
Self-aligned gate
Encyclopedia
A self-aligned gate, in electronics
, is a transistor
manufacturing feature whereby a highly doped gate electrode region of a MOSFET
transistor is used as a mask for the doping of the source and drain around it. This technique ensures that the gate will slightly overlap the edges of the source and drain.
The use of self-aligned gates is one of the many innovations that led to a big jump in computing power in the 1970s. Self-aligned gates are still used in most modern integrated circuit
processes.
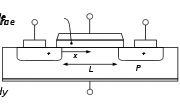 The self-aligned gate is used to improve the accuracy of the entire fabrication process. As devices became smaller and smaller during the 1970s, there was a need for a more precise and reliable way to fabricate MOSFETs. The gate regions would sometimes fail to overlap the source and drain. This resulted in a non-functional MOSFET. The solution was to create a new process that would eliminate the possibility of the gate not overlapping the source and drain. This solution was called "self-aligned gate" technology.
The self-aligned gate is used to improve the accuracy of the entire fabrication process. As devices became smaller and smaller during the 1970s, there was a need for a more precise and reliable way to fabricate MOSFETs. The gate regions would sometimes fail to overlap the source and drain. This resulted in a non-functional MOSFET. The solution was to create a new process that would eliminate the possibility of the gate not overlapping the source and drain. This solution was called "self-aligned gate" technology.
Innovations that made Self-Aligned Gate Technology possible
Certain innovations were required in order to make self-aligned gates:
Prior to these innovations, self-aligned gates had been demonstrated on metal-gate
devices, but their real impact was on silicon-gate devices.
It was independently invented by Robert W. Bower
(U.S. 3,472,712, issued October 14, 1969, filed October 27, 1966). The Bell Labs Kerwin et al. patent 3,475,234 was not filed until March 27, 1967, several months after R. W. Bower and H. D. Dill had published and presented the first publication of this work at the International Electron Device Meeting, Washington, D.C. in 1966.
However, in a legal action involving Bower and Dill, the Third Circuit Court of Appeals determined that Kerwin, Klein and Sarace were the true inventors of the self-aligned silicon gate transistor. On that basis, they were awarded the basic patent US 3,475,234 (the US patent system awards the basic patent to the party that first makes the invention, not the party that first files a patent application, per rules at that time). Bower's work described the self-aligned-gate MOSFET, made with both aluminum and polysilicon gates. It used both ion implantation and diffusion to form the source and drain using the gate electrode as the mask to define the source and drain regions. The Bell Labs team attended this meeting of the IEDM in 1966, and they discussed this work with Bower after his presentation in 1966. Bower believed he had first made the self-aligned gate using aluminum as the gate and, before presentation in 1966, made the device using polysilicon as the gate. However, he was not able to prove it to the apellate court, who sided with the Bell Labs team.
The self-aligned gate typically involves ion implantation
, another semiconductor process innovation of the 1960s. The histories of ion implantation and self-aligned gates are highly interrelated, as recounted in an in-depth history by R.B. Fair.
The first commercial product using self-aligned silicon-gate technology was the Fairchild
3708 8-bit analog multiplexor, in 1968, designed by Federico Faggin
.

Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, is a transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
manufacturing feature whereby a highly doped gate electrode region of a MOSFET
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The basic principle of this kind of transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925...
transistor is used as a mask for the doping of the source and drain around it. This technique ensures that the gate will slightly overlap the edges of the source and drain.
The use of self-aligned gates is one of the many innovations that led to a big jump in computing power in the 1970s. Self-aligned gates are still used in most modern integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
processes.
Introduction

Innovations that made Self-Aligned Gate Technology possible
Certain innovations were required in order to make self-aligned gates:
- a new process that would create the gates;
- a switch from amorphous siliconAmorphous siliconAmorphous silicon is the non-crystalline allotropic form of silicon. It can be deposited in thin films at low temperatures onto a variety of substrates, offering some unique capabilities for a variety of electronics.-Description:...
to polycrystalline siliconPolycrystalline siliconPolycrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, is a material consisting of small silicon crystals. It differs from single-crystal silicon, used for electronics and solar cells, and from amorphous silicon, used for thin film devices and solar cells....
. This is because amorphous silicon broke down during the oxide steps; - a method for etching polycrystalline siliconPolycrystalline siliconPolycrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, is a material consisting of small silicon crystals. It differs from single-crystal silicon, used for electronics and solar cells, and from amorphous silicon, used for thin film devices and solar cells....
(photolithographyPhotolithographyPhotolithography is a process used in microfabrication to selectively remove parts of a thin film or the bulk of a substrate. It uses light to transfer a geometric pattern from a photomask to a light-sensitive chemical "photoresist", or simply "resist," on the substrate...
); - a method to reduce the impurities present in silicon.
Prior to these innovations, self-aligned gates had been demonstrated on metal-gate
Metal gate
A metal gate, in the context of a lateral Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor MOS stack, is just that—the gate material is made from a metal.For decades, the industry had moved away from metal as the gate material in the MOS stack due to fabrication complications...
devices, but their real impact was on silicon-gate devices.
History
The self-aligned gate design was patented in 1969 by the team of Kerwin, Klein, and Sarace.It was independently invented by Robert W. Bower
Robert W. Bower
Dr. Robert W. Bower was born in Santa Monica, CA and is an applied physicist. Immediately after receiving his Ph.D. from The California Institute of Technology in 1973, he worked for over 25 years in many different professions: Engineer, Scientist, Department Head at University of California,...
(U.S. 3,472,712, issued October 14, 1969, filed October 27, 1966). The Bell Labs Kerwin et al. patent 3,475,234 was not filed until March 27, 1967, several months after R. W. Bower and H. D. Dill had published and presented the first publication of this work at the International Electron Device Meeting, Washington, D.C. in 1966.
However, in a legal action involving Bower and Dill, the Third Circuit Court of Appeals determined that Kerwin, Klein and Sarace were the true inventors of the self-aligned silicon gate transistor. On that basis, they were awarded the basic patent US 3,475,234 (the US patent system awards the basic patent to the party that first makes the invention, not the party that first files a patent application, per rules at that time). Bower's work described the self-aligned-gate MOSFET, made with both aluminum and polysilicon gates. It used both ion implantation and diffusion to form the source and drain using the gate electrode as the mask to define the source and drain regions. The Bell Labs team attended this meeting of the IEDM in 1966, and they discussed this work with Bower after his presentation in 1966. Bower believed he had first made the self-aligned gate using aluminum as the gate and, before presentation in 1966, made the device using polysilicon as the gate. However, he was not able to prove it to the apellate court, who sided with the Bell Labs team.
The self-aligned gate typically involves ion implantation
Ion implantation
Ion implantation is a materials engineering process by which ions of a material are accelerated in an electrical field and impacted into another solid. This process is used to change the physical, chemical, or electrical properties of the solid...
, another semiconductor process innovation of the 1960s. The histories of ion implantation and self-aligned gates are highly interrelated, as recounted in an in-depth history by R.B. Fair.
The first commercial product using self-aligned silicon-gate technology was the Fairchild
Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. is an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957, it was a pioneer in transistor and integrated circuit manufacturing...
3708 8-bit analog multiplexor, in 1968, designed by Federico Faggin
Federico Faggin
Federico Faggin , who received in 2010 the National Medal of Technology and Innovation by Barack Obama, the highest honor bestowed by the United States government on scientists, engineers, and inventors, at the White House in Washington, is an Italian-born and naturalized U.S...
.
Manufacturing process
The importance of self-aligned gates comes in the process used to make them. The process of using the gate oxide as a mask for the source and drain diffusion both simplifies the process and greatly improves the yield.Process steps
The following are the steps in creating a self-aligned gate:
- 1. Start with a bare silicon wafer.
- 2. Using a dry thermal oxidationThermal oxidationIn microfabrication, thermal oxidation is a way to produce a thin layer of oxide on the surface of a wafer. The technique forces an oxidizing agent to diffuse into the wafer at high temperature and react with it. The rate of oxide growth is often predicted by the Deal-Grove model...
process, a thin layer (5-200 nm) of gate oxideGate oxideThe gate oxide is the dielectric layer that separates the gate terminal of a MOSFET from the underlying source and drain terminals as well as the conductive channel that connects source and drain when the transistor is turned on. Gate oxide is formed by oxidizing the silicon of the channel to form...
(SiO2) is grown on the silicon wafer.
- 3. Using a chemical vapor depositionChemical vapor depositionChemical vapor deposition is a chemical process used to produce high-purity, high-performance solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In a typical CVD process, the wafer is exposed to one or more volatile precursors, which react and/or...
(CVD) process, a layer of polysilicon is grown on top of the gate oxide.
- 4. A layer of photoresistPhotoresistA photoresist is a light-sensitive material used in several industrial processes, such as photolithography and photoengraving to form a patterned coating on a surface.-Tone:Photoresists are classified into two groups: positive resists and negative resists....
is applied on top of the polysilicon.
- 5. A mask is placed on top of the photoresist and exposed to UV light; this breaks down the photoresist layer in areas where the mask didn't protect it.
- 6. Photoresist is exposed with a specialized developer solution. This is intended to remove the photoresist that was broken down by the UV light.
- 7. The polysilicon and gate oxide that is not covered by photoresist is etched away with a buffered ion etch process. This is usually an acid solution containing hydrofluoric acidHydrofluoric acidHydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride in water. It is a valued source of fluorine and is the precursor to numerous pharmaceuticals such as fluoxetine and diverse materials such as PTFE ....
.
- 8. The rest of the photoresist is stripped from the silicon wafer. There is now a wafer with a small rectangle of polysilicon and gate oxide.
- 9. The area outside the gate (the source and drain) is doped using a process called ion-implantation. This effectively uses the gate region as a mask for the implantation process.
- 10. The wafer is annealedAnnealing (metallurgy)Annealing, in metallurgy and materials science, is a heat treatment wherein a material is altered, causing changes in its properties such as strength and hardness. It is a process that produces conditions by heating to above the recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature, and...
in a high temperature furnace (>800 °C or 1,472 °F). This allows the source and drain to diffuse underneath the gate.

