
Social discount rate
Encyclopedia
Social discount rate is a measure used to help guide choices about the value of diverting funds to social projects. It is defined as "the appropriate value of r to use in computing present discount value for social investments". Determining this rate is not always easy and can be the subject of discrepancies in the true net benefit to certain projects, plans and policies.
where policy makers measure the social marginal cost
and the social marginal benefit for each project. Almost all new policies will not even be considered until after a cost-benefit analysis has been completed. The social discount rate can appear in both calculations either as future costs such as maintenance or as future benefits such as reduced pollution
emissions.
Calculating the true social marginal cost can be a lot easier than measuring the social marginal benefit. Because of the uncertainty involved with calculating benefits, problems may arise. Should you put a dollar amount on time based on average wages, contingent valuations or revealed preferences? One of the big problems today is putting a value on a life. While some might say that a life is priceless, economists usually state the value to be somewhere between three to ten million dollars. Another problem is that often the current generation will be paying for most of the costs while future generations will be reaping most of the benefit. Should we weight current and future benefits differently?
The proper discount rate should represent the opportunity cost
of what else the firm could accomplish with those same funds. If that means that the money could be instead used to invest in the private sector
that would yield 5% and that is the next best alternative for using that money then 5% would be the social discount rate. The government uses a variety of discount rates but something around seven percent is what the U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) recommends for a pretax rate of return on private investments.
such as the hurdle rate or the project appropriate discount rate
; so the mathematics are identical. The benefit or cost per dollar can be calculated by
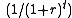
where r equals the SDR and t equals time. For benefits or costs that have no end it is just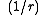
A higher SDR makes it less likely a social project will be funded. A higher SDR implies greater risks to the assumption that the benefits of the project will be reaped. A small increase in the social discount rate can matter enormously for benefits far into the future so it is very important to be as accurate as possible when choosing which rate to use.
There is a strong case for factoring in the equity issue when discounting benefits and costs of intergenerational projects such as those designed to combat climate change and environmental degradation.
The social discount rate is a reflection of a society’s relative valuation on today’s well-being versus well-being in the future. The appropriate selection of a social discount rate is crucial for cost-benefit analysis, and has important implications for resource allocations. There is wide diversity in social discount rates, with developed nations typically applying a lower rate (3–7%) than developing nations (8–15%).
The subject of a social discount rate, always a source of fierce debate between economists, has become highly controversial since the publication of the Stern Review
on the Economics of Climate Change. The publication exploded on the global warming scene in 2006 with its dire warning that global gross domestic product (GDP) was at future risk of a 20% reduction if there was a failure to invest 1% of world GDP now to reduce global warming. However, critics questioned the findings on the basis that they were arrived at using an extremely low discount rate of 1.4% used in economic modeling.
There is no consensus among economists and, according to the survey, no “one-size-fits-all” solution to the choice of social discount rate, owing to national variations. A regular reassessment and readjustment of the social discount rate used by each country is therefore required.
projects, such as funding the reduction of global warming
, place a greater valuation on future generations.
The range in the social discount rate for a cost-benefit analysis in this issue range from zero to over 3 percent. Some argue that the only reason for discounting future generations is that these generations might cease to exist in the future. Thus the rate should equal zero since the probability for such a catastrophic event is so low (assumed to be .01 percent per year).
This infers that there is equal weight given to all generations. The Stern Review
on the Economics of Climate Change is one such report that argues for zero discounting of future generations. While William D. Nordhaus of Yale
Use in cost benefit analysis
It may be used in estimating the value of creating a highway system, schools, or forcing environmental protection, for example. All of these things require a cost-benefit analysisCost-benefit analysis
Cost–benefit analysis , sometimes called benefit–cost analysis , is a systematic process for calculating and comparing benefits and costs of a project for two purposes: to determine if it is a sound investment , to see how it compares with alternate projects...
where policy makers measure the social marginal cost
Marginal cost
In economics and finance, marginal cost is the change in total cost that arises when the quantity produced changes by one unit. That is, it is the cost of producing one more unit of a good...
and the social marginal benefit for each project. Almost all new policies will not even be considered until after a cost-benefit analysis has been completed. The social discount rate can appear in both calculations either as future costs such as maintenance or as future benefits such as reduced pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
emissions.
Calculating the true social marginal cost can be a lot easier than measuring the social marginal benefit. Because of the uncertainty involved with calculating benefits, problems may arise. Should you put a dollar amount on time based on average wages, contingent valuations or revealed preferences? One of the big problems today is putting a value on a life. While some might say that a life is priceless, economists usually state the value to be somewhere between three to ten million dollars. Another problem is that often the current generation will be paying for most of the costs while future generations will be reaping most of the benefit. Should we weight current and future benefits differently?
The proper discount rate should represent the opportunity cost
Opportunity cost
Opportunity cost is the cost of any activity measured in terms of the value of the best alternative that is not chosen . It is the sacrifice related to the second best choice available to someone, or group, who has picked among several mutually exclusive choices. The opportunity cost is also the...
of what else the firm could accomplish with those same funds. If that means that the money could be instead used to invest in the private sector
Private sector
In economics, the private sector is that part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is run by private individuals or groups, usually as a means of enterprise for profit, and is not controlled by the state...
that would yield 5% and that is the next best alternative for using that money then 5% would be the social discount rate. The government uses a variety of discount rates but something around seven percent is what the U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) recommends for a pretax rate of return on private investments.
Calculation
The SDR is directly analogous to concepts found in corporate financeCorporate finance
Corporate finance is the area of finance dealing with monetary decisions that business enterprises make and the tools and analysis used to make these decisions. The primary goal of corporate finance is to maximize shareholder value while managing the firm's financial risks...
such as the hurdle rate or the project appropriate discount rate
Discount rate
The discount rate can mean*an interest rate a central bank charges depository institutions that borrow reserves from it, for example for the use of the Federal Reserve's discount window....
; so the mathematics are identical. The benefit or cost per dollar can be calculated by
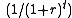
where r equals the SDR and t equals time. For benefits or costs that have no end it is just
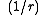
A higher SDR makes it less likely a social project will be funded. A higher SDR implies greater risks to the assumption that the benefits of the project will be reaped. A small increase in the social discount rate can matter enormously for benefits far into the future so it is very important to be as accurate as possible when choosing which rate to use.
There is a strong case for factoring in the equity issue when discounting benefits and costs of intergenerational projects such as those designed to combat climate change and environmental degradation.
The social discount rate is a reflection of a society’s relative valuation on today’s well-being versus well-being in the future. The appropriate selection of a social discount rate is crucial for cost-benefit analysis, and has important implications for resource allocations. There is wide diversity in social discount rates, with developed nations typically applying a lower rate (3–7%) than developing nations (8–15%).
The subject of a social discount rate, always a source of fierce debate between economists, has become highly controversial since the publication of the Stern Review
Stern Review
The Stern Review on the Economics of Climate Change is a 700-page report released for the British government on 30 October 2006 by economist Nicholas Stern, chair of the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at the London School of Economics and also chair of the Centre...
on the Economics of Climate Change. The publication exploded on the global warming scene in 2006 with its dire warning that global gross domestic product (GDP) was at future risk of a 20% reduction if there was a failure to invest 1% of world GDP now to reduce global warming. However, critics questioned the findings on the basis that they were arrived at using an extremely low discount rate of 1.4% used in economic modeling.
There is no consensus among economists and, according to the survey, no “one-size-fits-all” solution to the choice of social discount rate, owing to national variations. A regular reassessment and readjustment of the social discount rate used by each country is therefore required.
Differences between private and social
There are a number of qualitative differences between social and corporate discount rates and evaluation of projects associated with them. The governance of social project funding is different naturally, because estimating the benefits of social projects requires making ethically subtle choices about the benefits to others. For example if it was presumed that a meteor will wipe out all life in a few years the SDR is very high. Alternately if we presume that the population will have many new and wonderful choices capturing benefits (i.e. they will be more wealthy) in the future that too raises the SDR of creating any given benefit. For example, choices about the SDR of environmental protectionEnvironmental protection
Environmental protection is a practice of protecting the environment, on individual, organizational or governmental level, for the benefit of the natural environment and humans. Due to the pressures of population and our technology the biophysical environment is being degraded, sometimes permanently...
projects, such as funding the reduction of global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
, place a greater valuation on future generations.
Importance in global climate changes
This topic has recently been very controversial and highly debated. Since there is such a strong probability that the world will suffer significantly in the future due to global change in temperature, finding the correct social discount rate for the benefits of reducing CO2 emissions and other harmful greenhouse gases is very important.
"The choice of an appropriate social time discount rate has long been debated. Some very intelligent people have argued that giving future generations less weight than the current generation is “ethically indefensible.” Other equally intelligent people have argued that weighting generations equally leads to paradoxical and even nonsensical results."
The range in the social discount rate for a cost-benefit analysis in this issue range from zero to over 3 percent. Some argue that the only reason for discounting future generations is that these generations might cease to exist in the future. Thus the rate should equal zero since the probability for such a catastrophic event is so low (assumed to be .01 percent per year).
This infers that there is equal weight given to all generations. The Stern Review
Stern Review
The Stern Review on the Economics of Climate Change is a 700-page report released for the British government on 30 October 2006 by economist Nicholas Stern, chair of the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at the London School of Economics and also chair of the Centre...
on the Economics of Climate Change is one such report that argues for zero discounting of future generations. While William D. Nordhaus of Yale
"examines a model of climate change that is similar to the one used in the Stern Review but with a 3 percent social discount rate that slowly declines to 1 percent in 300 years rather than the 0.1 percent discount rate used in the Stern Review. In his model, the welfare of future generations is given less weight than the current generation’s welfare. He finds that preventive measures like a tax on carbon emissions are certainly required. But they are of a much smaller magnitude than those recommended in the [Stern] report."
See also
- Public policyPublic policyPublic policy as government action is generally the principled guide to action taken by the administrative or executive branches of the state with regard to a class of issues in a manner consistent with law and institutional customs. In general, the foundation is the pertinent national and...
- Applied information economicsApplied information economicsApplied information economics is a decision analysis method developed by Douglas W. Hubbard and partially described in his book How to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in Business . AIE is a method for the practical application of several proven methods from decision theory and...
- Financial analysisFinancial analysisFinancial analysis refers to an assessment of the viability, stability and profitability of a business, sub-business or project....
- Kaldor-Hicks efficiencyKaldor-Hicks efficiencyKaldor–Hicks efficiency, named for Nicholas Kaldor and John Hicks, also known as Kaldor–Hicks criterion, is a measure of economic efficiency that captures some of the intuitive appeal of Pareto efficiency, but has less stringent criteria and is hence applicable to more circumstances...
- Risk-benefit analysisRisk-benefit analysisRisk–benefit analysis is the comparison of the risk of a situation to its related benefits. Exposure to personal risk is recognized as a normal aspect of everyday life. We accept a certain level of risk in our lives as necessary to achieve certain benefits. In most of these risks we feel as though...
- Ramsey growth modelRamsey growth modelThe Ramsey–Cass–Koopmans model or the Ramsey growth model is a neo-classical model of economic growth based primarily on the work of the economist and mathematician Frank P. Ramsey, with significant extensions by David Cass and Tjalling Koopmans...

