
Scratch Drive Actuator
Encyclopedia
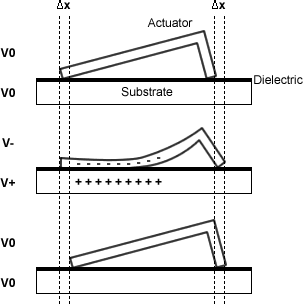
The actuator component can come in many shapes and sizes, depending on the fabrication method used. It can be visualised as an 'L'. The smaller end is called the 'bushing'.
The actuator sits on top of a substrate that has a thin insulating dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
layer on top. A voltage is applied between the actuator and the substrate and the resulting potential pulls the body of the actuator downwards. When this occurs, the brush is pushed forwards by a small amount and energy is stored in the strained actuator. When the voltage is removed, the actuator springs back into shape while the bushing remains in its new position. By applying a pulsed voltage, the SDA can be made to move forward.
The voltage is usually applied to the actuator by means of a 'tether'. This can consist of a rigid connector or a rail which the SDA follows.
The size of an SDA is typically measured on the μm scale.

