
Stagnation enthalpy
Encyclopedia
Stagnation Enthalpy or total enthalpy (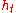 ) is the enthalpy
) is the enthalpy
of a flow at a stagnation point
. It is the enthalpy a flow would possess if brought to rest (zero speed) isentropically from speed .
.
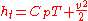
where,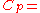 specific heat capacity at constant pressure and
specific heat capacity at constant pressure and  is the static temperature.
is the static temperature.
Stagnation enthalpy has units of energy, such that if enthalpy is thought of as the energy associated with the temperature
plus the energy associated with the pressure, the stagnation enthalpy adds a term associated with the kinetic energy of the fluid mass.
For a definition of stagnation enthalpy see:
http://ocw.mit.edu/ans7870/16/16.unified/thermoF03/chapter_6.htm
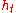 ) is the enthalpy
) is the enthalpyEnthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
of a flow at a stagnation point
Stagnation point
In fluid dynamics, a stagnation point is a point in a flow field where the local velocity of the fluid is zero. Stagnation points exist at the surface of objects in the flow field, where the fluid is brought to rest by the object...
. It is the enthalpy a flow would possess if brought to rest (zero speed) isentropically from speed
 .
.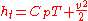
where,
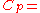 specific heat capacity at constant pressure and
specific heat capacity at constant pressure and  is the static temperature.
is the static temperature.Stagnation enthalpy has units of energy, such that if enthalpy is thought of as the energy associated with the temperature
Internal energy
In thermodynamics, the internal energy is the total energy contained by a thermodynamic system. It is the energy needed to create the system, but excludes the energy to displace the system's surroundings, any energy associated with a move as a whole, or due to external force fields. Internal...
plus the energy associated with the pressure, the stagnation enthalpy adds a term associated with the kinetic energy of the fluid mass.
See also
- Stagnation pressureStagnation pressureIn fluid dynamics, stagnation pressure is the static pressure at a stagnation point in a fluid flow.At a stagnation point the fluid velocity is zero and all kinetic energy has been converted into pressure energy . Stagnation pressure is equal to the sum of the free-stream dynamic pressure and...
- Stagnation temperatureStagnation temperatureIn thermodynamics and fluid mechanics, stagnation temperature is the temperature at a stagnation point in a fluid flow. At a stagnation point the speed of the fluid is zero and all of the kinetic energy has been converted to internal energy and is added to the local static enthalpy...
For a definition of stagnation enthalpy see:
http://ocw.mit.edu/ans7870/16/16.unified/thermoF03/chapter_6.htm

