
Self-diffusion
Encyclopedia
According to IUPAC definition, self-diffusion coefficient is the diffusion
coefficient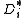 of species
of species 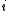 when the chemical potential
when the chemical potential
gradient
equals zero. It is linked to the diffusion coefficient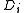 by the equation:
by the equation:
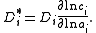
Here,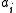 is the activity
is the activity
of the species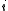 in the solution and
in the solution and 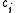 is the concentration of
is the concentration of 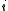 . This term is commonly assumed to be equal to the tracer diffusion determined by watching the movement of an isotope
. This term is commonly assumed to be equal to the tracer diffusion determined by watching the movement of an isotope
in the material of interest.
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
coefficient
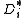 of species
of species 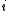 when the chemical potential
when the chemical potentialChemical potential
Chemical potential, symbolized by μ, is a measure first described by the American engineer, chemist and mathematical physicist Josiah Willard Gibbs. It is the potential that a substance has to produce in order to alter a system...
gradient
Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field that points in the direction of the greatest rate of increase of the scalar field, and whose magnitude is the greatest rate of change....
equals zero. It is linked to the diffusion coefficient
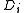 by the equation:
by the equation: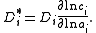
Here,
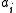 is the activity
is the activityActivity (chemistry)
In chemical thermodynamics, activity is a measure of the “effective concentration” of a species in a mixture, meaning that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution.By convention, activity...
of the species
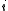 in the solution and
in the solution and 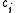 is the concentration of
is the concentration of 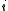 . This term is commonly assumed to be equal to the tracer diffusion determined by watching the movement of an isotope
. This term is commonly assumed to be equal to the tracer diffusion determined by watching the movement of an isotopeIsotopic labeling
Isotopic labeling is a technique for tracking the passage of a sample of substance through a system. The substance is 'labeled' by including unusual isotopes in its chemical composition...
in the material of interest.

