Spirochaeta americana
Encyclopedia
Spirochaeta americana is a relatively newly discovered single-celled extremophile
. This halo
alkaliphilic
and obligately anaerobic
bacteria can be found in the bleach-like highly alkaline, salty, deep waters of California
's Mono Lake
.
, and is chemotroph
ic in its metabolism
. Spirochaeta also have unique flagella
, sometimes called axial filaments, which run lengthwise between the cell membrane
and outer membrane
. These cause a twisting motion which allows the spirochaete to move about. Despite the extreme environment that they require, "their cell walls are very delicate, and it is difficult to keep them alive for long periods in the laboratory," says Dr. Elena Pikuta, one of the discoverers of S. americana.
 S. americana thrives in the lake-bottom mud of Lake Mono, a 13 mile wide former monomictic
S. americana thrives in the lake-bottom mud of Lake Mono, a 13 mile wide former monomictic
volcanic
basin
which is fed by numerous small Sierra
streams and which has no outflow except evaporation
and Californian aqueducts, thereby continually increasing the concentration of salts and other minerals in its waters. Further mineral enrichment of these waters also occur due to the volcanically active area, such as when Negit Island
erupted roughly 250 years ago.
Surviving in deep, salty, alkaline lake mud of Lake Mono, the extreme conditions in which S. americana thrive have prompted its discoverers to explore Antarctica's Lake Untersee
, hopefully to discover similar species.
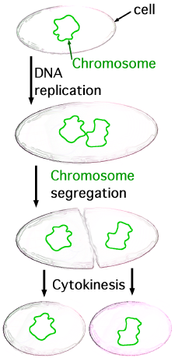 S. americana reproduces via transverse binary fission, where the cytoplasm
S. americana reproduces via transverse binary fission, where the cytoplasm
divides transversely between two sets of nuclei
, forming two dissimilar individuals, as do other Spirochaeta.
with optimal growth at 37 degrees and prefers a pH
balance of 9.5, similar to that of baking soda, hand soap, or a solution of household bleach in water.
S. americana is capable of metabolizing D-glucose
, fructose
, maltose
, sucrose
, starch
and D-mannitol
and has as its waste H2
, acetate
, ethanol
and formate
.
Extremophile
An extremophile is an organism that thrives in physically or geochemically extreme conditions that are detrimental to most life on Earth. In contrast, organisms that live in more moderate environments may be termed mesophiles or neutrophiles...
. This halo
Halophile
Halophiles are extremophile organisms that thrive in environments with very high concentrations of salt. The name comes from the Greek for "salt-loving". While the term is perhaps most often applied to some halophiles classified into the Archaea domain, there are also bacterial halophiles and some...
alkaliphilic
Alkaliphile
Alkaliphiles are microbes classified as extremophiles that thrive in alkaline environments with a pH of 9 to 11 such as playa lakes and carbonate-rich soils...
and obligately anaerobic
Anaerobic organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require oxygen for growth. It could possibly react negatively and may even die if oxygen is present...
bacteria can be found in the bleach-like highly alkaline, salty, deep waters of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
's Mono Lake
Mono Lake
Mono Lake is a large, shallow saline lake in Mono County, California, formed at least 760,000 years ago as a terminal lake in a basin that has no outlet to the ocean...
.
Physical characteristics
Like all Spirochaeta, S. americana has long helically coiled cells, is gram-negativeGram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain crystal violet dye in the Gram staining protocol. In a Gram stain test, a counterstain is added after the crystal violet, coloring all Gram-negative bacteria with a red or pink color...
, and is chemotroph
Chemotroph
Chemotrophs are organisms that obtain energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic or inorganic . The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototrophs, which utilize solar energy...
ic in its metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. Spirochaeta also have unique flagella
Flagellum
A flagellum is a tail-like projection that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and plays the dual role of locomotion and sense organ, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. There are some notable differences between prokaryotic and...
, sometimes called axial filaments, which run lengthwise between the cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
and outer membrane
Outer membrane
The bacterial outer membrane is found in Gram-negative bacteria. Its composition is distinct from that of the cytoplasmic membrane - among other things, the outer leaflet of the membrane includes a complex lipopolysaccharide whose lipid portion acts as an endotoxin - and it is linked to the cell's...
. These cause a twisting motion which allows the spirochaete to move about. Despite the extreme environment that they require, "their cell walls are very delicate, and it is difficult to keep them alive for long periods in the laboratory," says Dr. Elena Pikuta, one of the discoverers of S. americana.
Environment

Monomictic
Monomictic lakes are holomictic lakes that mix from top to bottom during one mixing period each year. Monomictic lakes may be subdivided into Cold and Warm types.-Cold monomictic lakes:...
volcanic
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
basin
Depression (geology)
A depression in geology is a landform sunken or depressed below the surrounding area. Depressions may be formed by various mechanisms.Structural or tectonic related:...
which is fed by numerous small Sierra
Sierra
Sierra can refer to:- Mountains and mountain ranges :* Sierra mountains * Sierra de Juárez, mountain range in Baja California, Mexico...
streams and which has no outflow except evaporation
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
and Californian aqueducts, thereby continually increasing the concentration of salts and other minerals in its waters. Further mineral enrichment of these waters also occur due to the volcanically active area, such as when Negit Island
Negit Island
Negit Island is an island in Mono Lake. Negit is a volcanic cone less than 2000 years old. It can be considered to be the northernmost of the Mono Craters. Negit is composed of three dark dacite lava flows....
erupted roughly 250 years ago.
Surviving in deep, salty, alkaline lake mud of Lake Mono, the extreme conditions in which S. americana thrive have prompted its discoverers to explore Antarctica's Lake Untersee
Lake Untersee
Lake Untersee is the largest surface freshwater lake in the interior of the Gruber Mountains of central Queen Maud Land in East Antarctica. It is situated to the southwest of the Schirmacher Oasis. The lake is approximately long and wide, with a surface area of , and a maximum depth of...
, hopefully to discover similar species.
Reproduction

Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
divides transversely between two sets of nuclei
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
, forming two dissimilar individuals, as do other Spirochaeta.
Growth and Metabolism
This bacteria grows in environments of 10 to 44 degrees CelsiusCelsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
with optimal growth at 37 degrees and prefers a pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
balance of 9.5, similar to that of baking soda, hand soap, or a solution of household bleach in water.
S. americana is capable of metabolizing D-glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
, fructose
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple monosaccharide found in many plants. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847...
, maltose
Maltose
Maltose , or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an αbond, formed from a condensation reaction. The isomer "isomaltose" has two glucose molecules linked through an α bond. Maltose is the second member of an important biochemical series of glucose chains....
, sucrose
Sucrose
Sucrose is the organic compound commonly known as table sugar and sometimes called saccharose. A white, odorless, crystalline powder with a sweet taste, it is best known for its role in human nutrition. The molecule is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose with the molecular formula...
, starch
Starch
Starch or amylum is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined together by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by all green plants as an energy store...
and D-mannitol
Mannitol
Mannitol is a white, crystalline organic compound with the formula . This polyol is used as an osmotic diuretic agent and a weak renal vasodilator...
and has as its waste H2
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, acetate
Acetate
An acetate is a derivative of acetic acid. This term includes salts and esters, as well as the anion found in solution. Most of the approximately 5 billion kilograms of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In...
, ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
and formate
Formate
Formate or methanoate is the ion CHOO− or HCOO− . It is the simplest carboxylate anion. It is produced in large amounts in the hepatic mitochondria of embryonic cells and in cancer cells by the folate cycle Formate or methanoate is the ion CHOO− or HCOO− (formic acid minus one hydrogen ion). It...
.

