
Satellite modem
Encyclopedia
A satellite modem or sat modem is a modem
used to establish data transfers using a communications satellite
as a relay
.
There is a wide range of satellite modems from cheap devices for home internet access to expensive multifunctional equipment for enterprise use.
A "modem" stands for "modulator-demodulator". A satellite modem's main function is to transform an input bitstream to a radio signal and vice versa. There are some devices that include only a demodulator (and no modulator, thus only allowing data to be downloaded by satellite) that are also referred to as "satellite modems". These devices are used in satellite Internet access
(in this case uploaded data is transferred through a conventional PSTN modem or an ADSL modem).
Data to be transmitted are transferred to a modem from Data terminal equipment
(e.g. a computer
). The modem usually has Intermediate frequency
(IF) output (that is, 50-200 MHz), however, sometimes the signal is modulated directly to L-band. In most cases frequency has to be converted using an upconverter
before amplification and transmission.
A modulated signal is a sequence of symbols, pieces of data represented by a corresponding signal state, e.g. a bit or a few bits, depending upon the modulation
scheme being used. Recovering a symbol clock (making a local symbol clock generator synchronous with the remote one) is one of the most important tasks of a demodulator.
Similarly, a signal received from a satellite is firstly downconverted (this is done by a Low-noise block converter
- LNB), then demodulated by a modem, and at last handled by data terminal equipment. The LNB is usually powered by the modem through the signal cable with 13 or 18 V DC
..
formats.
Popular modulation types being used for satellite communications:
The popular satellite error correction codes include:
Frame formats that are supported by various satellite modems include:
High-end modems also incorporate some additional features:
 Probably the best way of understanding modem's work is to look at its internal structure. A block diagram of a generic satellite modem is shown on the image. Almost all parts are optional.
Probably the best way of understanding modem's work is to look at its internal structure. A block diagram of a generic satellite modem is shown on the image. Almost all parts are optional.
. Then its frequency is converted if needed.
The purpose of the analog tract in the receiver is to convert signal's frequency, to adjust its power via an automatic gain control
circuit and to get its complex envelope components.
The input signal for the analog tract is at the intermediate frequency
or in the L-band, in the second case it must be firstly converted to IF. Then the signal is either sampled
or processed by the four-quadrant multiplier which produces the complex envelope components (I,Q) through multiplying it by the heterodyne frequency.
See Superheterodyne receiver
.
At last the signal passes through an anti-aliasing filter
and sampled
(digitized).
(IF). A modulator is generally a much simpler device than a demodulator, because it doesn't have to recover symbol and carrier frequencies.
A demodulator is one of the most important parts of the receiver. The exact structure of the demodulator is defined by a modulation
type. However, the fundamental concepts are similar. Moreover, it is possible to develop a demodulator which can process signals with different modulation types.
Digital demodulation implies that a symbol clock (and, in most cases, an intermediate frequency generator) at the receiving side have to be synchronous with those at the transmitting side. This is achieved by the following two circuits:
There are also additional components in the demodulator such as the Intersymbol interference
equalizer
.
If the analog signal was digitized without a four-quadrant multiplier, the complex envelope has to be calculated by a digital complex mixer.
Sometimes a digital automatic gain control
circuit is implemented in the demodulator.
ratio at the receiver is usually rather poor. Error correction works by adding an artificial redundancy to a data stream at the transmitting side, and using this redundancy to correct errors caused by noise and interference.
A FEC encoder applies an error correction code to the digital stream, adding redundancy.
A FEC decoder decodes the Forward error correction
code that is used in the specific signal.
For example, the Digital Video Broadcasting standard defines a concatenated code consisting of inner convolutional (standard NASA code, perforated, with rates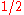 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 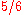 ,
,  ), interleaving and outer Reed-Solomon code (block length: 204 bytes, information block: 188 bytes, can correct up to 8 bytes in the block).
), interleaving and outer Reed-Solomon code (block length: 204 bytes, information block: 188 bytes, can correct up to 8 bytes in the block).
) that have a phase ambiguity, that is, a carrier can be restored in different ways. Differential coding
is used to resolve this ambiguity.
When differential coding is used, the data are deliberately made to depend not only on the current symbol, but also on the previous one.
Long '0'-only and '1'-only sequences create difficulties for timing recovery circuit.
Scramblers and descramblers are usually based on linear feedback shift registers.
A scrambler randomizes the data stream to be transmitted.
A descrambler restores the original stream from the scrambled one.
Scrambling shouldn't be confused with encryption, since it doesn't protect information from intruders.
transforms several digital streams into one stream. This is often referred to as 'Muxing.'
Generally, a demultiplexer is a device which transforms one multiplexed
data stream to several streams which it consists of. Satellite modem doesn't have so many outputs, so a demultiplexer here performs a drop
operation, allowing to choose channels that will be transferred to output.
A demultiplexer achieves this goal by maintaining frame synchronization.
 Satellite modems are often used for home internet access.
Satellite modems are often used for home internet access.
There are two different types, both employing the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) standard as their basis:
There are also industrial satellite modems intended to provide a permanent link. They are used, for example, in the Steel shankar network.
Modem
A modem is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data...
used to establish data transfers using a communications satellite
Communications satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite stationed in space for the purpose of telecommunications...
as a relay
Relay
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal , or where several circuits must be controlled...
.
There is a wide range of satellite modems from cheap devices for home internet access to expensive multifunctional equipment for enterprise use.
A "modem" stands for "modulator-demodulator". A satellite modem's main function is to transform an input bitstream to a radio signal and vice versa. There are some devices that include only a demodulator (and no modulator, thus only allowing data to be downloaded by satellite) that are also referred to as "satellite modems". These devices are used in satellite Internet access
Satellite Internet access
Satellite Internet access is Internet access provided through satellites. The service can be provided to users world-wide through low Earth orbit satellites. Geostationary satellites can offer higher data speeds, but their signals can not reach some polar regions of the world...
(in this case uploaded data is transferred through a conventional PSTN modem or an ADSL modem).
Satellite link
A satellite modem is not the only device needed to establish a communication channel. Other equipment that are essential for creating a satellite link include satellite antennas and frequency converters.Data to be transmitted are transferred to a modem from Data terminal equipment
Data terminal equipment
Data Terminal Equipment is an end instrument that converts user information into signals or reconverts received signals. These can also be called tail circuits. A DTE device communicates with the data circuit-terminating equipment...
(e.g. a computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
). The modem usually has Intermediate frequency
Intermediate frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency is a frequency to which a carrier frequency is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called...
(IF) output (that is, 50-200 MHz), however, sometimes the signal is modulated directly to L-band. In most cases frequency has to be converted using an upconverter
Upconverter
Upconverter can refer to:* Radio frequency upconverter, a heterodyne process* Video scaler* Block upconverter...
before amplification and transmission.
A modulated signal is a sequence of symbols, pieces of data represented by a corresponding signal state, e.g. a bit or a few bits, depending upon the modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
scheme being used. Recovering a symbol clock (making a local symbol clock generator synchronous with the remote one) is one of the most important tasks of a demodulator.
Similarly, a signal received from a satellite is firstly downconverted (this is done by a Low-noise block converter
Low-noise block converter
A low-noise block downconverter is the receiving device of a parabolic satellite dish antenna of the type commonly used for satellite TV reception...
- LNB), then demodulated by a modem, and at last handled by data terminal equipment. The LNB is usually powered by the modem through the signal cable with 13 or 18 V DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
..
Features
The main functions of a satellite modem are modulation and demodulation. Satellite communication standards also define error correction codes and framingFraming
Framing or enframing may refer to:* Framing , the most common carpentry work* Framing or Framing effect , terminology used in communication theory, sociology, and other disciplines where it relates to the construction and presentation of a fact or issue "framed" from a particular perspective*...
formats.
Popular modulation types being used for satellite communications:
- Binary phase shift keying (BPSK);
- Quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK);
- Orthogonal quadrature phase shift keying (OQPSK);
- 8PSK;
- Quadrature amplitude modulationQuadrature amplitude modulationQuadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
(QAM), especially 16QAM.
The popular satellite error correction codes include:
- Convolutional codeConvolutional codeIn telecommunication, a convolutional code is a type of error-correcting code in which* each m-bit information symbol to be encoded is transformed into an n-bit symbol, where m/n is the code rate and...
s:- with constraint length less than 10, usually decoded using a Viterbi algorithmViterbi algorithmThe Viterbi algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm for finding the most likely sequence of hidden states – called the Viterbi path – that results in a sequence of observed events, especially in the context of Markov information sources, and more generally, hidden Markov models...
(see Viterbi decoderViterbi decoderA Viterbi decoder uses the Viterbi algorithm for decoding a bitstream that has beenencoded using forward error correction based on a convolutional code....
); - with constraint length more than 10, usually decoded using a Fano algorithm (see Sequential decoder);
- with constraint length less than 10, usually decoded using a Viterbi algorithm
- Reed-Solomon codes usually concatenated with convolutional codes with an interleavingInterleavingIn computer science and telecommunication, interleaving is a way to arrange data in a non-contiguous way to increase performance.It is typically used:* In error-correction coding, particularly within data transmission, disk storage, and computer memory....
; - New modems support superior error correction codes (turbo codeTurbo codeIn information theory, turbo codes are a class of high-performance forward error correction codes developed in 1993, which were the first practical codes to closely approach the channel capacity, a theoretical maximum for the code rate at which reliable communication is still possible given a...
s and LDPC codes).
Frame formats that are supported by various satellite modems include:
- Intelsat business service (IBS) framing
- Intermediate data rate (IDR) framing
- MPEG-2MPEG-2MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
transport framing (used in DVB) - E1E-carrierIn digital telecommunications, where a single physical wire pair can be used to carry many simultaneous voice conversations by time-division multiplexing, worldwide standards have been created and deployed...
and T1Digital Signal 1Digital signal 1 is a T-carrier signaling scheme devised by Bell Labs. DS1 is a widely used standard in telecommunications in North America and Japan to transmit voice and data between devices. E1 is used in place of T1 outside North America, Japan, and South Korea...
framing
High-end modems also incorporate some additional features:
- Multiple data interfaces (like RS-232RS-232In telecommunications, RS-232 is the traditional name for a series of standards for serial binary single-ended data and control signals connecting between a DTE and a DCE . It is commonly used in computer serial ports...
, RS-422, V.35, G.703G.703G.703 is an ITU-T standard for transmitting voice or data over digital carriers such as T1 and E1. G.703 provides specifications for pulse code modulation .G.703 also specifies E0...
, LVDS, EthernetEthernetEthernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
); - Embedded Distant-end Monitor and Control (EDMAC), allowing to control the distant-end modem;
- Automatic Uplink Power Control (AUPC), that is, adjusting the output power to maintain a constant signal to noiseSignal to NoiseSignal to Noise is a graphic novel written by Neil Gaiman and illustrated by Dave McKean. It was originally serialised in the UK style magazine The Face, beginning in 1989, and collected as a graphic novel in 1992, published by Victor Gollancz Ltd in the UK and by Dark Horse Comics in the US.The...
ratio at the remote end; - Drop and insertDrop and insertIn a multichannel transmission system, a drop and insert is a process that diverts a portion of the multiplexed aggregate signal at an intermediate point, and introduces a different signal for subsequent transmission in the same position, e.g., time slot or frequency band, previously occupied by...
feature for a multiplexedMultiplexingThe multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
stream, allowing to replace some channels in it.
Internal structure

Analog tract
After a digital-to-analog conversion in the transmitter the signal passes through a reconstruction filterReconstruction filter
In a mixed-signal system , a reconstruction filter is used to construct a smooth analogue signal from a digital input, as in the case of a digital to analogue converter or other sampled data output device....
. Then its frequency is converted if needed.
The purpose of the analog tract in the receiver is to convert signal's frequency, to adjust its power via an automatic gain control
Automatic gain control
Automatic gain control is an adaptive system found in many electronic devices. The average output signal level is fed back to adjust the gain to an appropriate level for a range of input signal levels...
circuit and to get its complex envelope components.
The input signal for the analog tract is at the intermediate frequency
Intermediate frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency is a frequency to which a carrier frequency is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called...
or in the L-band, in the second case it must be firstly converted to IF. Then the signal is either sampled
Sampling (signal processing)
In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous signal to a discrete signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of samples ....
or processed by the four-quadrant multiplier which produces the complex envelope components (I,Q) through multiplying it by the heterodyne frequency.
See Superheterodyne receiver
Superheterodyne receiver
In electronics, a superheterodyne receiver uses frequency mixing or heterodyning to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency, which can be more conveniently processed than the original radio carrier frequency...
.
At last the signal passes through an anti-aliasing filter
Anti-aliasing filter
An anti-aliasing filter is a filter used before a signal sampler, to restrict the bandwidth of a signal to approximately satisfy the sampling theorem....
and sampled
Sampling (signal processing)
In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous signal to a discrete signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of samples ....
(digitized).
Modulator and demodulator
A digital modulator transforms a digital stream into a radio signal on Intermediate frequencyIntermediate frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency is a frequency to which a carrier frequency is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called...
(IF). A modulator is generally a much simpler device than a demodulator, because it doesn't have to recover symbol and carrier frequencies.
A demodulator is one of the most important parts of the receiver. The exact structure of the demodulator is defined by a modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
type. However, the fundamental concepts are similar. Moreover, it is possible to develop a demodulator which can process signals with different modulation types.
Digital demodulation implies that a symbol clock (and, in most cases, an intermediate frequency generator) at the receiving side have to be synchronous with those at the transmitting side. This is achieved by the following two circuits:
- timing recovery circuit, determining the borders of symbols;
- carrier recovery circuit, which determines the actual meaning of each symbol. There are modulation types (like frequency shift keying) that can be demodulated without carrier recovery (noncoherent demodulation) but this method is generally worse.
There are also additional components in the demodulator such as the Intersymbol interference
Intersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have similar effect as noise, thus making the communication less reliable...
equalizer
Equalizer
Equalizer or equaliser may refer to:*Equalization, the process of adjusting the strength of certain frequencies within a signal*An equalization filter for used audio and similar signals...
.
If the analog signal was digitized without a four-quadrant multiplier, the complex envelope has to be calculated by a digital complex mixer.
Sometimes a digital automatic gain control
Automatic gain control
Automatic gain control is an adaptive system found in many electronic devices. The average output signal level is fed back to adjust the gain to an appropriate level for a range of input signal levels...
circuit is implemented in the demodulator.
FEC coding
Error correction techniques are essential for satellite communications, because, due to satellite's limited power a signal to noiseSignal to Noise
Signal to Noise is a graphic novel written by Neil Gaiman and illustrated by Dave McKean. It was originally serialised in the UK style magazine The Face, beginning in 1989, and collected as a graphic novel in 1992, published by Victor Gollancz Ltd in the UK and by Dark Horse Comics in the US.The...
ratio at the receiver is usually rather poor. Error correction works by adding an artificial redundancy to a data stream at the transmitting side, and using this redundancy to correct errors caused by noise and interference.
A FEC encoder applies an error correction code to the digital stream, adding redundancy.
A FEC decoder decodes the Forward error correction
Forward error correction
In telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels....
code that is used in the specific signal.
For example, the Digital Video Broadcasting standard defines a concatenated code consisting of inner convolutional (standard NASA code, perforated, with rates
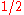 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 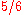 ,
,  ), interleaving and outer Reed-Solomon code (block length: 204 bytes, information block: 188 bytes, can correct up to 8 bytes in the block).
), interleaving and outer Reed-Solomon code (block length: 204 bytes, information block: 188 bytes, can correct up to 8 bytes in the block).Differential coding
There are several modulation types (such as PSK and QAMQuadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
) that have a phase ambiguity, that is, a carrier can be restored in different ways. Differential coding
Differential coding
In digital communications, differential coding is a technique used to provide unambiguous signal reception when using some types of modulation...
is used to resolve this ambiguity.
When differential coding is used, the data are deliberately made to depend not only on the current symbol, but also on the previous one.
Scrambling
Scrambling is a technique used to randomize a data stream to eliminate long '0'-only and '1'-only sequences and to assure energy dispersal.Long '0'-only and '1'-only sequences create difficulties for timing recovery circuit.
Scramblers and descramblers are usually based on linear feedback shift registers.
A scrambler randomizes the data stream to be transmitted.
A descrambler restores the original stream from the scrambled one.
Scrambling shouldn't be confused with encryption, since it doesn't protect information from intruders.
Multiplexing
A multiplexerMultiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer is a device that selects one of several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input into a single line. A multiplexer of 2n inputs has n select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output...
transforms several digital streams into one stream. This is often referred to as 'Muxing.'
Generally, a demultiplexer is a device which transforms one multiplexed
Multiplexing
The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
data stream to several streams which it consists of. Satellite modem doesn't have so many outputs, so a demultiplexer here performs a drop
Drop and insert
In a multichannel transmission system, a drop and insert is a process that diverts a portion of the multiplexed aggregate signal at an intermediate point, and introduces a different signal for subsequent transmission in the same position, e.g., time slot or frequency band, previously occupied by...
operation, allowing to choose channels that will be transferred to output.
A demultiplexer achieves this goal by maintaining frame synchronization.
Applications

There are two different types, both employing the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) standard as their basis:
- One-way satmodems (DVB-IP modems) use a return channel not based on communication with the satellite, such as telephoneTelephoneThe telephone , colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that transmits and receives sounds, usually the human voice. Telephones are a point-to-point communication system whose most basic function is to allow two people separated by large distances to talk to each other...
or cable.
- Two-way satmodems (DVB-RCS modems, also called astromodems) employ a satellite-based return channel as well; they do not need another connection. DVB-RCS is ETSI standardStandardizationStandardization is the process of developing and implementing technical standards.The goals of standardization can be to help with independence of single suppliers , compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality....
EN 301 790.
There are also industrial satellite modems intended to provide a permanent link. They are used, for example, in the Steel shankar network.
See also
- Communications satelliteCommunications satelliteA communications satellite is an artificial satellite stationed in space for the purpose of telecommunications...
- INTELSATIntelsatIntelsat, Ltd. is a communications satellite services provider.Originally formed as International Telecommunications Satellite Organization , it was—from 1964 to 2001—an intergovernmental consortium owning and managing a constellation of communications satellites providing international broadcast...
- Satellite Internet accessSatellite Internet accessSatellite Internet access is Internet access provided through satellites. The service can be provided to users world-wide through low Earth orbit satellites. Geostationary satellites can offer higher data speeds, but their signals can not reach some polar regions of the world...
- VSATVery small aperture terminalA very-small-aperture terminal , is a two-way satellite ground station or a stabilized maritime Vsat antenna with a dish antenna that is smaller than 3 meters. The majority of VSAT antennas range from 75 cm to 1.2 m. Data rates typically range from 56 kbps up to 4 Mbps...

