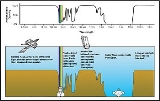
Skywave
Overview
Radio propagation
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves when they are transmitted, or propagated from one point on the Earth to another, or into various parts of the atmosphere...
of electromagnetic waves
Radio waves
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum longer than infrared light. Radio waves have frequencies from 300 GHz to as low as 3 kHz, and corresponding wavelengths from 1 millimeter to 100 kilometers. Like all other electromagnetic waves,...
bent (refracted) back to the Earth's surface by the ionosphere
Ionosphere
The ionosphere is a part of the upper atmosphere, comprising portions of the mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere, distinguished because it is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important part in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere...
. As a result of skywave propagation, a broadcast
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the distribution of audio and video content to a dispersed audience via any audio visual medium. Receiving parties may include the general public or a relatively large subset of thereof...
signal from a distant AM broadcasting
AM broadcasting
AM broadcasting is the process of radio broadcasting using amplitude modulation. AM was the first method of impressing sound on a radio signal and is still widely used today. Commercial and public AM broadcasting is carried out in the medium wave band world wide, and on long wave and short wave...
station at night, or from a shortwave radio station (or during sporadic E season
Sporadic E propagation
Sporadic E or Es is an unusual form of radio propagation using characteristics of the Earth's ionosphere. Whereas most forms of skywave propagation use the normal and cyclic ionization properties of the ionosphere's F region to refract radio signals back toward the Earth's surface, sporadic E...
, a low band TV station) can sometimes be heard as clearly as local stations.
(This is distinct from groundwave propagation, which is direct from transmitter to radio).
Unanswered Questions

