
Sommerfeld identity
Encyclopedia
The Sommerfeld identity is a mathematical identity, due Arnold Sommerfeld
, used in the theory of propagation of waves,
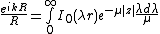
where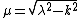
is to be taken with positive real part, to ensure the convergence of the integral and its vanishing in the limit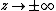 and
and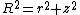 .
.
Here,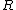 is the distance from the origin while
is the distance from the origin while  is the distance from the central axis of a cylinder as in the
is the distance from the central axis of a cylinder as in the 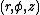 cylindrical coordinate system
cylindrical coordinate system
. The function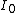 is a Bessel function
is a Bessel function
. Here the notation for Bessel functions follows the German convention, to be consistent with the original notation used by Sommerfeld. In English literature it is more common to use
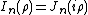 .
.
This identity is known as the Sommerfeld Identity [Ref.1,Pg.242].
An alternative form is
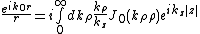
Where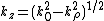
[Ref.2,Pg.66]. The notation used here is different form that above: is now the distance from the origin and
is now the distance from the origin and 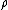 is the axial distance in a cylindrical system defined as
is the axial distance in a cylindrical system defined as 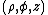 .
.
The physical interpretation is that a spherical wave can be expanded into a summation
of cylindrical waves in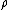 direction, multiplied by a plane wave
direction, multiplied by a plane wave
in the direction; see the Jacobi-Anger expansion. The summation has to be taken over all the wavenumbers
direction; see the Jacobi-Anger expansion. The summation has to be taken over all the wavenumbers 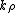 .
.
Arnold Sommerfeld
Arnold Johannes Wilhelm Sommerfeld was a German theoretical physicist who pioneered developments in atomic and quantum physics, and also educated and groomed a large number of students for the new era of theoretical physics...
, used in the theory of propagation of waves,
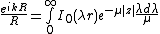
where
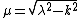
is to be taken with positive real part, to ensure the convergence of the integral and its vanishing in the limit
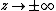 and
and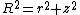 .
.Here,
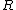 is the distance from the origin while
is the distance from the origin while  is the distance from the central axis of a cylinder as in the
is the distance from the central axis of a cylinder as in the 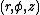 cylindrical coordinate system
cylindrical coordinate systemCylindrical coordinate system
A cylindrical coordinate system is a three-dimensional coordinate systemthat specifies point positions by the distance from a chosen reference axis, the direction from the axis relative to a chosen reference direction, and the distance from a chosen reference plane perpendicular to the axis...
. The function
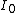 is a Bessel function
is a Bessel functionBessel function
In mathematics, Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli and generalized by Friedrich Bessel, are canonical solutions y of Bessel's differential equation:...
. Here the notation for Bessel functions follows the German convention, to be consistent with the original notation used by Sommerfeld. In English literature it is more common to use
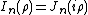 .
.This identity is known as the Sommerfeld Identity [Ref.1,Pg.242].
An alternative form is
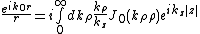
Where
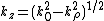
[Ref.2,Pg.66]. The notation used here is different form that above:
 is now the distance from the origin and
is now the distance from the origin and 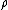 is the axial distance in a cylindrical system defined as
is the axial distance in a cylindrical system defined as 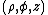 .
.The physical interpretation is that a spherical wave can be expanded into a summation
of cylindrical waves in
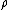 direction, multiplied by a plane wave
direction, multiplied by a plane wavePlane wave
In the physics of wave propagation, a plane wave is a constant-frequency wave whose wavefronts are infinite parallel planes of constant peak-to-peak amplitude normal to the phase velocity vector....
in the
 direction; see the Jacobi-Anger expansion. The summation has to be taken over all the wavenumbers
direction; see the Jacobi-Anger expansion. The summation has to be taken over all the wavenumbers 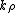 .
.

