
Spin magnetic moment
Encyclopedia
Basis for spin magnetic moments
A spin magnetic moment is induced by all charged particles. The electronElectron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
is an example of one such charged particle. A spin magnetic moment is created because a particle has physical properties known as spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
and electric charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
. The spin within classical physics would be an object that rotates axially around its center of mass. In quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, elementary particle
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle not known to have substructure; that is, it is not known to be made up of smaller particles. If an elementary particle truly has no substructure, then it is one of the basic building blocks of the universe from which...
s are points, which have no axis to revolve around. This means these particles do not have spin in a classical sense, as angular momentum
Angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
is defined by
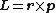 , but have the physical property of angular momentum (see Spin (physics)
, but have the physical property of angular momentum (see Spin (physics)Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
). Maxwell's theory of magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
s dictates that any moving charged particle creates a magnetic moment
Magnetic moment
The magnetic moment of a magnet is a quantity that determines the force that the magnet can exert on electric currents and the torque that a magnetic field will exert on it...
, and by definition, angular momentum designates movement. This is where the magnetic moment emerges in classical electromagnetism
Classical electromagnetism
Classical electromagnetism is a branch of theoretical physics that studies consequences of the electromagnetic forces between electric charges and currents...
. See Maxwell's equation
Calculation
We can calculate the observable spin magnetic moment (a vector), , for a sub-atomic particle with charge
, for a sub-atomic particle with charge 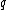 , mass
, mass 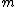 , and spin angular momentum
, and spin angular momentumSpin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
(also a vector),
 , via:
, via:where
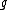 is a dimensionless number, called the g-factor. This number depends on the particle: it is
is a dimensionless number, called the g-factor. This number depends on the particle: it is 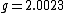 for the electron,
for the electron, 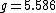 for the proton, and
for the proton, and 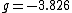 for the neutron. The proton and neutron are composed of quarks, which have a non-zero charge and a spin of
for the neutron. The proton and neutron are composed of quarks, which have a non-zero charge and a spin of 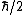 , and this must be taken into account when calculating their g-factors. Even though the neutron has a charge
, and this must be taken into account when calculating their g-factors. Even though the neutron has a charge 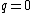 , its quarks give it a magnetic moment. The proton and electron's spin magnetic moments can be calculated by simply setting
, its quarks give it a magnetic moment. The proton and electron's spin magnetic moments can be calculated by simply setting  .
.The intrinsic electron magnetic dipole moment
Electron magnetic dipole moment
In atomic physics, the electron magnetic dipole moment is the magnetic moment of an electron caused by its intrinsic property of spin.-Magnetic moment of an electron:...
is approximately equal to the Bohr magneton because
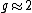 and the electron's spin is also
and the electron's spin is also  :
:Eq. (2) is normally written as
where μB is the Bohr magneton.
Just like the total spin angular momentum cannot be measured, neither can the total spin magnetic moment be measured. Equations (1) - (3) give the physical observable, that component of the magnetic moment measured along an axis, relative to or along the applied field direction. Conventionally, the z-axis is chosen but the observable values of the component of spin angular momentum along all three axes (assuming a Cartesian coordinate system) are each
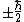 . However, in order to obtain the magnitude of the total spin angular momentum, wave mechanical corrections dictate that
. However, in order to obtain the magnitude of the total spin angular momentum, wave mechanical corrections dictate that 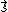 be replaced by its eigenvalue,
be replaced by its eigenvalue, 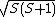 . In turn, calculation of the magnitude of the total spin magnetic moment requires that Eq. (3) be replaced by:
. In turn, calculation of the magnitude of the total spin magnetic moment requires that Eq. (3) be replaced by:Thus, for a single electron, with spin quantum number
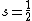 , the component of the magnetic moment along the field direction is, from Eq. (3),
, the component of the magnetic moment along the field direction is, from Eq. (3), 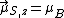 , or one BM, while the [magnitude of the] total spin magnetic moment is, from Eq. (4),
, or one BM, while the [magnitude of the] total spin magnetic moment is, from Eq. (4), 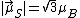 , or 1.73 BM.
, or 1.73 BM.The analysis is readily extended to the spin-only magnetic moment of an atom. For example, the total spin magnetic moment (sometimes referred to as the effective magnetic moment when the orbital moment contribution to the total magnetic moment is neglected) of a transition metal ion with a single d electron outside of closed shells (e.g. Ti3+) is 1.73 μB since S = 1/2, while an atom with two unpaired electrons (e.g. V3+) with S = 1 would have an effective magnetic moment of 2.83 μB.
Spin in chemistry
Spin magnetic moments create a basis for one of the most important principles in chemistry, the Pauli exclusion principlePauli exclusion principle
The Pauli exclusion principle is the quantum mechanical principle that no two identical fermions may occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. A more rigorous statement is that the total wave function for two identical fermions is anti-symmetric with respect to exchange of the particles...
. This principle, first suggested by Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli was an Austrian theoretical physicist and one of the pioneers of quantum physics. In 1945, after being nominated by Albert Einstein, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his "decisive contribution through his discovery of a new law of Nature, the exclusion principle or...
, governs most of modern-day chemistry. The theory plays further roles than just the explanations of doublet
Doublet (physics)
In quantum mechanics, a doublet is a quantum state of a system with a spin of 1/2, such that there are two allowed values of the spin component, −1/2 and +1/2. Quantum systems with two possible states are sometimes called two-level systems...
s within electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
. This additional quantum number
Quantum number
Quantum numbers describe values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of the quantum system. Perhaps the most peculiar aspect of quantum mechanics is the quantization of observable quantities. This is distinguished from classical mechanics where the values can range continuously...
, spin, became the basis for the modern standard model used today, which includes the use of Hund's rules, and an explanation of beta decay
Beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle is emitted from an atom. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus , while in the case of a...
.
History of spin magnetic moments
The idea of a spin angular momentum was first proposed in a 1925 publication by George UhlenbeckGeorge Eugene Uhlenbeck
George Eugene Uhlenbeck was a Dutch-American theoretical physicist.-Background and education:George Uhlenbeck was the son of Eugenius and Anne Beeger Uhlenbeck...
and Samuel Goudsmit
Samuel Abraham Goudsmit
Samuel Abraham Goudsmit was a Dutch-American physicist famous for jointly proposing the concept of electron spin with George Eugene Uhlenbeck in 1925.-Biography:...
to explain hyperfine splitting in atomic spectra. In 1928, Paul Dirac
Paul Dirac
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac, OM, FRS was an English theoretical physicist who made fundamental contributions to the early development of both quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics...
provided a rigorous theoretical foundation for the concept with his relativistic
Special relativity
Special relativity is the physical theory of measurement in an inertial frame of reference proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".It generalizes Galileo's...
equation of motion
Equation of motion
Equations of motion are equations that describe the behavior of a system in terms of its motion as a function of time...
for the wavefunction
Wavefunction
Not to be confused with the related concept of the Wave equationA wave function or wavefunction is a probability amplitude in quantum mechanics describing the quantum state of a particle and how it behaves. Typically, its values are complex numbers and, for a single particle, it is a function of...
of the electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
.
External links
- An Introduction to the Electronic Structure of Atoms and Molecules by Dr. Richard F.W. Bader (McMaster UniversityMcMaster UniversityMcMaster University is a public research university whose main campus is located in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is located on of land in the residential neighbourhood of Westdale, adjacent to Hamilton's Royal Botanical Gardens...
)

