
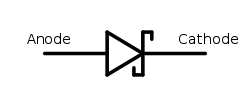
Schottky diode
Encyclopedia
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
with a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action. The cat's-whisker detectors used in the early days of wireless can be considered primitive Schottky diodes.
When current flows through a diode there is a small voltage drop across the diode terminals. A normal silicon diode has a voltage drop between 0.6–1.7 volts, while a Schottky diode voltage drop is between approximately 0.15–0.45 volts. This lower voltage drop can provide higher switching speed and better system efficiency.
Construction
A metal-semiconductor junction is formed between a metal and a semiconductor, creating a Schottky barrierSchottky barrier
A Schottky barrier, named after Walter H. Schottky, is a potential barrier formed at a metal–semiconductor junction which has rectifying characteristics, suitable for use as a diode...
(instead of a semiconductor–semiconductor junction as in conventional diodes). Typical metals used are molybdenum, platinum, chromium or tungsten; and the semiconductor would typically be N-type silicon. The metal side acts as the anode and N-type semiconductor acts as the cathode of the diode. This Schottky barrier results in both very fast switching and low forward voltage drop.
Reverse recovery time
The most important difference between p-nP-n junction
A p–n junction is formed at the boundary between a P-type and N-type semiconductor created in a single crystal of semiconductor by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy .If two separate pieces of material were used, this would...
and Schottky diode is reverse recovery time, when the diode switches from non-conducting to conducting state and vice versa. Where in a p-n diode the reverse recovery time can be in the order of hundreds of nanoseconds and less than 100 ns for fast diodes, Schottky diodes do not have a recovery time, as there is nothing to recover from (i.e. no charge carrier depletion region at the junction). The switching time is ~100 ps
Picosecond
A picosecond is 10−12 of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to 31,700 years....
for the small signal diodes, and up to tens of nanoseconds for special high-capacity power diodes. With p-n junction switching, there is also a reverse recovery current, which in high-power semiconductors brings increased EMI
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
noise. With Schottky diodes switching essentially instantly with only slight capacitive loading, this is much less of a concern.
It is often said that the Schottky diode is a "majority carrier" semiconductor device. This means that if the semiconductor body is doped n-type, only the n-type carriers (mobile electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s) play a significant role in normal operation of the device. The majority carriers are quickly injected into the conduction band of the metal contact on the other side of the diode to become free moving electrons. Therefore no slow, random recombination of n- and p- type carriers is involved, so that this diode can cease conduction faster than an ordinary p-n rectifier diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
. This property in turn allows a smaller device area, which also makes for a faster transition. This is another reason why Schottky diodes are useful in switch-mode power converters; the high speed of the diode means that the circuit can operate at frequencies in the range 200 kHz to 2 MHz, allowing the use of small inductor
Inductor
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
s and capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s with greater efficiency than would be possible with other diode types. Small-area Schottky diodes are the heart of RF detectors
Detector (radio)
A detector is a device that recovers information of interest contained in a modulated wave. The term dates from the early days of radio when all transmissions were in Morse code, and it was only necessary to detect the presence of a radio wave using a device such as a coherer without necessarily...
and mixers
Frequency mixer
In electronics a mixer or frequency mixer is a nonlinear electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum f1 + f2 and difference f1 -...
, which often operate up to 50 GHz.
Limitations
The most evident limitations of Schottky diodes are the relatively low reverse voltage rating for silicon-metal Schottky diodes, 50 V and below, and a relatively high reverse leakage currentReverse leakage current
Reverse leakage current in a semiconductor device is the current from that semiconductor device when the device is reverse biased.When a semiconductor device is reverse biased it should not conduct any current at all, even though, as a temperature effect, it will form electron-hole pairs at both...
. Diode designs have been improving over time. Voltage ratings now can reach 200 V.
Reverse leakage current, because it increases with temperature, leads to a thermal instability
Thermal runaway
Thermal runaway refers to a situation where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result...
issue. This often limits the useful reverse voltage to well below the actual rating.
Silicon carbide Schottky diode
Since 2001 another important invention was presented by CREE (NC, USA): a silicon carbideSilicon carbide
Silicon carbide , also known as carborundum, is a compound of silicon and carbon with chemical formula SiC. It occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite. Silicon carbide powder has been mass-produced since 1893 for use as an abrasive...
(SiC) Schottky diode. SiC Schottky diodes have about 40 times lower reverse leakage current compared to silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
Schottky diodes. , they are available from several manufacturers in variants up to 1700 V.
Silicon carbide has a high thermal conductivity and temperature has little influence on its switching and thermal characteristics. With special packaging it is possible to have operating junction temperatures of over 500 K
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
, which allows passive radiation
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation....
cooling in aerospace
Aerospace
Aerospace comprises the atmosphere of Earth and surrounding space. Typically the term is used to refer to the industry that researches, designs, manufactures, operates, and maintains vehicles moving through air and space...
applications.
Voltage clamping
While standard silicon diodes have a forward voltage drop of about 0.6 voltVolt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s and germanium diodes 0.3 volts, Schottky diodes' voltage drop at forward biases of around 1 mA is in the range 0.15 V to 0.46 V (see the 1N5817 and 1N5711 datasheets found online at manufacturer's websites), which makes them useful in voltage clamping applications
Clamper (electronics)
A clamper is an electronic circuit that prevents a signal from exceeding a certain defined magnitude by shifting its DC value. The clamper does not restrict the peak-to-peak excursion of the signal, but moves it up or down by a fixed value...
and prevention of transistor saturation. This is due to the higher current density
Current density
Current density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge is the electric charge, in which case the associated current density is the electric current per unit area of cross section, but the term current density can also be applied to other conserved...
in the Schottky diode.
Reverse current / discharge protection
Schottky diodes are used in photovoltaic (PV) systems to prevent a reverse current flowing through the PV modules. For instance, they are used in stand-alone ("off-grid") systems to prevent batteriesBattery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
from discharging through the solar cells at night, and in grid-connected systems with multiple strings connected in parallel, in order to prevent reverse current flowing from adjacent strings through shaded strings if the bypass diodes have failed.
Power supply
They are also used as rectifiers in switched-mode power suppliesSwitched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
; the low forward voltage and fast recovery time leads to increased efficiency.
Schottky diodes can be used in power supply "OR"ing circuits in products that have both an internal battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
and a mains adapter input, or similar. However, the high reverse leakage current presents a problem in this case, as any high-impedance voltage sensing circuit (e.g. monitoring the battery voltage or detecting whether a mains adaptor is present) will see the voltage from the other power source through the diode leakage.
Designation
Commonly encountered Schottky diodes include the 1N5817 series (1 AmpereAmpere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
) rectifiers. Schottky metal-semiconductor junctions are featured in the successors to the 7400
7400 series
The 7400 series of transistor-transistor logic integrated circuits are historically important as the first widespread family of TTL integrated circuit logic. It was used to build the mini and mainframe computers of the 1960s and 1970s...
TTL family of logic devices, the 74S, 74LS and 74ALS series, where they are employed as clamps in parallel with the collector-base junctions of the bipolar transistors to prevent their saturation, thereby greatly reducing their turn-off delays.
Small signal Schottky diodes like the 1N5711, 1N6263, 1SS106, 1SS108 or the BAT41–43, 45–49 series are widely used in high frequency applications as detectors, mixers and nonlinear elements, and have replaced germanium diodes, rendering them obsolete. They are also suitable for ESD
Electrostatic discharge
Electrostatic discharge is a serious issue in solid state electronics, such as integrated circuits. Integrated circuits are made from semiconductor materials such as silicon and insulating materials such as silicon dioxide...
protection of ESD sensitive devices like III-V-semiconductor devices, laser diode
Laser diode
The laser diode is a laser where the active medium is a semiconductor similar to that found in a light-emitting diode. The most common type of laser diode is formed from a p-n junction and powered by injected electric current...
s and, to a lesser extent, exposed lines of CMOS
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
circuitry.
Alternatives
When less power dissipation is desired a MOSFETMOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The basic principle of this kind of transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925...
and a control circuit can be used instead, in an operation mode known as active rectification
Active rectification
Active rectification, or synchronous rectification, is a technique for improving the efficiency of rectification by replacing diodes with actively-controlled switches such as transistors, usually power MOSFETs or power BJTs...
.
A super diode
Precision rectifier
The precision rectifier, which is also known as a super diode, is a configuration obtained with an operational amplifier in order to have a circuit behaving like an ideal diode and rectifier. It can be useful for high-precision signal processing....
consisting of a pn-diode or Schottky diode and an operational amplifier provides an almost perfect diode characteristic due to the effect of negative feedback, although its use is restricted to frequencies the operational amplifier used can handle.
See also
- Schottky barrierSchottky barrierA Schottky barrier, named after Walter H. Schottky, is a potential barrier formed at a metal–semiconductor junction which has rectifying characteristics, suitable for use as a diode...
- Schottky effect (Schottky emission)
- Heterostructure barrier varactorHeterostructure barrier varactorThe Heterostructure barrier varactor is semiconductor diode with an anti-symmetric current-voltage relationship and a symmetric capacitance-voltage relationship, as shown in the graph to the right. The device was invented by Erik Kollberg together with Anders Rydberg in 1989 at Chalmers University...
diode - Active rectificationActive rectificationActive rectification, or synchronous rectification, is a technique for improving the efficiency of rectification by replacing diodes with actively-controlled switches such as transistors, usually power MOSFETs or power BJTs...

