
Silicon monoxide
Encyclopedia
Silicon monoxide is the chemical compound with the formula SiO. In the vapour phase it is a diatomic molecule. It has been detected in stellar objects and it has been described as the most common oxide of silicon in the universe.
When SiO gas is cooled rapidly it condenses to form a brown/black polymeric glass
y material,(SiO)n, which is available commercially and used to deposit films of SiO. Glassy (SiO)n is air and moisture sensitive. Its surface readily oxidizes in air at room temperature giving a SiO2 surface layer that protects the material from further oxidation. However, (SiO)n irreversibly disproportionates
into SiO2 and Si in a few hours between 400 and 800°C and very rapidly between 1,000 and 1440°C, although the reaction does not go to completion.
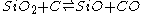
Complete reduction of SiO2 with twice the amount of carbon yields elemental silicon and twice the amount of carbon monoxide. In 1890, the German chemist Clemens Winkler
(the discoverer of germanium) was the first to attempt to synthesize SiO by heating silicon dioxide with silicon in a combustion furnace.
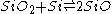
However, Winkler was not able to produce the monoxide since the temperature of the mixture was only around 1000°C. The experiment was repeated in 1905 by Henry Noel Potter (1869–1942), a Westinghouse
engineer. Using an electric furnace, Potter was able to attain a temperature of 1700°C and observe the generation of SiO. Potter also investigated the properties and applications of the solid form of SiO.
Because of the volatility of SiO, silica can be removed from ores or minerals by heating them with silicon to produce gaseous SiO in this manner. However, due to the difficulties associated with accurately measuring its vapor pressure and because of the dependency on the specifics of the experimental design, various values have been reported in the literature for the vapor pressure of SiO (g). For the pSiO above molten silicon in a quartz (SiO2) crucible at the melting point of silicon, one study yielded a value of 0.002 atm. For the direct vaporization of pure, amorphous SiO solid, 0.001 atm has been reported. For a coating system, at the phase boundary between SiO2 and a silicide, 0.01 atm was reported.
Silica itself, or refractories containing SiO2, can be reduced with H2 or CO at high temperatures, e.g.:
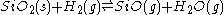
As the SiO product volatilizes off (is removed), the equilibrium shifts to the right, resulting in the continued consumption of SiO2. Based on the dependence of the rate of silica weight loss on the gas flow rate normal to the interface, the rate of this reduction appears to be controlled by convective diffusion or mass transfer from the reacting surface.
. However, the SiO triple bond has a calculated bond length of 1.50 pm and a bond energy of 794 kJ/mol, which are also very close to those reported for SiO. The SiO double bond structure is, notably, an exception to Lewis' octet rule
for molecules composed of the light main group elements, whereas the SiO triple bond satisfies this rule. That anomaly not withstanding, the observation that monomeric SiO is short-lived and that (SiO)n oligomer
s with n = 2,3,4,5 are known, all having closed ring structures in which the silicon atoms are connected through bridging oxygen atoms (i.e. each oxygen atom is singly bonded to two silicon atoms; no Si-Si bonds), suggests the Si=O double bond structure, with a hypovalent silicon atom, is likely for the monomer.
SiO condensed with F2
, Cl2
or COS, followed by irradiation with light, the planar molecules OSiF2,(Si-O 148 pm); OSiCl2, (Si-O 149 pm) and linear OSiS (Si-O 149 pm, Si-S 190 pm) are produced.
SiO condensed with oxygen atoms generated by microwave discharge produces molecular SiO2 which has a linear structure.
When metal atoms are co-deposited (i.e.: Na, Al, Pd, Ag, Au) triatomic molecules are produced with linear, (AlSiO and PdSiO), non-linear (AgSiO and AuSiO), and ring (NaSiO) structures.
and amorphous Si
with some chemical bonding at the interface of the Si and SiO2 phases.
When SiO gas is cooled rapidly it condenses to form a brown/black polymeric glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
y material,(SiO)n, which is available commercially and used to deposit films of SiO. Glassy (SiO)n is air and moisture sensitive. Its surface readily oxidizes in air at room temperature giving a SiO2 surface layer that protects the material from further oxidation. However, (SiO)n irreversibly disproportionates
Disproportionation
Disproportionation, also known as dismutation is used to describe a specific type of redox reaction in which a species is simultaneously reduced and oxidized so as to form two different products....
into SiO2 and Si in a few hours between 400 and 800°C and very rapidly between 1,000 and 1440°C, although the reaction does not go to completion.
Formation of SiO
The first precise report on the formation of SiO was in 1887 by the chemist Charles F. Maybery (1850–1927) at the Case School of Applied Science in Cleveland. Maybery claimed that SiO formed as an amorphous greenish-yellow substance with a vitreous luster when silica was reduced with charcoal in the absence of metals in an electric furnace. The substance was always found at the interface between the charcoal and silica particles. By investigating some of the chemical properties of the substance, its specific gravity, and a combustion analysis, Maybery deduced that the substance must be SiO. The equation representing the partial chemical reduction of SiO2 with C can be represented as: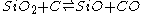
Complete reduction of SiO2 with twice the amount of carbon yields elemental silicon and twice the amount of carbon monoxide. In 1890, the German chemist Clemens Winkler
Clemens Winkler
Clemens Alexander Winkler was a German chemist who discovered the element germanium in 1886, solidifying Dmitri Mendeleev's theory of periodicity.- Life :...
(the discoverer of germanium) was the first to attempt to synthesize SiO by heating silicon dioxide with silicon in a combustion furnace.
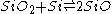
However, Winkler was not able to produce the monoxide since the temperature of the mixture was only around 1000°C. The experiment was repeated in 1905 by Henry Noel Potter (1869–1942), a Westinghouse
Westinghouse Electric (1886)
Westinghouse Electric was an American manufacturing company. It was founded in 1886 as Westinghouse Electric Company and later renamed Westinghouse Electric Corporation by George Westinghouse. The company purchased CBS in 1995 and became CBS Corporation in 1997...
engineer. Using an electric furnace, Potter was able to attain a temperature of 1700°C and observe the generation of SiO. Potter also investigated the properties and applications of the solid form of SiO.
Because of the volatility of SiO, silica can be removed from ores or minerals by heating them with silicon to produce gaseous SiO in this manner. However, due to the difficulties associated with accurately measuring its vapor pressure and because of the dependency on the specifics of the experimental design, various values have been reported in the literature for the vapor pressure of SiO (g). For the pSiO above molten silicon in a quartz (SiO2) crucible at the melting point of silicon, one study yielded a value of 0.002 atm. For the direct vaporization of pure, amorphous SiO solid, 0.001 atm has been reported. For a coating system, at the phase boundary between SiO2 and a silicide, 0.01 atm was reported.
Silica itself, or refractories containing SiO2, can be reduced with H2 or CO at high temperatures, e.g.:
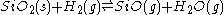
As the SiO product volatilizes off (is removed), the equilibrium shifts to the right, resulting in the continued consumption of SiO2. Based on the dependence of the rate of silica weight loss on the gas flow rate normal to the interface, the rate of this reduction appears to be controlled by convective diffusion or mass transfer from the reacting surface.
Gaseous (Molecular) SiO
Silicon monoxide molecules have been trapped in an argon matrix cooled by helium. The SiO bond length determined from SiO molecules isolated in argon is between 148.9 pm and 1.51 pm. This bond length is similar to the Si=O double bonds (rSiO = 1.48 pm) in matrix isolated linear, molecular, SiO2 (O=S=O), indicative of the absence of a triple bond as in COCarbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
. However, the SiO triple bond has a calculated bond length of 1.50 pm and a bond energy of 794 kJ/mol, which are also very close to those reported for SiO. The SiO double bond structure is, notably, an exception to Lewis' octet rule
Octet rule
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that states that atoms of low The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that states that atoms of low The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that states that atoms of low (The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that states that atoms of low (...
for molecules composed of the light main group elements, whereas the SiO triple bond satisfies this rule. That anomaly not withstanding, the observation that monomeric SiO is short-lived and that (SiO)n oligomer
Oligomer
In chemistry, an oligomer is a molecule that consists of a few monomer units , in contrast to a polymer that, at least in principle, consists of an unlimited number of monomers. Dimers, trimers, and tetramers are oligomers. Many oils are oligomeric, such as liquid paraffin...
s with n = 2,3,4,5 are known, all having closed ring structures in which the silicon atoms are connected through bridging oxygen atoms (i.e. each oxygen atom is singly bonded to two silicon atoms; no Si-Si bonds), suggests the Si=O double bond structure, with a hypovalent silicon atom, is likely for the monomer.
SiO condensed with F2
Fluorine
Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic...
, Cl2
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
or COS, followed by irradiation with light, the planar molecules OSiF2,(Si-O 148 pm); OSiCl2, (Si-O 149 pm) and linear OSiS (Si-O 149 pm, Si-S 190 pm) are produced.
SiO condensed with oxygen atoms generated by microwave discharge produces molecular SiO2 which has a linear structure.
When metal atoms are co-deposited (i.e.: Na, Al, Pd, Ag, Au) triatomic molecules are produced with linear, (AlSiO and PdSiO), non-linear (AgSiO and AuSiO), and ring (NaSiO) structures.
Solid (Polymeric) SiO
Potter reported SiO solid as yellowish-brown in color and as being an electrical and thermal insulator. The solid burns in oxygen and decomposes water with the liberation of hydrogen. It dissolves in warm alkali hydroxides and in hydrofluoric acid. Although Potter reported the heat of combustion of SiO to be 200 to 800 calories higher than that of an equilibrium mixture of Si and SiO2 (which could, arguably, be used as evidence that SiO is a unique chemical compound), recent microscopy and spectroscopy studies suggest that amorphous solid SiO is best considered as an inhomogeneous mixture of amorphous SiO2Silicon dioxide
The chemical compound silicon dioxide, also known as silica , is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula '. It has been known for its hardness since antiquity...
and amorphous Si
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
with some chemical bonding at the interface of the Si and SiO2 phases.

