Stryker's reagent
Encyclopedia
Stryker's reagent
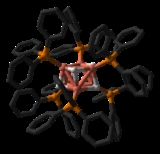
Stryker's reagent ([(PPh3)CuH]6, also known as the Osborn complex, is a hexameric copper hydride ligated with triphenylphosphine
. It is a brick red crystalline solid that is very sensitive to air. Stryker's reagent is a mild hydride source and is used in homogeneous catalysis of conjugate reduction reactions of various compounds (enones, enoates, etc).
and sodium tert-butoxide, and pressurized hydrogen
. It can be directly prepared from copper(II) salts as well. If stored under an inert atmosphere (e.g. argon, nitrogen) it has indefinite shelf life. Brief exposure to the oxygen does not destroy its activity significantly, although solvents used with Stryker's reagent should be rigorously degassed. It can effect highly regioselective conjugate reductions of various carbonyl derivatives including unsaturated aldehydes, ketones, and esters. This reagent was assigned as the "Reagent of the year" in 1991 for its functional group tolerance, high overall efficiency, and mild reaction conditions in the reduction reactions. Stryker's reagent is used in a catalytic amount where it is regenerated in the reaction in situ using a stoichiometric hydride source, often being molecular hydrogen or silanes
Stryker's reagent ([(PPh3)CuH]6, also known as the Osborn complex, is a hexameric copper hydride ligated with triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P3 - often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature...
. It is a brick red crystalline solid that is very sensitive to air. Stryker's reagent is a mild hydride source and is used in homogeneous catalysis of conjugate reduction reactions of various compounds (enones, enoates, etc).
Preparation and Stability
Stryker's reagent is prepared from copper(I) tert-butoxide, generated in situ from copper(I) chlorideCopper(I) chloride
Copper chloride, commonly called cuprous chloride, is the lower chloride of copper, with the formula CuCl. The substance is a white solid sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid...
and sodium tert-butoxide, and pressurized hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
. It can be directly prepared from copper(II) salts as well. If stored under an inert atmosphere (e.g. argon, nitrogen) it has indefinite shelf life. Brief exposure to the oxygen does not destroy its activity significantly, although solvents used with Stryker's reagent should be rigorously degassed. It can effect highly regioselective conjugate reductions of various carbonyl derivatives including unsaturated aldehydes, ketones, and esters. This reagent was assigned as the "Reagent of the year" in 1991 for its functional group tolerance, high overall efficiency, and mild reaction conditions in the reduction reactions. Stryker's reagent is used in a catalytic amount where it is regenerated in the reaction in situ using a stoichiometric hydride source, often being molecular hydrogen or silanes

