
Shaken baby syndrome
Encyclopedia
Shaken baby syndrome is a triad of medical symptoms: subdural hematoma
, retinal hemorrhage, and brain swelling from which doctors, consistent with current medical understanding, infer child abuse
caused by intentional shaking. In a majority of cases there is no visible sign of external trauma.
SBS is often fatal and can cause severe brain damage
, resulting in lifelong disability. Estimated death rates (mortality
) among infants with SBS range from 15% to 38%; the median is 20%–25%. Up to half of deaths related to child abuse are reportedly due to shaken baby syndrome. Nonfatal consequences of SBS include varying degrees of visual impairment (including blindness
), motor impairment (e.g. cerebral palsy
) and cognitive impairment
s.
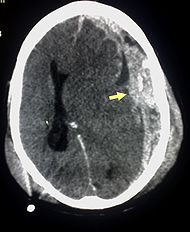 The characteristic injuries associated with SBS include retinal hemorrhages, multiple fractures of the long bones, and subdural hematoma
The characteristic injuries associated with SBS include retinal hemorrhages, multiple fractures of the long bones, and subdural hematoma
s (bleeding in the brain). These signs have evolved through the years as the accepted and recognized signs of child abuse and the shaken baby syndrome. Medical professionals strongly suspect shaking as the cause of injuries when a baby or small child presents with retinal hemorrhage, fractures
, soft tissue
injuries or subdural hematoma, that cannot be explained by accidental trauma or other medical conditions. About three quarters of cases involve retinal hemorrhaging. Additional effects of SBS are diffuse axonal injury
, oxygen deprivation
and swelling of the brain
, which can raise intracranial pressure
and damage delicate brain tissue. A recent study found the prevalence of retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma was 78%, but only 5.3% in nonabusive pediatric head trauma.
Victims of SBS may display irritability, failure to thrive
, alterations in eating patterns, lethargy, vomiting
, seizure
s, bulging or tense fontanels (the soft spots on an infant's head), increased size of the head, altered breathing, and dilated pupil
s.
Fracture
s of the vertebrae, long bones, and ribs may also be associated with SBS. Dr. John Caffey reported in 1972 that metaphyseal avulsions (small fragments of bone had been torn off where the periosteum covering the bone and the cortical bone
are tightly bound together) and "bones on both the proximal and distal sides of a single joint are affected, especially at the knee".
The type of injuries caused by shaking injury are usually not caused by falls and impacts from normal play, which are mostly linear forces. The type of shaking that is necessary to cause SBS is very violent and would be clearly recognizable to an observer as dangerous and potentially deadly. The mechanism of ocular abnormalities appears to be related to vitreoretinal traction, with movement of the vitreous contributing to development of the characteristic retinal hemorrhages. These ocular findings correlate well with intracranial abnormalities.
in general. New parents, babysitters, and other caregivers can be warned about the dangers of shaking infants. A child's crying and irritation are common triggers for the frustration that can lead to violence in the caregiver. Some experts offer caregivers strategies to cope with their own frustrations.
 SBS may be misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed, and caregivers may lie or be unaware of the mechanism of injury. Commonly, there are no externally visible signs of the condition,. Examination by an experienced ophthalmologist is often critical in diagnosing shaken baby syndrome, as particular forms of ocular bleeding are quite characteristic. No alternative condition mimics all of the symptoms of SBS exactly, but those that must be ruled out include hydrocephalus
SBS may be misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed, and caregivers may lie or be unaware of the mechanism of injury. Commonly, there are no externally visible signs of the condition,. Examination by an experienced ophthalmologist is often critical in diagnosing shaken baby syndrome, as particular forms of ocular bleeding are quite characteristic. No alternative condition mimics all of the symptoms of SBS exactly, but those that must be ruled out include hydrocephalus
, sudden infant death syndrome
(SIDS), seizure disorders, and infectious
or congenital diseases like meningitis
and metabolic disorders. CT scanning and magnetic resonance imaging
are used to diagnose the condition. Conditions that may accompany SBS include bone fracture
s, injury to the cervical spine (in the neck), hemorrhaging of the retina
(in the eye), cerebral hemorrhage or atrophy
, hydrocephalus
, and papilledema
(swelling of the optic disc
).
(the pressure within the skull), draining of fluid from the cerebral ventricles, and, if an intracranial hematoma is present, draining of the hematoma.
One third of these patients die, one third survives with a major neurological condition, and only one third survives in good condition. The most frequent neurological impairments are learning disabilities, seizure disorders, speech disabilities, hydrocephalus
, cerebral palsy
, and visual disorders.
and emotional stress, resulting for example from financial troubles, are other risk factors for aggression and impulsiveness in caregivers. Both males and females can inflict SBS, but the abusers are more often male. Although it had been previously speculated that SBS was an isolated event, a history of prior child abuse is a common finding in cases of SBS. In an estimated 33–40% of cases, evidence of prior head injuries, such as old intracranial bleeds, is present.
or both. In 1971, Dr. Norman Guthkelch proposed that whiplash injury caused subdural hemorrhage in infants by tearing the veins in the subdural space. Development of computed tomography
and magnetic resonance imaging
techniques in the 1970s and 1980s advanced the ability to diagnose the syndrome.
heard four appeals of SBS convictions: one case was dropped, the sentence was reduced for one, and two convictions were upheld. The court found that the classic triad of retinal hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, and acute encephalopathy
are not 100% diagnostic of SBS and that clinical history is also important. In the Court's ruling, they upheld the clinical concept of SBS but dismissed one case and reduced another from murder to manslaughter. In their words: "Whilst a strong pointer to NAHI [non-accidental head injury] on its own we do not think it possible to find that it must automatically and necessarily lead to a diagnosis of NAHI. All the circumstances, including the clinical picture, must be taken into account."
The court invalidated a "unified hypothesis" proposed by Geddes and colleagues as an alternative mechanism for the subdural and retinal hemorrhage found in suspected cases of SBS. The unified hypothesis proposed that the hemorrhage was not caused by shearing of subdural and retinal veins but rather by cerebral hypoxia
, increased intracranial pressure
, and increased pressure in the brain's blood vessels. The court reported that "the unified hypothesis [could] no longer be regarded as a credible or alternative cause of the triad of injuries": subdural haemorrhage, retinal bleeding and encephalopathy
due to hypoxemia
(low blood oxygen) found in suspected SBS.
On January 31, 2008, the Wisconsin Court of Appeals granted Audrey A. Edmonds a new trial based on "competing credible medical opinions in determining whether there is a reasonable doubt as to Edmunds's guilt." Specifically, the appeals court found that "Edmunds presented evidence that was not discovered until after her conviction, in the form of expert medical testimony, that a significant and legitimate debate in the medical community has developed in the past ten years over whether infants can be fatally injured through shaking alone, whether an infant may suffer head trauma and yet experience a significant lucid interval prior to death, and whether other causes may mimic the symptoms traditionally viewed as indicating shaken baby or shaken impact syndrome."
The terms non-accidental trauma or "abusive head trauma" have been suggested instead of "SBS".
deficiency. This contested hypothesis is based upon a speculated marginal, near scorbutic condition or lack of essential nutrient(s) repletion and a potential elevated histamine level. However symptoms consistent with increased histamine
levels, such as low blood pressure and allergic symptoms, are not commonly associated with scurvy
as clinically significant vitamin C deficiency. A literature review of this hypothesis in the journal Pediatrics International
"From the available information in the literature, concluded that there was no convincing evidence to conclude that vitamin C deficiency can be considered to be a cause of shaken baby syndrome."
The proponents of such hypotheses often question the adequacy of nutrient tissue levels, especially vitamin C, for those children currently or recently ill, bacterial infections, those with higher individual requirements, those suffering from environmental challenges (e.g. allergies), and perhaps transient vaccination-related stresses. Given that patients presenting with suspected SBS would constitute only the most severely affected group of children with nutritionally deficiencies, one would expect a larger number of individuals seen with milder symptoms. At the time of this writing, infantile scurvy in the United states is practically nonexistent. No cases of scurvy
mimicking SBS or Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
have been reported, and scurvy typically occurs later in infancy, rarely causes death or intracranial bleeding, and is accompanied by other changes of the bones and skin and invariably an unusually deficient dietary history.
abnormality in cases of inflicted head injury in the very young is diffuse
hypoxic brain damage, not DAI,
and suggested two possible explanations: either the unmyelinated axon of the immature cerebral hemispheres is relatively resistant to traumatic damage, or in shaking-type injuries the brain is not exposed to the forces necessary to produce DAI.
The BBC has made a documentary in 3 parts that covers arguments for and against the diagnosis of SBS.
Subdural hematoma
A subdural hematoma or subdural haematoma , also known as a subdural haemorrhage , is a type of haematoma, a form of traumatic brain injury. Blood gathers within the outermost meningeal layer, between the dura mater, which adheres to the skull, and the arachnoid mater, which envelops the brain...
, retinal hemorrhage, and brain swelling from which doctors, consistent with current medical understanding, infer child abuse
Child abuse
Child abuse is the physical, sexual, emotional mistreatment, or neglect of a child. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Department of Children And Families define child maltreatment as any act or series of acts of commission or omission by a parent or...
caused by intentional shaking. In a majority of cases there is no visible sign of external trauma.
SBS is often fatal and can cause severe brain damage
Brain damage
"Brain damage" or "brain injury" is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors...
, resulting in lifelong disability. Estimated death rates (mortality
Mortality rate
Mortality rate is a measure of the number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit time...
) among infants with SBS range from 15% to 38%; the median is 20%–25%. Up to half of deaths related to child abuse are reportedly due to shaken baby syndrome. Nonfatal consequences of SBS include varying degrees of visual impairment (including blindness
Blindness
Blindness is the condition of lacking visual perception due to physiological or neurological factors.Various scales have been developed to describe the extent of vision loss and define blindness...
), motor impairment (e.g. cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy is an umbrella term encompassing a group of non-progressive, non-contagious motor conditions that cause physical disability in human development, chiefly in the various areas of body movement....
) and cognitive impairment
Cognitive deficit
Cognitive deficit, also known as cognitive impairment is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to cognitive performance...
s.
Signs and symptoms

Subdural hematoma
A subdural hematoma or subdural haematoma , also known as a subdural haemorrhage , is a type of haematoma, a form of traumatic brain injury. Blood gathers within the outermost meningeal layer, between the dura mater, which adheres to the skull, and the arachnoid mater, which envelops the brain...
s (bleeding in the brain). These signs have evolved through the years as the accepted and recognized signs of child abuse and the shaken baby syndrome. Medical professionals strongly suspect shaking as the cause of injuries when a baby or small child presents with retinal hemorrhage, fractures
Bone fracture
A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the bone...
, soft tissue
Soft tissue
In anatomy, the term soft tissue refers to tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body, not being bone. Soft tissue includes tendons, ligaments, fascia, skin, fibrous tissues, fat, and synovial membranes , and muscles, nerves and blood vessels .It is sometimes...
injuries or subdural hematoma, that cannot be explained by accidental trauma or other medical conditions. About three quarters of cases involve retinal hemorrhaging. Additional effects of SBS are diffuse axonal injury
Diffuse axonal injury
Diffuse axonal injury is one of the most common and devastating types of traumatic brain injury, meaning that damage occurs over a more widespread area than in focal brain injury. DAI, which refers to extensive lesions in white matter tracts, is one of the major causes of unconsciousness and...
, oxygen deprivation
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
and swelling of the brain
Cerebral edema
Cerebral edema or cerebral œdema is an excess accumulation of water in the intracellular or extracellular spaces of the brain.-Vasogenic:Due to a breakdown of tight endothelial junctions which make up the blood-brain barrier...
, which can raise intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
and damage delicate brain tissue. A recent study found the prevalence of retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma was 78%, but only 5.3% in nonabusive pediatric head trauma.
Victims of SBS may display irritability, failure to thrive
Failure to thrive
Failure to thrive is a medical term which is used in both pediatric and adult human medicine, as well as veterinary medicine ....
, alterations in eating patterns, lethargy, vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
, seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s, bulging or tense fontanels (the soft spots on an infant's head), increased size of the head, altered breathing, and dilated pupil
Pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to enter the retina. It appears black because most of the light entering the pupil is absorbed by the tissues inside the eye. In humans the pupil is round, but other species, such as some cats, have slit pupils. In...
s.
Fracture
Fracture
A fracture is the separation of an object or material into two, or more, pieces under the action of stress.The word fracture is often applied to bones of living creatures , or to crystals or crystalline materials, such as gemstones or metal...
s of the vertebrae, long bones, and ribs may also be associated with SBS. Dr. John Caffey reported in 1972 that metaphyseal avulsions (small fragments of bone had been torn off where the periosteum covering the bone and the cortical bone
Cortical bone
Cortical bone, synonymous with compact bone, is one of the two types of osseous tissue that form bones. Cortical bone facilitates bone's main functions: to support the whole body, protect organs, provide levers for movement, and store and release chemical elements, mainly calcium. As its name...
are tightly bound together) and "bones on both the proximal and distal sides of a single joint are affected, especially at the knee".
Mechanism
SBS results from rotational acceleration of the head. Rotational injury is especially damaging and likely to occur in shaking trauma.The type of injuries caused by shaking injury are usually not caused by falls and impacts from normal play, which are mostly linear forces. The type of shaking that is necessary to cause SBS is very violent and would be clearly recognizable to an observer as dangerous and potentially deadly. The mechanism of ocular abnormalities appears to be related to vitreoretinal traction, with movement of the vitreous contributing to development of the characteristic retinal hemorrhages. These ocular findings correlate well with intracranial abnormalities.
Prevention
Prevention is similar to the prevention of child abuseChild abuse
Child abuse is the physical, sexual, emotional mistreatment, or neglect of a child. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Department of Children And Families define child maltreatment as any act or series of acts of commission or omission by a parent or...
in general. New parents, babysitters, and other caregivers can be warned about the dangers of shaking infants. A child's crying and irritation are common triggers for the frustration that can lead to violence in the caregiver. Some experts offer caregivers strategies to cope with their own frustrations.
Diagnosis

Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus , also known as "water in the brain," is a medical condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, or cavities, of the brain. This may cause increased intracranial pressure inside the skull and progressive enlargement of the head,...
, sudden infant death syndrome
Sudden infant death syndrome
Sudden infant death syndrome is marked by the sudden death of an infant that is unexpected by medical history, and remains unexplained after a thorough forensic autopsy and a detailed death scene investigation. An infant is at the highest risk for SIDS during sleep, which is why it is sometimes...
(SIDS), seizure disorders, and infectious
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
or congenital diseases like meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and less commonly by certain drugs...
and metabolic disorders. CT scanning and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
are used to diagnose the condition. Conditions that may accompany SBS include bone fracture
Bone fracture
A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the bone...
s, injury to the cervical spine (in the neck), hemorrhaging of the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
(in the eye), cerebral hemorrhage or atrophy
Atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations , poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, disuse or lack of exercise or disease intrinsic to the tissue itself...
, hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus , also known as "water in the brain," is a medical condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, or cavities, of the brain. This may cause increased intracranial pressure inside the skull and progressive enlargement of the head,...
, and papilledema
Papilledema
Papilledema is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare....
(swelling of the optic disc
Optic disc
The optic disc or optic nerve head is the location where ganglion cell axons exit the eye to form the optic nerve. There are no light sensitive rods or cones to respond to a light stimulus at this point. This causes a break in the visual field called "the blind spot" or the "physiological blind spot"...
).
Treatment
Treatment involves monitoring of intracranial pressureIntracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
(the pressure within the skull), draining of fluid from the cerebral ventricles, and, if an intracranial hematoma is present, draining of the hematoma.
Prognosis
Prognosis depends on severity and can range from total recovery to severe disability to death when the injury is severe.One third of these patients die, one third survives with a major neurological condition, and only one third survives in good condition. The most frequent neurological impairments are learning disabilities, seizure disorders, speech disabilities, hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus , also known as "water in the brain," is a medical condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, or cavities, of the brain. This may cause increased intracranial pressure inside the skull and progressive enlargement of the head,...
, cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy is an umbrella term encompassing a group of non-progressive, non-contagious motor conditions that cause physical disability in human development, chiefly in the various areas of body movement....
, and visual disorders.
Epidemiology
Small children are at particularly high risk for the abuse that causes SBS given the large difference in size between the small child and an adult. SBS usually occurs in children under the age of two but may occur in those up to age five.Risk factors
Caregivers that are at risk for becoming abusive often have unrealistic expectations of the child and may display "role reversal", expecting the child to fulfill the needs of the caregiver. Substance abuseSubstance abuse
A substance-related disorder is an umbrella term used to describe several different conditions associated with several different substances .A substance related disorder is a condition in which an individual uses or abuses a...
and emotional stress, resulting for example from financial troubles, are other risk factors for aggression and impulsiveness in caregivers. Both males and females can inflict SBS, but the abusers are more often male. Although it had been previously speculated that SBS was an isolated event, a history of prior child abuse is a common finding in cases of SBS. In an estimated 33–40% of cases, evidence of prior head injuries, such as old intracranial bleeds, is present.
History
In 1946, the concept of SBS and the term "whiplash shaken infant syndrome" was introduced by Dr. John Caffey, a pediatric radiologist. The term described a set of symptoms found with little or no external evidence of head trauma, including retinal hemorrhages and intracranial hemorrhages with subdural or subarachnoid bleedingSubarachnoid hemorrhage
A subarachnoid hemorrhage , or subarachnoid haemorrhage in British English, is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the brain...
or both. In 1971, Dr. Norman Guthkelch proposed that whiplash injury caused subdural hemorrhage in infants by tearing the veins in the subdural space. Development of computed tomography
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
techniques in the 1970s and 1980s advanced the ability to diagnose the syndrome.
Concerns raised by SBS pioneer
Dr. Norman Guthkelch stated in 2011,"I don't think that the famous triad, however well some people think it's defined, can ever be so well-defined that you can say that and nothing else cause it — that meaning shaking." He is also concerned by the number of cases similar to one he reviewed in Arizona that he concluded that child likely died of natural causes not SBS stating, "I think I used the expression in my report, 'I wouldn't hang a cat on the evidence of shaking, as presented.' "Legal issues
In July 2005, the Court of Appeals in the United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
heard four appeals of SBS convictions: one case was dropped, the sentence was reduced for one, and two convictions were upheld. The court found that the classic triad of retinal hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, and acute encephalopathy
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy means disorder or disease of the brain. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of global brain dysfunction; this syndrome can be caused by many different illnesses.-Terminology:...
are not 100% diagnostic of SBS and that clinical history is also important. In the Court's ruling, they upheld the clinical concept of SBS but dismissed one case and reduced another from murder to manslaughter. In their words: "Whilst a strong pointer to NAHI [non-accidental head injury] on its own we do not think it possible to find that it must automatically and necessarily lead to a diagnosis of NAHI. All the circumstances, including the clinical picture, must be taken into account."
The court invalidated a "unified hypothesis" proposed by Geddes and colleagues as an alternative mechanism for the subdural and retinal hemorrhage found in suspected cases of SBS. The unified hypothesis proposed that the hemorrhage was not caused by shearing of subdural and retinal veins but rather by cerebral hypoxia
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
, increased intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
, and increased pressure in the brain's blood vessels. The court reported that "the unified hypothesis [could] no longer be regarded as a credible or alternative cause of the triad of injuries": subdural haemorrhage, retinal bleeding and encephalopathy
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy means disorder or disease of the brain. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of global brain dysfunction; this syndrome can be caused by many different illnesses.-Terminology:...
due to hypoxemia
Hypoxemia
Hypoxemia is generally defined as decreased partial pressure of oxygen in blood, sometimes specifically as less than or causing hemoglobin oxygen saturation of less than 90%.-Distinction from anemia and hypoxia:...
(low blood oxygen) found in suspected SBS.
On January 31, 2008, the Wisconsin Court of Appeals granted Audrey A. Edmonds a new trial based on "competing credible medical opinions in determining whether there is a reasonable doubt as to Edmunds's guilt." Specifically, the appeals court found that "Edmunds presented evidence that was not discovered until after her conviction, in the form of expert medical testimony, that a significant and legitimate debate in the medical community has developed in the past ten years over whether infants can be fatally injured through shaking alone, whether an infant may suffer head trauma and yet experience a significant lucid interval prior to death, and whether other causes may mimic the symptoms traditionally viewed as indicating shaken baby or shaken impact syndrome."
The terms non-accidental trauma or "abusive head trauma" have been suggested instead of "SBS".
Vitamin C deficiency
Some authors have suggested that certain cases of suspected shaken baby syndrome may result from vitamin CVitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
deficiency. This contested hypothesis is based upon a speculated marginal, near scorbutic condition or lack of essential nutrient(s) repletion and a potential elevated histamine level. However symptoms consistent with increased histamine
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
levels, such as low blood pressure and allergic symptoms, are not commonly associated with scurvy
Scurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. The chemical name for vitamin C, ascorbic acid, is derived from the Latin name of scurvy, scorbutus, which also provides the adjective scorbutic...
as clinically significant vitamin C deficiency. A literature review of this hypothesis in the journal Pediatrics International
Pediatrics International
Pediatrics International is a peer reviewed open access journal for pediatrics, published in English by the Japan Pediatrics Society....
"From the available information in the literature, concluded that there was no convincing evidence to conclude that vitamin C deficiency can be considered to be a cause of shaken baby syndrome."
The proponents of such hypotheses often question the adequacy of nutrient tissue levels, especially vitamin C, for those children currently or recently ill, bacterial infections, those with higher individual requirements, those suffering from environmental challenges (e.g. allergies), and perhaps transient vaccination-related stresses. Given that patients presenting with suspected SBS would constitute only the most severely affected group of children with nutritionally deficiencies, one would expect a larger number of individuals seen with milder symptoms. At the time of this writing, infantile scurvy in the United states is practically nonexistent. No cases of scurvy
Scurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. The chemical name for vitamin C, ascorbic acid, is derived from the Latin name of scurvy, scorbutus, which also provides the adjective scorbutic...
mimicking SBS or Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
Sudden infant death syndrome
Sudden infant death syndrome is marked by the sudden death of an infant that is unexpected by medical history, and remains unexplained after a thorough forensic autopsy and a detailed death scene investigation. An infant is at the highest risk for SIDS during sleep, which is why it is sometimes...
have been reported, and scurvy typically occurs later in infancy, rarely causes death or intracranial bleeding, and is accompanied by other changes of the bones and skin and invariably an unusually deficient dietary history.
Gestational problems
Gestational problems affecting both mother and fetus, the birthing process, prematurity and nutritional deficits can accelerate skeletal and hemorrhagic pathologies that can also mimic SBS, even before birth. Because the age of suspected SBS victims is usually older than those patients suffering from birth-related problems, the distinction is usually not problematic.Diffuse injury
A 2001 study reported that the predominant histologicalHistology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
abnormality in cases of inflicted head injury in the very young is diffuse
Focal and diffuse brain injury
Focal and diffuse brain injury are ways to classify brain injury: focal injury occurs in a specific location, while diffuse injury occurs over a more widespread area. It is common for both focal and diffuse damage to occur as the result of the same event; many traumatic brain injuries have aspects...
hypoxic brain damage, not DAI,
and suggested two possible explanations: either the unmyelinated axon of the immature cerebral hemispheres is relatively resistant to traumatic damage, or in shaking-type injuries the brain is not exposed to the forces necessary to produce DAI.
Force
There has been controversy regarding the amount of force required to produce the brain damage seen in shaken baby syndrome. A biomechanical experiment in 2005 demonstrated that "forceful shaking can severely injure or kill an infant, this is because the cervical spine would be severely injured and not because subdural hematomas would be caused by high head rotational accelerations... an infant head subjected to the levels of rotational velocity and acceleration called for in the SBS literature, would experience forces on the infant neck far exceeding the limits for structural failure of the cervical spine. Furthermore, shaking cervical spine injury can occur at much lower levels of head velocity and acceleration than those reported for SBS." A detailed explanation of the calculations was provided in a "Letter To The Editors" in February 2006.The BBC has made a documentary in 3 parts that covers arguments for and against the diagnosis of SBS.
See also
- Baby Shaker - An application removed by Apple that allowed the user to shake their phone until an image of a cartoon baby on the screen died.
- Charles Randal SmithCharles Randal SmithCharles Randal Smith was a Canadian pathologist who was the head pediatric forensic pathologist at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, Ontario, from 1982 to 2003. The quality of his autopsies, and the resulting criminal charges and convictions of several people, have been called into...
- Canadian Pathologist who conducted flawed autopsies and whose expert testimony in Shaken Baby Syndrome cases resulted in several wrongful convictions. - Louise Woodward case - English au pair convicted of involuntary manslaughter in the 1997 death of Matthew Eappen.
- Alan YurkoAlan YurkoAlan Yurko, born , was sentenced to life in prison + 10 years without parole for the murder of his son while on parole for burglary, due to shaken baby syndrome. However, the conviction was overturned on appeal and was released from prison on August 27, 2004.Alan Yurko's infant son was born...
- sentenced to life in prison + 10 years (1998) without parole for the murder of his son, due to shaken baby syndrome. Later released after appeal.
Further reading
This American legal review contains an extensive examination of the divergent views of the scientific literature, in addition to examining the divergent views of the legal parameters involving a trial.External links
- http://lawreview.wustl.edu/inprint/87/1/dtuerkheimer.pdf The Next Innocence Project: Shaken Baby Syndrome and the Criminal Courts. Deborah Tuerkheimer. Washington University Law Review. Volume 87 Number 1,2009
- National Child Abuse Defense & Resource Center.org - National Child Abuse Defense & Resource Center
- http://www.bmj.com/cgi/content/full/328/7442/719 British Medical Journal 2004:328:719-720 (27 March)
- http://journals.lww.com/topicsinmri/Abstract/2007/02000/Imaging_of_the_Central_Nervous_System_in_Suspected.4.aspx Imaging of the Central Nervous System in Suspected or Alleged Nonaccidental Injury, Including the Mimics.Barnes, Patrick D. MD; Krasnokutsky, Michael MD. Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: February 2007 - Volume 18 - Issue 1 - pp 53–74
- National Center on Shaken Baby Syndrome National Center on Shaken Baby Syndrome (NCSBS)
- http://www.childabuselaw.info/lawnews/Lyons_G_SBS_Utah_Law_Review_2003.pdf Shaken Baby Syndrome: A Questionable Scientific Syndrome and a Dangerous Legal Concept. Utah Law Review
- http://www.madisonmagazine.com/Madison-Magazine/July-2009/Oh-Baby/ Madison magazine. article: Oh baby by Melanie Radzicki McManus
- http://www.madisonmagazine.com/Madison-Magazine/July-2009/Oh-Baby/Motion_to_Dismiss_Audrey_Edmunds.pdf State's motion to dismiss prosecution in shaken baby syndrome case.
- http://epresence.med.utoronto.ca/1/watch/516.aspx Centre for Forensic Science and Medicine SeminarChild Abuse - Nonaccidental Injury (NAI) presenter(s) Patrick D. Barnes Power Point Presentation. Lecture notes and references.
- http://www.jameslefanu.com/research/wrongful-diagnosis-of-child-abuse-a-master-theory Wrongful Diagnosis of Child Abuse - A Master Theory. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. VOLUME 98, NUMBER 6, 2005

