sealy Gosset is famous as a statistician, best known by his pen name Student and for his work on Student's t-distribution....
, who introduced the t-statistic and t-test in 1908, while working for the GuinnessGuinnessGuinness is a popular Irish dry stout that originated in the brewery of Arthur Guinness at St. James's Gate, Dublin. Guinness is directly descended from the porter style that originated in London in the early 18th century and is one of the most successful beer brands worldwide, brewed in almost...
breweryBreweryA brewery is a dedicated building for the making of beer, though beer can be made at home, and has been for much of beer's history. A company which makes beer is called either a brewery or a brewing company....
in Dublin, Ireland.
Related concepts
z-score: If the population parameters are known, then rather than computing the t-statistic, one can compute the z-score; analogously, rather than using a t-test, one uses a z-testZ-testA Z-test is any statistical test for which the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis can be approximated by a normal distribution. Due to the central limit theorem, many test statistics are approximately normally distributed for large samples...
. This is rare outside of standardized testing.
Studentized residualStudentized residualIn statistics, a studentized residual is the quotient resulting from the division of a residual by an estimate of its standard deviation. Typically the standard deviations of residuals in a sample vary greatly from one data point to another even when the errors all have the same standard...
: In regression analysisRegression analysisIn statistics, regression analysis includes many techniques for modeling and analyzing several variables, when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables...
, the standard errors of the estimators at different data points vary (compare the middle versus endpoints of a simple linear regressionSimple linear regressionIn statistics, simple linear regression is the least squares estimator of a linear regression model with a single explanatory variable. In other words, simple linear regression fits a straight line through the set of n points in such a way that makes the sum of squared residuals of the model as...
), and thus one must divide the different residuals by different estimates for the error, yielding what are called studentized residualStudentized residualIn statistics, a studentized residual is the quotient resulting from the division of a residual by an estimate of its standard deviation. Typically the standard deviations of residuals in a sample vary greatly from one data point to another even when the errors all have the same standard...
s.
See also
- F-testF-testAn F-test is any statistical test in which the test statistic has an F-distribution under the null hypothesis.It is most often used when comparing statistical models that have been fit to a data set, in order to identify the model that best fits the population from which the data were sampled. ...
- Student's t-distribution
- Student's t-testStudent's t-testA t-test is any statistical hypothesis test in which the test statistic follows a Student's t distribution if the null hypothesis is supported. It is most commonly applied when the test statistic would follow a normal distribution if the value of a scaling term in the test statistic were known...
External links
- What is a t statistic? at The Children's Mercy Hospital
- F-test

