
Standard enthalpy change of vaporization
Encyclopedia
.png)
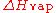 ), also known as the heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the energy
), also known as the heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the energyEnergy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
required to transform a given quantity of a substance into a gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
at a given pressure (often atmospheric pressure).
It is often measured at the normal boiling point of a substance; although tabulated values are usually corrected to 298 K
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
, the correction is often smaller than the uncertainty
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
in the measured value.
The heat of vaporization is temperature-dependent, though a constant heat of vaporization can be assumed for small temperature ranges and below Tr<<1.0. The heat of vaporization diminishes with increasing temperature and it vanishes completely at the critical temperature (Tr=1) because above the critical temperature the liquid
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
and vapor
Vapor
A vapor or vapour is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical point....
phases no longer co-exist.
Units
Values are usually quoted in JJoule
The joule ; symbol J) is a derived unit of energy or work in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy expended in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre , or in passing an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second...
/mol
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
or kJ/mol (molar enthalpy of vaporization), although kJ/kg or J/g (specific heat of vaporization), and older units like kcal
Calorie
The calorie is a pre-SI metric unit of energy. It was first defined by Nicolas Clément in 1824 as a unit of heat, entering French and English dictionaries between 1841 and 1867. In most fields its use is archaic, having been replaced by the SI unit of energy, the joule...
/mol, cal/g and Btu
British thermal unit
The British thermal unit is a traditional unit of energy equal to about 1055 joules. It is approximately the amount of energy needed to heat of water, which is exactly one tenth of a UK gallon or about 0.1198 US gallons, from 39°F to 40°F...
/lb are sometimes still used, among others.
Physical model for vaporization
A simple physical model for the liquid-gas phase transformation has been proposed recently. It is suggested that the energy required to free an atom from the liquid is equivalent to the energy needed to overcome the surface resistance of the liquid. The model allows calculating the latent heat by multiplying the maximum surface area covering an atom (Fig. 1) with the surface tension and the number of atoms in the liquid. The calculated latent heat of vaporization values for the investigated 45 elements agrees well with experiments.Enthalpy of condensation
The enthalpy of condensation (or heat of condensation) is by definition equal to the enthalpy of vaporization with the opposite sign: enthalpy changes of vaporization are always positive (heatHeat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
is absorbed by the substance), whereas enthalpy changes of condensation are always negative (heat is released by the substance).
Thermodynamic background
.png)
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
has a particularly low enthalpy of vaporization, 0.0845 kJ/mol, as the van der Waals force
Van der Waals force
In physical chemistry, the van der Waals force , named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds or to the electrostatic interaction of ions with one another or with neutral...
s between helium atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s are particularly weak. On the other hand, the molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s in liquid water are held together by relatively strong hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
s, and its enthalpy of vaporization, 40.65 kJ/mol, is more than five times the energy required to heat the same quantity of water from 0 °C to 100 °C (cp
Heat capacity
Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount...
= 75.3 J K−1 mol−1). Care must be taken, however, when using enthalpies of vaporization to measure the strength of intermolecular forces, as these forces may persist to an extent in the gas phase (as is the case with hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula HF. This colorless gas is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the aqueous form as hydrofluoric acid, and thus is the precursor to many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers . HF is widely used in the...
), and so the calculated value of the bond strength
Bond strength
In chemistry, bond strength is measured between two atoms joined in a chemical bond. It is the degree to which each atom linked to another atom contributes to the valency of this other atom...
will be too low. This is particularly true of metals, which often form covalently bonded
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding....
molecules in the gas phase: in these cases, the enthalpy of atomization must be used to obtain a true value of the bond energy
Bond energy
In chemistry, bond energy is the measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. It is the heat required to break one Mole of molecules into their individual atoms. For example, the carbon-hydrogen bond energy in methane E is the enthalpy change involved with breaking up one molecule of methane into...
.
An alternative description is to view the enthalpy of condensation as the heat which must be released to the surroundings to compensate for the drop in entropy
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
when a gas condenses to a liquid. As the liquid and gas are in equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
at the boiling point (Tb), ΔvG
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
= 0, which leads to:

As neither entropy nor enthalpy
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
vary greatly with temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, it is normal to use the tabulated standard values without any correction for the difference in temperature from 298 K. A correction must be made if the pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
is different from 100 kPa
Pascal (unit)
The pascal is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square metre...
, as the entropy of a gas is proportional to its pressure (or, more precisely, to its fugacity
Fugacity
In chemical thermodynamics, the fugacity of a real gas is an effective pressure which replaces the true mechanical pressure in accurate chemical equilibrium calculations. It is equal to the pressure of an ideal gas which has the same chemical potential as the real gas. For example, nitrogen gas ...
): the entropies of liquids vary little with pressure, as the compressibility of a liquid is small.
These two definitions are equivalent: the boiling point is the temperature at which the increased entropy of the gas phase overcomes the intermolecular forces. As a given quantity of matter always has a higher entropy in the gas phase than in a condensed phase (
 is always positive), and from
is always positive), and from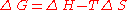 ,
,the Gibbs free energy
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
change falls with increasing temperature: gases are favored at higher temperatures, as is observed in practice.
Vaporization enthalpy of electrolyte solutions
Estimation of the enthalpy of vaporization of electrolyte solutions can be simply carried out using equations based on the chemical thermodynamic models, such as Pitzer model or TCPC model.Elements
Enthalpies of vaporization of the elements in kJ/mol, measured at their respective normal boiling points| Group Periodic table group In chemistry, a group is a vertical column in the periodic table of the chemical elements. There are 18 groups in the standard periodic table, including the d-block elements, but excluding the f-block elements.... → |
1 Alkali metal The alkali metals are a series of chemical elements in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkali metals comprise the group 1 elements, along with hydrogen. The alkali metals are lithium , sodium , potassium , rubidium , caesium , and francium... |
2 Alkaline earth metal The alkaline earth metals are a group in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkaline earth metals are called the group 2 elements. Previously, they were called the Group IIA elements . The alkaline earth metals contain beryllium , magnesium , calcium , strontium , barium and... |
3 Group 3 element The group 3 elements are a group of chemical elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group... |
4 Group 4 element The Group 4 elements are a group of chemical elements in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, Group 4 of the periodic table contains titanium , zirconium , hafnium and rutherfordium . This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table... |
5 Group 5 element A Group 5 element is a chemical element in the fifth group in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, Group 5 of the periodic table contains vanadium , niobium , tantalum and dubnium . This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table... |
6 Group 6 element A Group 6 element is one in the series of elements in group 6 in the periodic table, which consists of the transition metals chromium , molybdenum , tungsten , and seaborgium .... |
7 Group 7 element A Group 7 element is one in the series of elements in group 7 in the periodic table, which consists of manganese , technetium , rhenium , and bohrium... |
8 Group 8 element A Group 8 element is one in the series of elements in group 8 in the periodic table, which consists of the transition metals iron , ruthenium , osmium and hassium .... |
9 Group 9 element In modern IUPAC nomenclature, Group 9 of the periodic table contains the elements cobalt , rhodium , iridium , and meitnerium . These are all d-block transition metals... |
10 Group 10 element A Group 10 element is one in the series of elements in group 10 in the periodic table, which consists of the transition metals nickel , palladium , platinum , and darmstadtium .... |
11 Group 11 element A Group 11 element is one in the series of elements in group 11 in the periodic table, consisting of transition metals which are the traditional coinage metals of copper , silver , and gold... |
12 Group 12 element A group 12 element is one of the elements in group 12 in the periodic table. This includes zinc , cadmium and mercury . The further inclusion of copernicium in group 12 is supported by recent experiments on individual Cn atoms... |
13 Boron group The boron group is the series of elements in group 13 of the periodic table, comprising boron , aluminium , gallium , indium , thallium , and ununtrium . The elements in the boron group are characterized by having three electrons in their outer energy levels... |
14 Carbon group The carbon group is a periodic table group consisting of carbon , silicon , germanium , tin , lead , and ununquadium .... |
15 Nitrogen group The nitrogen group is a periodic table group consisting of nitrogen , phosphorus , arsenic , antimony , bismuth and ununpentium .... |
16 Chalcogen The chalcogens are the chemical elements in group 16 of the periodic table. This group is also known as the oxygen family... |
17 Halogen The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine... |
18 Noble gas The noble gases are a group of chemical elements with very similar properties: under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases, with very low chemical reactivity... |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↓ Period Periodic table period In the periodic table of the elements, elements are arranged in a series of rows so that those with similar properties appear in vertical columns. Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells; with each group across a period, the elements have one more proton and electron... |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 Period 1 element A period 1 element is one of the chemical elements in the first row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical... |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 Period 2 element A period 2 element is one of the chemical elements in the second row of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to... |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 Period 3 element A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical... |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 Period 4 element A period 4 element is one of the chemical elements in the fourth row of the periodic table of the elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour... |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 Period 5 element A period 5 element is one of the chemical elements in the fifth row of the periodic table of the elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour... |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 Period 6 element A period 6 element is one of the chemical elements in the sixth row of the periodic table of the elements, including the lanthanides... |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 Period 7 element A period 7 element is one of the chemical elements in the seventh row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical... |
||||||||||||||||||||
| * Lanthanide Lanthanide The lanthanide or lanthanoid series comprises the fifteen metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57 through 71, from lanthanum through lutetium... s |
||||||||||||||||||||
| ** Actinide Actinide The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium... s |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 0–10 kJ/mol | 10–100 kJ/mol | 100–300 kJ/mol | >300 kJ/mol |
Other common substances
Enthalpies of vaporization of common substances, measured at their respective standard boiling points:| Compound | Heat of vaporization (kJ mol-1) | Heat of vaporization (kJ kg−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonia Ammonia Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or... |
23.35 | 1371 |
| Butane Butane Butane is a gas with the formula C4H10 that is an alkane with four carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of two structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, butane refers only to the unbranched n-butane isomer; the other one being called "methylpropane" or... |
21.0 | 320 |
| Ethanol Ethanol Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a... |
38.6 | 841 |
| Hydrogen Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... |
0.46 | 451.9 |
| Methane Methane Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel... |
8.19 | 760 |
| Methanol Methanol Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol... |
35.3 | 1104 |
| Propane Propane Propane is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula , normally a gas, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as a fuel for engines, oxy-gas torches, barbecues, portable stoves, and residential central... |
15.7 | 356 |
| Phosphine Phosphine Phosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas. Pure phosphine is odourless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphine... |
14.6 | 429.4 |
| Water Water Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a... |
40.65 | 2257 |
See also
- Enthalpy of fusionEnthalpy of fusionThe enthalpy of fusion is the change in enthalpy resulting from heating one mole of a substance to change its state from a solid to a liquid. The temperature at which this occurs is the melting point....
- Enthalpy of sublimationEnthalpy of sublimationThe enthalpy of sublimation, or heat of sublimation, is defined as the heat required to sublime one mole of the substance at a given combination of temperature and pressure, usually standard temperature and pressure...
- Joback methodJoback methodThe Joback method predicts eleven important and commonly used pure component thermodynamic properties from molecular structure only.- Group Contribution Method :The Joback method is a group contribution method...
(Estimation of the heat of vaporization at the normal boiling point from molecular structures)

