
Solid state dye lasers
Encyclopedia
Solid state dye laser
s (SSDL) were introduced in 1967 by Soffer and McFarland. In these solid state lasers, the gain medium is a laser dye
-doped organic matrix such as poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), rather than a liquid solution of the dye. These authors used rhodamine 6G
-doped PMMA.
In the 1990s, new forms of improved PMMA, such as modified PMMA, with high optical quality characteristics were introduced. This improved gain medium was central to the demonstration of the first tunable narrow-linewidth solid-state dye laser oscillators, by Duarte
, which were later optimized to deliver pulse emission in the kW regime at single-longitudinal-mode linewidths
of ≈ 350 MHz (or
≈ 350 MHz (or 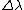 ≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm). These tunable laser oscillators use multiple-prism grating architectures yielding very high intracavity dispersions that can be nicely quantified using the multiple-prism grating
≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm). These tunable laser oscillators use multiple-prism grating architectures yielding very high intracavity dispersions that can be nicely quantified using the multiple-prism grating
equations.
Additional developments in solid-state dye lasers were demonstrated with the introduction of distributed feedback laser designs in 1999 and waveguides in 2002.
The SSDL research field has been rather active in the 21st century, and various new dye-doped solid-state organic matrices have been discovered. Notable among these new gain media are organic-inorganic dye-doped polymer-nanoparticle composites. An additional form of organic-inorganic dye-doped solid state laser gain media are the ORMOSILs
.
Dye laser
A dye laser is a laser which uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths. The wide bandwidth makes them particularly suitable for tunable lasers and...
s (SSDL) were introduced in 1967 by Soffer and McFarland. In these solid state lasers, the gain medium is a laser dye
Laser dye
Laser dyes are very large organic molecules with molecular weights of a few hundred mu. When one of these organic molecules is dissolved in a suitable liquid solvent it can be used as gain medium in a dye laser. Laser dye solutions absorb at shorter wavelengths end emit at longer wavelengths...
-doped organic matrix such as poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), rather than a liquid solution of the dye. These authors used rhodamine 6G
Rhodamine 6G
Rhodamine 6G is a chemical compound and a dye. It is often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers...
-doped PMMA.
In the 1990s, new forms of improved PMMA, such as modified PMMA, with high optical quality characteristics were introduced. This improved gain medium was central to the demonstration of the first tunable narrow-linewidth solid-state dye laser oscillators, by Duarte
F. J. Duarte
F. J. Duarte is a laser physicist and author/editor of several well-known books on tunable lasers. He introduced the generalized multiple-prism dispersion theory and has discovered various multiple-prism grating oscillator laser configurations...
, which were later optimized to deliver pulse emission in the kW regime at single-longitudinal-mode linewidths
Laser linewidth
←Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam.Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence and spectral coherence. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence of the laser, spectral coherence is evaluated by measuring the laser...
of
 ≈ 350 MHz (or
≈ 350 MHz (or 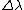 ≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm). These tunable laser oscillators use multiple-prism grating architectures yielding very high intracavity dispersions that can be nicely quantified using the multiple-prism grating
≈ 0.0004 nm at a laser wavelength of 590 nm). These tunable laser oscillators use multiple-prism grating architectures yielding very high intracavity dispersions that can be nicely quantified using the multiple-prism gratingMultiple-prism dispersion theory
The first description of multiple-prism arrays, and multiple-prism dispersion, was given by Newton in his book Opticks. Prism pair expanders were introduced by Brewster in 1813. A modern mathematical description of the single-prism dispersion was given by Born and Wolf in 1959...
equations.
Additional developments in solid-state dye lasers were demonstrated with the introduction of distributed feedback laser designs in 1999 and waveguides in 2002.
The SSDL research field has been rather active in the 21st century, and various new dye-doped solid-state organic matrices have been discovered. Notable among these new gain media are organic-inorganic dye-doped polymer-nanoparticle composites. An additional form of organic-inorganic dye-doped solid state laser gain media are the ORMOSILs
Ormosil
Ormosil is a shorthand phrase for organically modified silica or organically modified silicate. These are engineered materials that show great promise in a wide range of applications such as:...
.
See also
- Dye laserDye laserA dye laser is a laser which uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths. The wide bandwidth makes them particularly suitable for tunable lasers and...
s - Laser dyeLaser dyeLaser dyes are very large organic molecules with molecular weights of a few hundred mu. When one of these organic molecules is dissolved in a suitable liquid solvent it can be used as gain medium in a dye laser. Laser dye solutions absorb at shorter wavelengths end emit at longer wavelengths...
s - Laser linewidthLaser linewidth←Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam.Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence and spectral coherence. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence of the laser, spectral coherence is evaluated by measuring the laser...
- Tunable laserTunable laserA tunable laser is a laser whose wavelength of operation can be altered in a controlled manner. While all laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength, only a few types of lasers allow continuous tuning over a significant wavelength range....
s - Multiple-prism grating laser oscillators

