
Sheffer sequence
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a Sheffer sequence or poweroid is a polynomial sequence
, i.e., a sequence { pn(x) : n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ... } of polynomial
s in which the index of each polynomial equals its degree, satisfying conditions related to the umbral calculus
in combinatorics. They are named for Isadore M. Sheffer
.
Define a linear operator Q on polynomials in x by
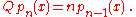
This determines Q on all polynomials. The polynomial sequence pn is a Sheffer sequence if the linear operator Q just defined is shift-equivariant. Here we define a linear operator Q on polynomials to be shift-equivariant if whenever f(x) = g(x + a) is a "shift" of g(x), then (Qf)(x) = (Qg)(x + a), i.e., Q commutes with every "shift operator". Such a Q is a delta operator.
under the operation of umbral composition of polynomial sequences, defined as follows. Suppose { pn(x) : n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ... } and { qn(x) : n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ... } are polynomial sequences, given by

Then the umbral composition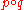 is the polynomial sequence whose nth term is
is the polynomial sequence whose nth term is
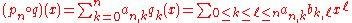
(the subscript n appears in pn, since this is the n term of that sequence, but not in q, since this refers to the sequence as a whole rather than one of its terms).
The neutral element of this group is the standard monomial basis
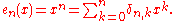
Two important subgroups are the group of Appell sequences, which are those sequences for which the operator Q is mere differentiation, and the group of sequences of binomial type, which are those that satisfy the identity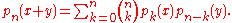
A Sheffer sequence { pn(x): n = 0, 1, 2, ... } is of binomial type if and only if both
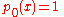
and
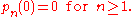
The group of Appell sequences is abelian
; the group of sequences of binomial type is not. The group of Appell sequences is a normal subgroup
; the group of sequences of binomial type is not. The group of Sheffer sequences is a semidirect product
of the group of Appell sequences and the group of sequences of binomial type. It follows that each coset
of the group of Appell sequences contains exactly one sequence of binomial type. Two Sheffer sequences are in the same such coset if and only if the operator Q described above – called the "delta operator" of that sequence – is the same linear operator in both cases. (Generally, a delta operator is a shift-equivariant linear operator on polynomials that reduces degree by one. The term is due to F. Hildebrandt.)
If sn(x) is a Sheffer sequence and pn(x) is the one sequence of binomial type that shares the same delta operator, then
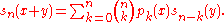
Sometimes the term Sheffer sequence is defined to mean a sequence that bears this relation to some sequence of binomial type.
In particular, if { sn(x) } is an Appell sequence, then
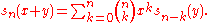
The sequence of Hermite polynomials
, the sequence of Bernoulli polynomials
, and the monomial
s { xn : n = 0, 1, 2, ... } are examples of Appell sequences.
A Sheffer sequence pn is characterised by its exponential generating function
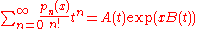
where A and B are (formal) power series in t. Sheffer sequences are thus examples of generalized Appell polynomials and hence have an associated recurrence relation
.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a Sheffer sequence or poweroid is a polynomial sequence
Polynomial sequence
In mathematics, a polynomial sequence is a sequence of polynomials indexed by the nonnegative integers 0, 1, 2, 3, ..., in which each index is equal to the degree of the corresponding polynomial...
, i.e., a sequence { pn(x) : n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ... } of polynomial
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
s in which the index of each polynomial equals its degree, satisfying conditions related to the umbral calculus
Umbral calculus
In mathematics before the 1970s, the term umbral calculus referred to the surprising similarity between seemingly unrelated polynomial equations and certain shadowy techniques used to 'prove' them. These techniques were introduced by and are sometimes called Blissard's symbolic method...
in combinatorics. They are named for Isadore M. Sheffer
Isadore M. Sheffer
Isadore Mitchell Sheffer was an American mathematician best known for the Sheffer sequence. Born in Massachusetts, he lived a large portion of his life in State College, Pennsylvania, where he was a Professor of Mathematics at Pennsylvania State University.He received his PhD from Harvard...
.
Definition
Fix a polynomial sequence pn.Define a linear operator Q on polynomials in x by

This determines Q on all polynomials. The polynomial sequence pn is a Sheffer sequence if the linear operator Q just defined is shift-equivariant. Here we define a linear operator Q on polynomials to be shift-equivariant if whenever f(x) = g(x + a) is a "shift" of g(x), then (Qf)(x) = (Qg)(x + a), i.e., Q commutes with every "shift operator". Such a Q is a delta operator.
Properties
The set of all Sheffer sequences is a groupGroup (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with an operation that combines any two of its elements to form a third element. To qualify as a group, the set and the operation must satisfy a few conditions called group axioms, namely closure, associativity, identity...
under the operation of umbral composition of polynomial sequences, defined as follows. Suppose { pn(x) : n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ... } and { qn(x) : n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ... } are polynomial sequences, given by

Then the umbral composition
 is the polynomial sequence whose nth term is
is the polynomial sequence whose nth term is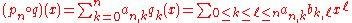
(the subscript n appears in pn, since this is the n term of that sequence, but not in q, since this refers to the sequence as a whole rather than one of its terms).
The neutral element of this group is the standard monomial basis
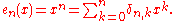
Two important subgroups are the group of Appell sequences, which are those sequences for which the operator Q is mere differentiation, and the group of sequences of binomial type, which are those that satisfy the identity
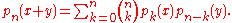
A Sheffer sequence { pn(x): n = 0, 1, 2, ... } is of binomial type if and only if both
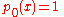
and
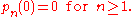
The group of Appell sequences is abelian
Abelian group
In abstract algebra, an abelian group, also called a commutative group, is a group in which the result of applying the group operation to two group elements does not depend on their order . Abelian groups generalize the arithmetic of addition of integers...
; the group of sequences of binomial type is not. The group of Appell sequences is a normal subgroup
Normal subgroup
In abstract algebra, a normal subgroup is a subgroup which is invariant under conjugation by members of the group. Normal subgroups can be used to construct quotient groups from a given group....
; the group of sequences of binomial type is not. The group of Sheffer sequences is a semidirect product
Semidirect product
In mathematics, specifically in the area of abstract algebra known as group theory, a semidirect product is a particular way in which a group can be put together from two subgroups, one of which is a normal subgroup. A semidirect product is a generalization of a direct product...
of the group of Appell sequences and the group of sequences of binomial type. It follows that each coset
Coset
In mathematics, if G is a group, and H is a subgroup of G, and g is an element of G, thenA coset is a left or right coset of some subgroup in G...
of the group of Appell sequences contains exactly one sequence of binomial type. Two Sheffer sequences are in the same such coset if and only if the operator Q described above – called the "delta operator" of that sequence – is the same linear operator in both cases. (Generally, a delta operator is a shift-equivariant linear operator on polynomials that reduces degree by one. The term is due to F. Hildebrandt.)
If sn(x) is a Sheffer sequence and pn(x) is the one sequence of binomial type that shares the same delta operator, then
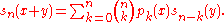
Sometimes the term Sheffer sequence is defined to mean a sequence that bears this relation to some sequence of binomial type.
In particular, if { sn(x) } is an Appell sequence, then
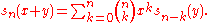
The sequence of Hermite polynomials
Hermite polynomials
In mathematics, the Hermite polynomials are a classical orthogonal polynomial sequence that arise in probability, such as the Edgeworth series; in combinatorics, as an example of an Appell sequence, obeying the umbral calculus; in numerical analysis as Gaussian quadrature; and in physics, where...
, the sequence of Bernoulli polynomials
Bernoulli polynomials
In mathematics, the Bernoulli polynomials occur in the study of many special functions and in particular the Riemann zeta function and the Hurwitz zeta function. This is in large part because they are an Appell sequence, i.e. a Sheffer sequence for the ordinary derivative operator...
, and the monomial
Monomial
In mathematics, in the context of polynomials, the word monomial can have one of two different meanings:*The first is a product of powers of variables, or formally any value obtained by finitely many multiplications of a variable. If only a single variable x is considered, this means that any...
s { xn : n = 0, 1, 2, ... } are examples of Appell sequences.
A Sheffer sequence pn is characterised by its exponential generating function
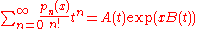
where A and B are (formal) power series in t. Sheffer sequences are thus examples of generalized Appell polynomials and hence have an associated recurrence relation
Recurrence relation
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation that recursively defines a sequence, once one or more initial terms are given: each further term of the sequence is defined as a function of the preceding terms....
.
Examples
Examples of polynomial sequences which are Sheffer sequences include:- The Abel polynomials;
- The Bernoulli polynomialsBernoulli polynomialsIn mathematics, the Bernoulli polynomials occur in the study of many special functions and in particular the Riemann zeta function and the Hurwitz zeta function. This is in large part because they are an Appell sequence, i.e. a Sheffer sequence for the ordinary derivative operator...
; - The central factorial polynomials;
- The Hermite polynomialsHermite polynomialsIn mathematics, the Hermite polynomials are a classical orthogonal polynomial sequence that arise in probability, such as the Edgeworth series; in combinatorics, as an example of an Appell sequence, obeying the umbral calculus; in numerical analysis as Gaussian quadrature; and in physics, where...
; - The Laguerre polynomialsLaguerre polynomialsIn mathematics, the Laguerre polynomials, named after Edmond Laguerre ,are the canonical solutions of Laguerre's equation:x\,y + \,y' + n\,y = 0\,which is a second-order linear differential equation....
; - The Mahler polynomials;
- The monomialMonomialIn mathematics, in the context of polynomials, the word monomial can have one of two different meanings:*The first is a product of powers of variables, or formally any value obtained by finitely many multiplications of a variable. If only a single variable x is considered, this means that any...
s { xn : n = 0, 1, 2, ... } ; - The Mott polynomialsMott polynomialsIn mathematics the Mott polynomials sn are polynomials introduced by who applied them to a problem in the theory of electrons.They are given by exp = \sum_ns_nt^n/n!...
;
External links
- Sheffer Sequence at MathWorldMathWorldMathWorld is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Digital Library grant to the University of Illinois at...

