
Spacetime topology
Encyclopedia
Spacetime topology, the topological structure
of spacetime
, is a subject studied primarily in general relativity
. This physical theory models gravitation
as a Lorentzian manifold (a spacetime
) and the concepts of topology
thus become important in analysing local as well as global aspects of spacetime. The study of spacetime topology is especially important in physical cosmology
.
topology. Here the open set
s are the image of open sets in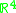 .
.
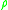 in which a subset
in which a subset 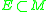 is open if for every timelike curve
is open if for every timelike curve  there is a set
there is a set  in the manifold topology such that
in the manifold topology such that  .
.
It is the finest topology which induces the same topology as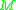 does on timelike curves.
does on timelike curves.
, separable but not locally compact
.
A base
for the topology is sets of the form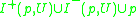 for some point
for some point 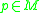 and some convex normal neighbourhood
and some convex normal neighbourhood 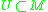 .
.
(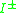 denote the chronological past and future).
denote the chronological past and future).
such that both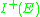 and
and 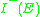 are open for all subsets
are open for all subsets 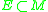 .
.
Here the base
of open set
s for the topology are sets of the form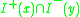 for some points
for some points 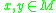 .
.
This topology coincides with the manifold topology if and only if the manifold is strongly causal but in general it is coarser.
Note, that in mathematics, an Alexandrov topology
on a partial order is usually taken to be the coarsest topology in which only the upper sets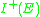 are required to be open. Nowadays, the correct mathematical term for the Alexandrov topology on spacetime would be the interval topology, but when Kronheimer and Penrose introduced the term this difference in nomenclature was not as clear, and in physics the term Alexandrov topology remains in use.
are required to be open. Nowadays, the correct mathematical term for the Alexandrov topology on spacetime would be the interval topology, but when Kronheimer and Penrose introduced the term this difference in nomenclature was not as clear, and in physics the term Alexandrov topology remains in use.
Topological space
Topological spaces are mathematical structures that allow the formal definition of concepts such as convergence, connectedness, and continuity. They appear in virtually every branch of modern mathematics and are a central unifying notion...
of spacetime
Spacetime
In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model that combines space and time into a single continuum. Spacetime is usually interpreted with space as being three-dimensional and time playing the role of a fourth dimension that is of a different sort from the spatial dimensions...
, is a subject studied primarily in general relativity
General relativity
General relativity or the general theory of relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916. It is the current description of gravitation in modern physics...
. This physical theory models gravitation
Gravitation
Gravitation, or gravity, is a natural phenomenon by which physical bodies attract with a force proportional to their mass. Gravitation is most familiar as the agent that gives weight to objects with mass and causes them to fall to the ground when dropped...
as a Lorentzian manifold (a spacetime
Spacetime
In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model that combines space and time into a single continuum. Spacetime is usually interpreted with space as being three-dimensional and time playing the role of a fourth dimension that is of a different sort from the spatial dimensions...
) and the concepts of topology
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
thus become important in analysing local as well as global aspects of spacetime. The study of spacetime topology is especially important in physical cosmology
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
.
Manifold topology
As with any manifold, a spacetime possesses a natural manifoldManifold
In mathematics , a manifold is a topological space that on a small enough scale resembles the Euclidean space of a specific dimension, called the dimension of the manifold....
topology. Here the open set
Open set
The concept of an open set is fundamental to many areas of mathematics, especially point-set topology and metric topology. Intuitively speaking, a set U is open if any point x in U can be "moved" a small amount in any direction and still be in the set U...
s are the image of open sets in
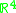 .
.Path or Zeeman topology
Definition: The topology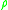 in which a subset
in which a subset 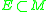 is open if for every timelike curve
is open if for every timelike curve  there is a set
there is a set  in the manifold topology such that
in the manifold topology such that  .
.It is the finest topology which induces the same topology as
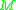 does on timelike curves.
does on timelike curves.Properties
Strictly finer than the manifold topology. It is therefore HausdorffHausdorff space
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a Hausdorff space, separated space or T2 space is a topological space in which distinct points have disjoint neighbourhoods. Of the many separation axioms that can be imposed on a topological space, the "Hausdorff condition" is the most frequently...
, separable but not locally compact
Locally compact space
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a topological space is called locally compact if, roughly speaking, each small portion of the space looks like a small portion of a compact space.-Formal definition:...
.
A base
Base (topology)
In mathematics, a base B for a topological space X with topology T is a collection of open sets in T such that every open set in T can be written as a union of elements of B. We say that the base generates the topology T...
for the topology is sets of the form
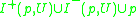 for some point
for some point 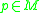 and some convex normal neighbourhood
and some convex normal neighbourhood 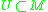 .
.(
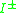 denote the chronological past and future).
denote the chronological past and future).Alexandrov topology
The Alexandrov topology on spacetime, is the coarsest topologyComparison of topologies
In topology and related areas of mathematics comparison of topologies refers to the fact that two topological structures on a given set may stand in relation to each other. The set of all possible topologies on a given set forms a partially ordered set...
such that both
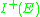 and
and 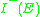 are open for all subsets
are open for all subsets 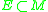 .
.Here the base
Base (topology)
In mathematics, a base B for a topological space X with topology T is a collection of open sets in T such that every open set in T can be written as a union of elements of B. We say that the base generates the topology T...
of open set
Open set
The concept of an open set is fundamental to many areas of mathematics, especially point-set topology and metric topology. Intuitively speaking, a set U is open if any point x in U can be "moved" a small amount in any direction and still be in the set U...
s for the topology are sets of the form
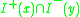 for some points
for some points 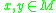 .
.This topology coincides with the manifold topology if and only if the manifold is strongly causal but in general it is coarser.
Note, that in mathematics, an Alexandrov topology
Alexandrov topology
In topology, an Alexandrov space is a topological space in which the intersection of any family of open sets is open. It is an axiom of topology that the intersection of any finite family of open sets is open...
on a partial order is usually taken to be the coarsest topology in which only the upper sets
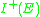 are required to be open. Nowadays, the correct mathematical term for the Alexandrov topology on spacetime would be the interval topology, but when Kronheimer and Penrose introduced the term this difference in nomenclature was not as clear, and in physics the term Alexandrov topology remains in use.
are required to be open. Nowadays, the correct mathematical term for the Alexandrov topology on spacetime would be the interval topology, but when Kronheimer and Penrose introduced the term this difference in nomenclature was not as clear, and in physics the term Alexandrov topology remains in use.

