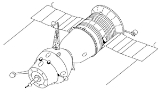
Soyuz 7K-OK
Encyclopedia
The manned Soyuz spacecraft can be classified into design generations. Soyuz 1
through Soyuz 11
(1967–1971) were first-generation vehicles, carrying a crew of up to three without spacesuits and distinguished from those following by their bent solar panel
s and their use of the Igla
automatic docking navigation system, which required special radar antennas. The first unmanned test of this version was Cosmos-133
, launched on Nov. 28, 1966. This first generation was called Soyuz 7K-OK and encompassed the original Soyuz and Salyut 1
Soyuz. Variations within it were primarily docking fixtures; the first nine examples had no internal hatch and crew transfer had to take place by means of spacewalks
, employing spacesuits kept in the orbital module, which functioned as an airlock, as done on Soyuz 4
and 5
. This version was used up to 1971.
Soyuz 1
Soyuz 1 was a manned spaceflight of the Soviet space program. Launched into orbit on April 23, 1967 carrying cosmonaut Colonel Vladimir Komarov, Soyuz 1 was the first flight of the Soyuz spacecraft...
through Soyuz 11
Soyuz 11
Soyuz 11 was the first manned mission to arrive at the world's first space station, Salyut 1. The mission arrived at the space station on June 7, 1971 and departed on June 30, 1971. The mission ended in disaster when the crew capsule depressurized during preparations for re-entry, killing the...
(1967–1971) were first-generation vehicles, carrying a crew of up to three without spacesuits and distinguished from those following by their bent solar panel
Photovoltaic module
A solar panel is a packaged, connected assembly of solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells...
s and their use of the Igla
Igla (spacecraft docking system)
The IGLA docking system was a Russian radio telemetry system for automated docking of Soyuz . The first prototypes were made in late 1965. On 30 October 1967, the first automated docking of Soyuz unmanned spacecraft took place.-Problems:...
automatic docking navigation system, which required special radar antennas. The first unmanned test of this version was Cosmos-133
Cosmos 133
Kosmos 133 was a Soviet Soyuz programme test satellite launched from the Baikonur cosmodrome aboard a Vostok rocket. It was the first test flight of the Soyuz 7K-OK earth orbit spacecraft. It was a planned "all up" test with a second Soyuz to be launched the following day and automatically dock...
, launched on Nov. 28, 1966. This first generation was called Soyuz 7K-OK and encompassed the original Soyuz and Salyut 1
Salyut 1
Salyut 1 was the first space station of any kind, launched by the USSR on April 19, 1971. It was launched unmanned using a Proton-K rocket. Its first crew came later in Soyuz 10, but was unable to dock completely; its second crew launched in Soyuz 11 and remained on board for 23 days...
Soyuz. Variations within it were primarily docking fixtures; the first nine examples had no internal hatch and crew transfer had to take place by means of spacewalks
Extra-vehicular activity
Extra-vehicular activity is work done by an astronaut away from the Earth, and outside of a spacecraft. The term most commonly applies to an EVA made outside a craft orbiting Earth , but also applies to an EVA made on the surface of the Moon...
, employing spacesuits kept in the orbital module, which functioned as an airlock, as done on Soyuz 4
Soyuz 4
Soyuz 4 was launched on January 14, 1969. On board the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft was cosmonaut Vladimir Shatalov on his first flight. The aim of the mission was to dock with Soyuz 5, transfer two crew members from that spacecraft, and return to Earth...
and 5
Soyuz 5
Soyuz 5 was a Soyuz mission using the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft launched by the Soviet Union on January 15, 1969, which docked with Soyuz 4 in orbit...
. This version was used up to 1971.
Unmanned and test missions
- Cosmos 133Cosmos 133Kosmos 133 was a Soviet Soyuz programme test satellite launched from the Baikonur cosmodrome aboard a Vostok rocket. It was the first test flight of the Soyuz 7K-OK earth orbit spacecraft. It was a planned "all up" test with a second Soyuz to be launched the following day and automatically dock...
- Cosmos 140Cosmos 140Kosmos 140 was an unmanned flight of the Soyuz spacecraft. It was the third attempted test flight of the Soyuz 7K-OK model, after orbital and launch failures of the first two Soyuz spacecraft. The spacecraft suffered attitude control problems and excessive fuel consumption in orbit, but remained...
- Cosmos 186
- Cosmos 188
- Cosmos 212Cosmos 212Kosmos 212 was one of a series of Soviet Soyuz programme test spacecraft whose purpose was to further test and develop the passenger version. Scientific data and measurements were relayed to earth by multichannel telemetry systems equipped with space-borne memory units. Kosmos 212 and Kosmos 213...
- Cosmos 213Cosmos 213Kosmos 213 was one of a series of Soviet Soyuz programme test spacecraft whose purpose was to further test and develop the passenger version. Scientific data and measurements were relayed to earth by multichannel telemetry systems equipped with space-borne memory units. Kosmos 212 and Kosmos 213...
- Cosmos 238Cosmos 238Kosmos 238 was the final test series of the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft prior to the launch of Soyuz 3. It tested the orbital maneuvering system, reentry, descent and landing systems that had been modified and improved after the Soyuz 1 accident....
- Soyuz 2Soyuz 2Soyuz 2 was an unpiloted spacecraft in the Soyuz family intended to perform a docking maneuver with Soyuz 3. Although the two craft approached closely, the docking did not take place.-Other uses of name:...
Manned missions
- Soyuz 1Soyuz 1Soyuz 1 was a manned spaceflight of the Soviet space program. Launched into orbit on April 23, 1967 carrying cosmonaut Colonel Vladimir Komarov, Soyuz 1 was the first flight of the Soyuz spacecraft...
- Soyuz 3Soyuz 3Soyuz 3 was a spaceflight mission launched by the Soviet Union on October 26, 1968. For four consecutive days, Commander Georgy Beregovoy piloted the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft through eighty-one orbits of Earth.-Crew:-Backup crew:...
- Soyuz 4Soyuz 4Soyuz 4 was launched on January 14, 1969. On board the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft was cosmonaut Vladimir Shatalov on his first flight. The aim of the mission was to dock with Soyuz 5, transfer two crew members from that spacecraft, and return to Earth...
- Soyuz 5Soyuz 5Soyuz 5 was a Soyuz mission using the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft launched by the Soviet Union on January 15, 1969, which docked with Soyuz 4 in orbit...
- Soyuz 6Soyuz 6Soyuz 6 was part of a joint mission with Soyuz 7 and Soyuz 8 that saw three Soyuz spacecraft in orbit together at the same time, carrying seven cosmonauts...
- Soyuz 7Soyuz 7Soyuz 7 was part of a joint mission with Soyuz 6 and Soyuz 8 that saw three Soyuz spacecraft in orbit together at the same time, carrying seven cosmonauts....
- Soyuz 8Soyuz 8Soyuz 8 was part of a joint mission with Soyuz 6 and Soyuz 7 that saw three Soyuz spacecraft in orbit together at the same time, carrying seven cosmonauts....
- Soyuz 9Soyuz 9Soyuz 9 was a 1970 Soviet manned space flight. The two-man crew of Andrian Nikolayev and Vitali Sevastyanov broke the five-year-old space endurance record with their nearly 18-day flight...
External links
- Russia New Russian spaceship will be able to fly to Moon - space corp
- RSC Energia: Concept Of Russian Manned Space Navigation Development
- Mir Hardware Heritage
- David S.F. Portree, Mir Hardware Heritage, NASA RP-1357, 1995
- Mir Hardware Heritage (wikisource)
- Information on Soyuz spacecraft
- OMWorld's ASTP Docking Trainer Page
- NASA - Russian Soyuz TMA Spacecraft Details
- Space Adventures circum-lunar mission - details

