SahysMod
Encyclopedia
SahysMod is a computer program for the prediction of the salinity of soil moisture, groundwater
and drainage water, the depth of the watertable, and the drain
discharge in irrigated
agricultural lands, using different hydrogeologic and aquifer
conditions, varying water management options, including the use of ground water for irrigation, and several crop rotation schedules, whereby the spatial variations are accounted for through a network of polygons.
Application references :
that is easier to operate and that requires a simpler data structure
then most currently available models. Therefore, the SahysMod program was designed keeping in mind a relative simplicity of operation to facilitate the use by field technicians, engineers and project planners instead of specialized geo-hydrologists.
It aims at using input data that are generally available, or that can be estimated with reasonable accuracy, or that can be measured with relative ease. Although the calculations are done numerically and have to be repeated many times, the final results can be checked by hand using the formulas in this manual.
SahysMod's objective
is to predict the long-term hydro-salinity
in terms of general trend
s, not to arrive at exact predictions of how, for example, the situation would be on the first of April in ten years from now.
Further, SahysMod gives the option of the re-use of drainage and well
water (e.g. for irrigation
) and it can account for farmer
s' responses to waterlogging
, soil salinity, water scarcity and over-pumping from the aquifer
. Also it offers the possibility to introduce subsurface drainage systems at varying depths and with varying capacities so that they can be optimized
.
Other features of SahysMod are found in the next section.
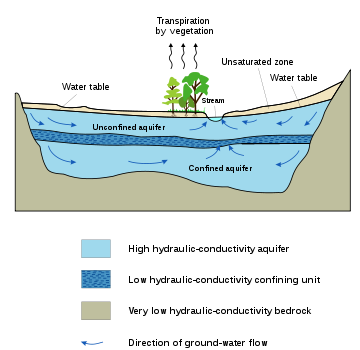 The model calculates the ground water levels and the incoming and outgoing ground water flows between the polygon
The model calculates the ground water levels and the incoming and outgoing ground water flows between the polygon
s by a numerical solution of the well-known Boussinesq equation
. The levels and flows influence each other mutually.
The ground water situation is further determined by the vertical groundwater recharge that is calculated from the agronomic water balance
. These depend again on the levels of the ground water.
When semi-confined aquifer
s are present, the resistance to vertical flow in the slowly permeable top-layer and the overpressure in the aquifer, if any, are taken into account.
Hydraulic boundary conditions are given as hydraulic head
s in the external nodes in combination with the hydraulic conductivity
between internal and external nodes. If one wishes to impose a zero flow condition
at the external nodes, the conductivity can be set at zero.
Further, aquifer
flow conditions can be given for the internal nodes. These are required when a geological fault line is present at the bottom of the aquifer or when flow occurs between the main aquifer and a deeper aquifer separated by a semi-confining layer.
The depth of the water table
, the rainfall and salt concentrations of the deeper layers are assumed to be the same over the whole polygon. Other parameters can very within the polygons according to type of crops and cropping rotation schedule.
factors depend on the level of the water table
, which again depends on some of the water-balance factors. Due to these mutual influences there can be non-linear changes throughout the season. Therefore, the computer program
performs daily calculations. For this purpose, the seasonal water-balance factors given with the inpu] are reduced automatically to daily values. The calculated seasonal water-balance factors, as given in the output, are obtained by summations of the daily calculated values. Groundwater
levels and soil salinity (the state variable
s) at the end of the season are found by accumulating the daily changes of water and salt storage.
In some cases the program may detect that the time step must be taken less than 1 day for better accuracy. The necessary adjustments are made automatically.
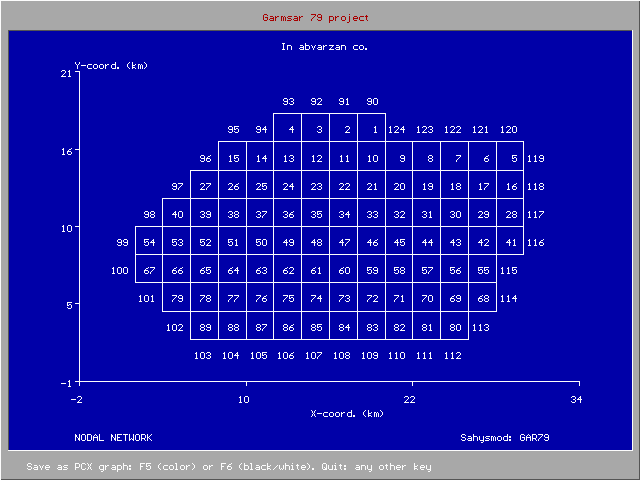 The model permits a maximum of 240 internal and 120 external polygon
The model permits a maximum of 240 internal and 120 external polygon
s with a minimum of 3 and a maximum of 6 sides each. The subdivision of the area into polygons, based on nodal points with known coordinates, should be governed by the characteristics of the distribution of the crop
ping, irrigation
, drainage
and groundwater
characteristics over the study area.
The nodes must be numbered, which can be done at will. With an index one indicates whether the node is internal or external. Nodes can be added and removed at will or changed from internal to external or vice versa. Through another index one indicates whether the internal nodes have an unconfined or semi-confined aquifer. This can also be changed at will.
Nodal network relations are to be given indicating the neighboring polygon numbers of each node. The program then calculates the surface area of each polygon, the distance between the nodes and the length of the sides between them using the Thiessen principle.
The hydraulic conductivity
can vary for each side of the polygons.
The depth of the water table
, the rainfall and salt
concentrations of the deeper layers are assumed to be the same over the whole polygon. Other parameters can very within the polygons according to type of crops and cropping rotation schedule.
(like rainfall, potential evaporation
, irrigation
, use of drain and well water for irrigation, runoff
), and the aquifer hydrology (e.g., pumping from wells
). The other water balance
components (like actual evaporation, downward percolation
, upward capillary rise, subsurface drainage, groundwater flow
) are given as output.
The quantity of drainage water, as output, is determined by two drainage intensity factors for drainage above and below drain level respectively (to be given with the input data) and the height of the water table above the given drain level. This height results from the computed water balance Further, a drainage reduction factor can be applied to simulate a limited operation of the drainage system. Variation of the drainage intensity factors and the drainage reduction factor gives the opportunity to simulate the impact of different drainage options.
To obtain accuracy in the computations of the ground water flow (sect. 2.8), the actual evaporation and the capillary rise, the computer calculations are done on a daily basis. For this purpose, the seasonal hydrological data are divided by the number of days per season to obtain daily values. The daily values are added to yield seasonal values.
 The groups, expressed in fractions of the total area, may consist of combinations of crop
The groups, expressed in fractions of the total area, may consist of combinations of crop
s or just of a single kind of crop. For example, as the A-type crops one may specify the lightly irrigated cultures, and as the B type the more heavily irrigated ones, such as sugarcane
and rice
. But one can also take A as rice and B as sugar cane, or perhaps tree
s and orchard
s. A, B and/or U crops can be taken differently in different seasons, e.g. A=wheat
plus barley
in winter and A=maize
in summer while B=vegetable
s in winter and B=cotton
in summer. Non-irrigated land can be specified in two ways: (1) as U = 1−A−B and (2) as A and/or B with zero irrigation. A combination can also be made.
Further, a specification must be given of the seasonal rotation
of the different land use
s over the total area, e.g. full rotation, no rotation at all, or incomplete rotation. This occurs with a rotation index. The rotations are taken over the seasons within the year. To obtain rotations over the years it is advisable to introduce annual input changes as explained
When a fraction A1, B1 and/or U1 differs from the fraction A2, B2 and/or U2 in another season, because the irrigation regime changes in the different seasons, the program will detect that a certain rotation occurs. If one wishes to avoid this, one may specify the same fractions in all seasons (A2=A1, B2=B1, U2=U1) but the crops and irrigation quantities may be different and may need to be proportionally adjusted. One may even specify irrigated land (A or B) with zero irrigation, which is the same as un-irrigated land (U).
Cropping rotation
schedules vary widely in different parts of the world. Creative combinations of area fractions, rotation indexes, irrigation quantities and annual input changes can accommodate many types of agricultural practices.
Variation of the area fractions and/or the rotational schedule gives the opportunity to simulate the impact of different agricultural practices on the water and salt balance.
The upper soil reservoir is defined by the soil depth, from which water can evaporate or be taken up by plant roots. It can be taken equal to the root zone. It can be saturated, unsaturated, or partly saturated, depending on the water balance. All water movements in this zone are vertical, either upward or downward, depending on the water balance. (In a future version of Sahysmod, the upper soil reservoir may be divided into two equal parts to detect the trend in the vertical salinity distribution.)
The transition zone can also be saturated, unsaturated or partly saturated. All flows in this zone are horizontal, except the flow to subsurface drains, which is radial.
If a horizontal subsurface drainage system is present, this must be placed in the transition zone, which is then divided into two parts: an upper transition zone (above drain level) and a lower transition zone (below drain level).
If one wishes to distinguish an upper and lower part of the transition zone in the absence of a subsurface drainage system, one may specify in the input data a drainage system with zero intensity.
The aquifer has mainly horizontal flow. Pumped wells
, if present, receive their water from the aquifer only. The flow in the aquifer is determined in dependence of spatially varying depths of the aquifer, levels of the water table, and hydraulic conductivity
.
SahysMod permits the introduction of phreatic (unconfined) and semi-confined aquifers. The latter may develop a hydraulic over or under pressure below the slowly permeable top-layer (aquitard).
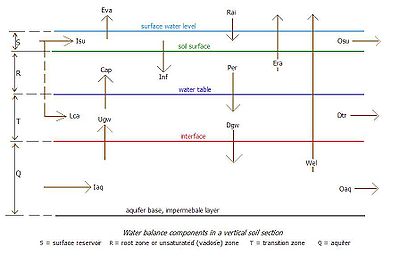 The agricultural water balance
The agricultural water balance
s are calculated for each soil reservoir separately as shown in the article Hydrology (agriculture)
. The excess water leaving one reservoir is converted into incoming water for the next reservoir. The three soil reservoirs can be assigned different thickness and storage coefficients, to be given as input data. When, in a particular situation the transition zone or the aquifer is not present, they must be given a minimum thickness of 0.1 m.
The depth of the water table
at the end of the previous time step, calculated from the water balance
s, is assumed to be the same within each polygon
. If this assumption is not acceptable, the area must be divided into a larger number of polygons.
Under certain conditions, the height of the water table influences the water-balance components. For example a rise of the water table towards the soil surface may lead to an increase of capillary rise, actual evaporation, and subsurface drainage, or a decrease of percolation losses. This, in turn, leads to a change of the water-balance, which again influences the height of the water table, etc. This chain of reactions is one of the reasons why Sahysmod has been developed into a computer program
, in which the computations are made day by day to account for the chain of reactions with a sufficient degree of accuracy.
can be accomplished through drains or pumped wells.
The subsurface drains, if any, are characterized by drain depth and drainage capacity. The drains are located in the transition zone. The subsurface drainage facility can be applied to natural or artificial drainage systems. The functioning of an artificial drainage system can be regulated through a drainage control factor.
By installing a drainage system with zero capacity one obtains the opportunity to have separate water and salt balances in the transition above and below drain level.
The pumped wells
, if any, are located in the aquifer. Their functioning is characterized by the well discharge
.
The drain and well water can be used for irrigation
through a (re)use factor. This may have an impact on the water and salt balance and on the irrigation efficiency or sufficiency.
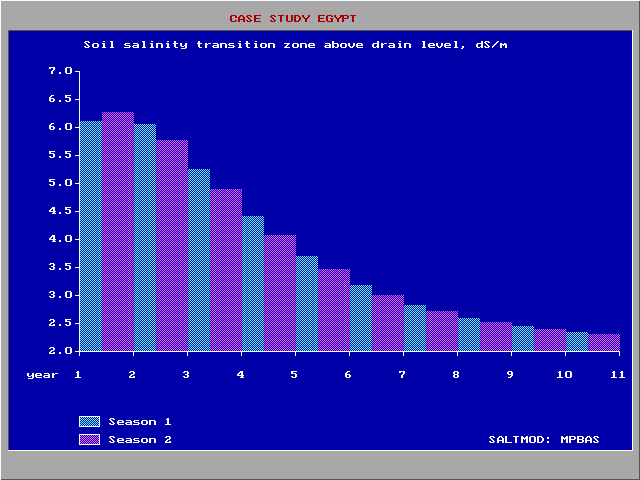 The salt balance
The salt balance
s are calculated for each soil reservoir separately. They are based on their water balances
, using the salt concentrations of the incoming and outgoing water. Some concentrations must be given as input data, like the initial salt concentrations of the water in the different soil reservoirs, of the irrigation water and of the incoming groundwater in the aquifer. The concentrations are expressed in terms of electric conductivity (EC in dS/m). When the concentrations are known in terms of g salt/l water, the rule of thumb: 1 g/l -> 1.7 dS/m can be used. Usually, salt concentrations of the soil are expressed in ECe, the electric conductivity of an extract of a saturated soil paste. In Sahysmod, the salt concentration is expressed as the EC of the soil moisture when saturated under field conditions. As a rule, one can use the conversion rate EC : ECe = 2 : 1. The principles used are correspond to those described in the article soil salinity control.
Salt concentrations of outgoing water (either from one reservoir into the other or by subsurface drainage) are computed on the basis of salt balances, using different leaching or salt mixing efficiencies to be given with the input data. The effects of different leaching efficiencies can be simulated varying their input value.
If drain or well water is used for irrigation, the method computes the salt concentration of the mixed irrigation water in the course of the time and the subsequent impact on the soil and ground water salinity, which again influences the salt concentration of the drain and well water. By varying the fraction of used drain or well water (through the input), the long term impact of different fractions can be simulated.
The dissolution
of solid soil minerals or the chemical precipitation
of poorly soluble salts is not included in the computation method. However, but to some extent, it can be accounted for through the input data, e.g. increasing or decreasing the salt concentration of the irrigation water or of the incoming water in the aquifer
. In a future version, the precipitation of gypsum may be introduced.
and soil salinity can be automatically accounted for. The method can gradually decrease:
The farmers' responses influence the water and salt balances, which, in turn, slows down the process of water logging and salinization. Ultimately a new equilibrium situation will arise.
The user can also introduce farmers' responses by manually changing the relevant input data. Perhaps it will be useful first to study the automatic farmers' responses and their effect first and thereafter decide what the farmers' responses will be in the view of the user.
The program also offers the possibility to follow historic records with annually changing input values (e.g. rainfall, irrigation, cropping rotations), the calculations must be made year by year. If this possibility is chosen, the program creates a transfer file by which the final conditions of the previous year (e.g. water table and salinity) are automatically used as the initial conditions for the subsequent period. This facility makes it also possible to use various generated rainfall sequences drawn randomly from a known rainfall probability distribution and to obtain a stochastic prediction of the resulting output parameters.
Some input parameters should not be changed, like the nodal network relations, the system geometry
, the thickness of the soil layers, and the total porosity
, otherwise illogical jumps occur in the water and salt balances. These parameters are also stored in the transfer file, so that any impermissible change is overruled by the transfer data. In some cases of incorrect changes, the program will stop and request the user to adjust the input.
 The output is given for each season of any year during any number of years, as specified with the input data. The output data comprise hydrological and salinity aspects.
The output is given for each season of any year during any number of years, as specified with the input data. The output data comprise hydrological and salinity aspects.
 As the soil salinity is very variable from place to place (figure left) SaltMod includes frequency distributions
As the soil salinity is very variable from place to place (figure left) SaltMod includes frequency distributions
in the output. The figure was made with the CumFreq program http://www.waterlog.info/cumfreq.htm .
The output data are filed in the form of tables that can be inspected directly, through the user menu, that calls selected groups of data either for a certain polygon
over time, or for a certain season over the polygons.
Also, the program has the facility to store the selected data in a spreadsheet
format for further analysis and for import into a mapping program.
A user interface to assist with the production of maps of output parameters is still in development.
Different users may wish to establish different cause-effect relationships. The program offers only a limited number of standard graphics
, as it is not possible to foresee all different uses that may be made. This is the reason why the possibility for further analysis through spreadsheet programs was created.
Although the computations need many iterations, all the end results can be checked by hand using the equations presented in the manual.
Groundwater
Groundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock...
and drainage water, the depth of the watertable, and the drain
Tile drainage
Tile drainage is an agriculture practice that removes excess water from soil subsurface. Whereas irrigation is the practice of adding additional water when the soil is naturally too dry, drainage brings soil moisture levels down for optimal crop growth...
discharge in irrigated
Surface irrigation
Surface irrigation is defined as the group of application techniques where water is applied and distributed over the soil surface by gravity. It is by far the most common form of irrigation throughout the world and has been practiced in many areas virtually unchanged for thousands of years.Surface...
agricultural lands, using different hydrogeologic and aquifer
Aquifer
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
conditions, varying water management options, including the use of ground water for irrigation, and several crop rotation schedules, whereby the spatial variations are accounted for through a network of polygons.
Application references :
Rationale
There is a need for a computer programComputer program
A computer program is a sequence of instructions written to perform a specified task with a computer. A computer requires programs to function, typically executing the program's instructions in a central processor. The program has an executable form that the computer can use directly to execute...
that is easier to operate and that requires a simpler data structure
Data structure
In computer science, a data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.Different kinds of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks...
then most currently available models. Therefore, the SahysMod program was designed keeping in mind a relative simplicity of operation to facilitate the use by field technicians, engineers and project planners instead of specialized geo-hydrologists.
It aims at using input data that are generally available, or that can be estimated with reasonable accuracy, or that can be measured with relative ease. Although the calculations are done numerically and have to be repeated many times, the final results can be checked by hand using the formulas in this manual.
SahysMod's objective
Goal
A goal is an objective, or a projected computation of affairs, that a person or a system plans or intends to achieve.Goal, GOAL or G.O.A.L may also refer to:Sport...
is to predict the long-term hydro-salinity
Salinity
Salinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
in terms of general trend
Trend estimation
Trend estimation is a statistical technique to aid interpretation of data. When a series of measurements of a process are treated as a time series, trend estimation can be used to make and justify statements about tendencies in the data...
s, not to arrive at exact predictions of how, for example, the situation would be on the first of April in ten years from now.
Further, SahysMod gives the option of the re-use of drainage and well
Water well
A water well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, boring or drilling to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The well water is drawn by an electric submersible pump, a trash pump, a vertical turbine pump, a handpump or a mechanical pump...
water (e.g. for irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
) and it can account for farmer
Farmer
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, who raises living organisms for food or raw materials, generally including livestock husbandry and growing crops, such as produce and grain...
s' responses to waterlogging
Waterlogging
Waterlogging or water logging may refer to:* Waterlogging , saturation of the soil by groundwater sufficient to prevent or hinder agriculture...
, soil salinity, water scarcity and over-pumping from the aquifer
Aquifer
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
. Also it offers the possibility to introduce subsurface drainage systems at varying depths and with varying capacities so that they can be optimized
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
.
Other features of SahysMod are found in the next section.
Calculation of aquifer conditions in polygons

Polygon
In geometry a polygon is a flat shape consisting of straight lines that are joined to form a closed chain orcircuit.A polygon is traditionally a plane figure that is bounded by a closed path, composed of a finite sequence of straight line segments...
s by a numerical solution of the well-known Boussinesq equation
Boussinesq approximation
In fluid dynamics, the Boussinesq approximation is used in the field of buoyancy-driven flow . It states that density differences are sufficiently small to be neglected, except where they appear in terms multiplied by g, the acceleration due to gravity...
. The levels and flows influence each other mutually.
The ground water situation is further determined by the vertical groundwater recharge that is calculated from the agronomic water balance
Hydrology (agriculture)
Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
. These depend again on the levels of the ground water.
When semi-confined aquifer
Aquifer
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
s are present, the resistance to vertical flow in the slowly permeable top-layer and the overpressure in the aquifer, if any, are taken into account.
Hydraulic boundary conditions are given as hydraulic head
Hydraulic head
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a specific measurement of water pressure above a geodetic datum. It is usually measured as a water surface elevation, expressed in units of length, at the entrance of a piezometer...
s in the external nodes in combination with the hydraulic conductivity
Hydraulic conductivity
Hydraulic conductivity, symbolically represented as K, is a property of vascular plants, soil or rock, that describes the ease with which water can move through pore spaces or fractures. It depends on the intrinsic permeability of the material and on the degree of saturation...
between internal and external nodes. If one wishes to impose a zero flow condition
Flow conditioning
Flow conditioning ensures that the “real world” environment closely resembles the “laboratory” environment for proper performance of inferential flowmeters like orifice, turbine, coriolis, ultrasonic etc.- Types of Flow :...
at the external nodes, the conductivity can be set at zero.
Further, aquifer
Aquifer
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
flow conditions can be given for the internal nodes. These are required when a geological fault line is present at the bottom of the aquifer or when flow occurs between the main aquifer and a deeper aquifer separated by a semi-confining layer.
The depth of the water table
Water table
The water table is the level at which the submarine pressure is far from atmospheric pressure. It may be conveniently visualized as the 'surface' of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. However, saturated conditions may extend above the water table as...
, the rainfall and salt concentrations of the deeper layers are assumed to be the same over the whole polygon. Other parameters can very within the polygons according to type of crops and cropping rotation schedule.
Seasonal approach
The model is based on seasonal input data and returns seasonal outputs. The number of seasons per year can be chosen between a minimum of one and a maximum of four. One can distinguish for example dry, wet, cold, hot, irrigation or fallow seasons. Reasons of not using smaller input/output periods are:- short-term (e.g., daily) inputs would require much information ,which, in large areas, may not be readily available;
- short-term outputs would lead to immense output files ,which would be difficult to manage and interpret;
- this model is especially developed to predict long term trends, and predictions for the future are more reliably made on a seasonal (long term) than on a daily (short term) basis, due to the high variability of short term data;
- though the precision of the predictions for the future may be limited, a lot is gained when the trend is sufficiently clear. For example, it need not be a major constraint to the design of appropriate soil salinity control measures when a certain salinity level, predicted by SahysMod to occur after 20 years, will in reality occur after 15 or 25 years.
Computational time steps
Many water balanceWater balance
In hydrology, a water balance equation can be used to describe the flow of water in and out of a system. A system can be one of several hydrological domains, such as a column of soil or a drainage basin....
factors depend on the level of the water table
Water table
The water table is the level at which the submarine pressure is far from atmospheric pressure. It may be conveniently visualized as the 'surface' of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. However, saturated conditions may extend above the water table as...
, which again depends on some of the water-balance factors. Due to these mutual influences there can be non-linear changes throughout the season. Therefore, the computer program
Computer program
A computer program is a sequence of instructions written to perform a specified task with a computer. A computer requires programs to function, typically executing the program's instructions in a central processor. The program has an executable form that the computer can use directly to execute...
performs daily calculations. For this purpose, the seasonal water-balance factors given with the inpu] are reduced automatically to daily values. The calculated seasonal water-balance factors, as given in the output, are obtained by summations of the daily calculated values. Groundwater
Groundwater
Groundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock...
levels and soil salinity (the state variable
State variable
A state variable is one of the set of variables that describe the "state" of a dynamical system. Intuitively, the state of a system describes enough about the system to determine its future behaviour...
s) at the end of the season are found by accumulating the daily changes of water and salt storage.
In some cases the program may detect that the time step must be taken less than 1 day for better accuracy. The necessary adjustments are made automatically.
Polygonal network

Polygon
In geometry a polygon is a flat shape consisting of straight lines that are joined to form a closed chain orcircuit.A polygon is traditionally a plane figure that is bounded by a closed path, composed of a finite sequence of straight line segments...
s with a minimum of 3 and a maximum of 6 sides each. The subdivision of the area into polygons, based on nodal points with known coordinates, should be governed by the characteristics of the distribution of the crop
Crop
Crop may refer to:* Crop, a plant grown and harvested for agricultural use* Crop , part of the alimentary tract of some animals* Crop , a modified whip used in horseback riding or disciplining humans...
ping, irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, drainage
Drainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of surface and sub-surface water from an area. Many agricultural soils need drainage to improve production or to manage water supplies.-Early history:...
and groundwater
Groundwater
Groundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock...
characteristics over the study area.
The nodes must be numbered, which can be done at will. With an index one indicates whether the node is internal or external. Nodes can be added and removed at will or changed from internal to external or vice versa. Through another index one indicates whether the internal nodes have an unconfined or semi-confined aquifer. This can also be changed at will.
Nodal network relations are to be given indicating the neighboring polygon numbers of each node. The program then calculates the surface area of each polygon, the distance between the nodes and the length of the sides between them using the Thiessen principle.
The hydraulic conductivity
Hydraulic conductivity
Hydraulic conductivity, symbolically represented as K, is a property of vascular plants, soil or rock, that describes the ease with which water can move through pore spaces or fractures. It depends on the intrinsic permeability of the material and on the degree of saturation...
can vary for each side of the polygons.
The depth of the water table
Water table
The water table is the level at which the submarine pressure is far from atmospheric pressure. It may be conveniently visualized as the 'surface' of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. However, saturated conditions may extend above the water table as...
, the rainfall and salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
concentrations of the deeper layers are assumed to be the same over the whole polygon. Other parameters can very within the polygons according to type of crops and cropping rotation schedule.
Hydrological data
The method uses seasonal water balance components as input data. These are related to the surface hydrologyHydrology
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets, including the hydrologic cycle, water resources and environmental watershed sustainability...
(like rainfall, potential evaporation
Potential evaporation
Potential evaporation or potential evapotranspiration is defined as the amount of evaporation that would occur if a sufficient water source were available. If the actual evapotranspiration is considered the net result of atmospheric demand for moisture from a surface and the ability of the...
, irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, use of drain and well water for irrigation, runoff
Surface runoff
Surface runoff is the water flow that occurs when soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain, meltwater, or other sources flows over the land. This is a major component of the water cycle. Runoff that occurs on surfaces before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source...
), and the aquifer hydrology (e.g., pumping from wells
Water well
A water well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, boring or drilling to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The well water is drawn by an electric submersible pump, a trash pump, a vertical turbine pump, a handpump or a mechanical pump...
). The other water balance
Water balance
In hydrology, a water balance equation can be used to describe the flow of water in and out of a system. A system can be one of several hydrological domains, such as a column of soil or a drainage basin....
components (like actual evaporation, downward percolation
Percolation
In physics, chemistry and materials science, percolation concerns the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials...
, upward capillary rise, subsurface drainage, groundwater flow
Groundwater flow
Groundwater flow is defined as the "...part of streamflow that has infiltrated the ground, has entered the phreatic zone, and has been discharged into a stream channel, via springs or seepage water". In hydrogeology it is measured by the Groundwater flow equation.- See also :*Subsurface...
) are given as output.
The quantity of drainage water, as output, is determined by two drainage intensity factors for drainage above and below drain level respectively (to be given with the input data) and the height of the water table above the given drain level. This height results from the computed water balance Further, a drainage reduction factor can be applied to simulate a limited operation of the drainage system. Variation of the drainage intensity factors and the drainage reduction factor gives the opportunity to simulate the impact of different drainage options.
To obtain accuracy in the computations of the ground water flow (sect. 2.8), the actual evaporation and the capillary rise, the computer calculations are done on a daily basis. For this purpose, the seasonal hydrological data are divided by the number of days per season to obtain daily values. The daily values are added to yield seasonal values.
Cropping patterns/rotations
The input data on irrigation, evaporation, and surface runoff are to be specified per season for three kinds of agricultural practices, which can be chosen at the discretion of the user:- A: irrigated land with crops of group A
- B: irrigated land with crops of group B
- U: non-irrigated land with rain-fed crops or fallow land

Crop
Crop may refer to:* Crop, a plant grown and harvested for agricultural use* Crop , part of the alimentary tract of some animals* Crop , a modified whip used in horseback riding or disciplining humans...
s or just of a single kind of crop. For example, as the A-type crops one may specify the lightly irrigated cultures, and as the B type the more heavily irrigated ones, such as sugarcane
Sugarcane
Sugarcane refers to any of six to 37 species of tall perennial grasses of the genus Saccharum . Native to the warm temperate to tropical regions of South Asia, they have stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sugar, and measure two to six metres tall...
and rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
. But one can also take A as rice and B as sugar cane, or perhaps tree
Tree
A tree is a perennial woody plant. It is most often defined as a woody plant that has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground on a single main stem or trunk with clear apical dominance. A minimum height specification at maturity is cited by some authors, varying from 3 m to...
s and orchard
Orchard
An orchard is an intentional planting of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit or nut-producing trees which are grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of large gardens, where they serve an aesthetic as well as a productive...
s. A, B and/or U crops can be taken differently in different seasons, e.g. A=wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
plus barley
Barley
Barley is a major cereal grain, a member of the grass family. It serves as a major animal fodder, as a base malt for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various health foods...
in winter and A=maize
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
in summer while B=vegetable
Vegetable
The noun vegetable usually means an edible plant or part of a plant other than a sweet fruit or seed. This typically means the leaf, stem, or root of a plant....
s in winter and B=cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
in summer. Non-irrigated land can be specified in two ways: (1) as U = 1−A−B and (2) as A and/or B with zero irrigation. A combination can also be made.
Further, a specification must be given of the seasonal rotation
Crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of dissimilar types of crops in the same area in sequential seasons.Crop rotation confers various benefits to the soil. A traditional element of crop rotation is the replenishment of nitrogen through the use of green manure in sequence with cereals...
of the different land use
Land use
Land use is the human use of land. Land use involves the management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment such as fields, pastures, and settlements. It has also been defined as "the arrangements, activities and inputs people undertake in a certain land cover...
s over the total area, e.g. full rotation, no rotation at all, or incomplete rotation. This occurs with a rotation index. The rotations are taken over the seasons within the year. To obtain rotations over the years it is advisable to introduce annual input changes as explained
When a fraction A1, B1 and/or U1 differs from the fraction A2, B2 and/or U2 in another season, because the irrigation regime changes in the different seasons, the program will detect that a certain rotation occurs. If one wishes to avoid this, one may specify the same fractions in all seasons (A2=A1, B2=B1, U2=U1) but the crops and irrigation quantities may be different and may need to be proportionally adjusted. One may even specify irrigated land (A or B) with zero irrigation, which is the same as un-irrigated land (U).
Cropping rotation
Crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of dissimilar types of crops in the same area in sequential seasons.Crop rotation confers various benefits to the soil. A traditional element of crop rotation is the replenishment of nitrogen through the use of green manure in sequence with cereals...
schedules vary widely in different parts of the world. Creative combinations of area fractions, rotation indexes, irrigation quantities and annual input changes can accommodate many types of agricultural practices.
Variation of the area fractions and/or the rotational schedule gives the opportunity to simulate the impact of different agricultural practices on the water and salt balance.
Soil strata, type of aquifer
SahysMod accepts four different reservoirs of which three are in the soil profile:- s: a surface reservoir,
- r: an upper (shallow) soil reservoir or root zone,
- x: an intermediate soil reservoir or transition zone,
- q: a deep reservoir or main aquiferAquiferAn aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
.
The upper soil reservoir is defined by the soil depth, from which water can evaporate or be taken up by plant roots. It can be taken equal to the root zone. It can be saturated, unsaturated, or partly saturated, depending on the water balance. All water movements in this zone are vertical, either upward or downward, depending on the water balance. (In a future version of Sahysmod, the upper soil reservoir may be divided into two equal parts to detect the trend in the vertical salinity distribution.)
The transition zone can also be saturated, unsaturated or partly saturated. All flows in this zone are horizontal, except the flow to subsurface drains, which is radial.
If a horizontal subsurface drainage system is present, this must be placed in the transition zone, which is then divided into two parts: an upper transition zone (above drain level) and a lower transition zone (below drain level).
If one wishes to distinguish an upper and lower part of the transition zone in the absence of a subsurface drainage system, one may specify in the input data a drainage system with zero intensity.
The aquifer has mainly horizontal flow. Pumped wells
Water well
A water well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, boring or drilling to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The well water is drawn by an electric submersible pump, a trash pump, a vertical turbine pump, a handpump or a mechanical pump...
, if present, receive their water from the aquifer only. The flow in the aquifer is determined in dependence of spatially varying depths of the aquifer, levels of the water table, and hydraulic conductivity
Hydraulic conductivity
Hydraulic conductivity, symbolically represented as K, is a property of vascular plants, soil or rock, that describes the ease with which water can move through pore spaces or fractures. It depends on the intrinsic permeability of the material and on the degree of saturation...
.
SahysMod permits the introduction of phreatic (unconfined) and semi-confined aquifers. The latter may develop a hydraulic over or under pressure below the slowly permeable top-layer (aquitard).
Agricultural water balances

Water balance
In hydrology, a water balance equation can be used to describe the flow of water in and out of a system. A system can be one of several hydrological domains, such as a column of soil or a drainage basin....
s are calculated for each soil reservoir separately as shown in the article Hydrology (agriculture)
Hydrology (agriculture)
Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
. The excess water leaving one reservoir is converted into incoming water for the next reservoir. The three soil reservoirs can be assigned different thickness and storage coefficients, to be given as input data. When, in a particular situation the transition zone or the aquifer is not present, they must be given a minimum thickness of 0.1 m.
The depth of the water table
Water table
The water table is the level at which the submarine pressure is far from atmospheric pressure. It may be conveniently visualized as the 'surface' of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. However, saturated conditions may extend above the water table as...
at the end of the previous time step, calculated from the water balance
Water balance
In hydrology, a water balance equation can be used to describe the flow of water in and out of a system. A system can be one of several hydrological domains, such as a column of soil or a drainage basin....
s, is assumed to be the same within each polygon
Polygon
In geometry a polygon is a flat shape consisting of straight lines that are joined to form a closed chain orcircuit.A polygon is traditionally a plane figure that is bounded by a closed path, composed of a finite sequence of straight line segments...
. If this assumption is not acceptable, the area must be divided into a larger number of polygons.
Under certain conditions, the height of the water table influences the water-balance components. For example a rise of the water table towards the soil surface may lead to an increase of capillary rise, actual evaporation, and subsurface drainage, or a decrease of percolation losses. This, in turn, leads to a change of the water-balance, which again influences the height of the water table, etc. This chain of reactions is one of the reasons why Sahysmod has been developed into a computer program
Computer program
A computer program is a sequence of instructions written to perform a specified task with a computer. A computer requires programs to function, typically executing the program's instructions in a central processor. The program has an executable form that the computer can use directly to execute...
, in which the computations are made day by day to account for the chain of reactions with a sufficient degree of accuracy.
Drains, wells, and re-use
The sub-surface drainageDrainage system (Agriculture)
An agricultural drainage system is a system by which the water level on or in the soil is controlled to enhance agricultural crop production.-Classification:Figure 1 classifies the various types of drainage systems...
can be accomplished through drains or pumped wells.
The subsurface drains, if any, are characterized by drain depth and drainage capacity. The drains are located in the transition zone. The subsurface drainage facility can be applied to natural or artificial drainage systems. The functioning of an artificial drainage system can be regulated through a drainage control factor.
By installing a drainage system with zero capacity one obtains the opportunity to have separate water and salt balances in the transition above and below drain level.
The pumped wells
Water well
A water well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, boring or drilling to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The well water is drawn by an electric submersible pump, a trash pump, a vertical turbine pump, a handpump or a mechanical pump...
, if any, are located in the aquifer. Their functioning is characterized by the well discharge
Discharge
Discharge in the context to expel or to "let go" may refer to:* A military discharge, issued when a member of the armed forces is released from service* Termination of employment, the end of an employee's duration with an employer...
.
The drain and well water can be used for irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
through a (re)use factor. This may have an impact on the water and salt balance and on the irrigation efficiency or sufficiency.
Salt balances

Salt balance
Salt balance may refer to*Osmoregulation*Soil salinity*Salt balance in the soil...
s are calculated for each soil reservoir separately. They are based on their water balances
Hydrology (agriculture)
Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
, using the salt concentrations of the incoming and outgoing water. Some concentrations must be given as input data, like the initial salt concentrations of the water in the different soil reservoirs, of the irrigation water and of the incoming groundwater in the aquifer. The concentrations are expressed in terms of electric conductivity (EC in dS/m). When the concentrations are known in terms of g salt/l water, the rule of thumb: 1 g/l -> 1.7 dS/m can be used. Usually, salt concentrations of the soil are expressed in ECe, the electric conductivity of an extract of a saturated soil paste. In Sahysmod, the salt concentration is expressed as the EC of the soil moisture when saturated under field conditions. As a rule, one can use the conversion rate EC : ECe = 2 : 1. The principles used are correspond to those described in the article soil salinity control.
Salt concentrations of outgoing water (either from one reservoir into the other or by subsurface drainage) are computed on the basis of salt balances, using different leaching or salt mixing efficiencies to be given with the input data. The effects of different leaching efficiencies can be simulated varying their input value.
If drain or well water is used for irrigation, the method computes the salt concentration of the mixed irrigation water in the course of the time and the subsequent impact on the soil and ground water salinity, which again influences the salt concentration of the drain and well water. By varying the fraction of used drain or well water (through the input), the long term impact of different fractions can be simulated.
The dissolution
Solvation
Solvation, also sometimes called dissolution, is the process of attraction and association of molecules of a solvent with molecules or ions of a solute...
of solid soil minerals or the chemical precipitation
Precipitation (chemistry)
Precipitation is the formation of a solid in a solution or inside anothersolid during a chemical reaction or by diffusion in a solid. When the reaction occurs in a liquid, the solid formed is called the precipitate, or when compacted by a centrifuge, a pellet. The liquid remaining above the solid...
of poorly soluble salts is not included in the computation method. However, but to some extent, it can be accounted for through the input data, e.g. increasing or decreasing the salt concentration of the irrigation water or of the incoming water in the aquifer
Aquifer
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
. In a future version, the precipitation of gypsum may be introduced.
Farmers' responses
If required, farmers' responses to waterloggingWaterlogging
Waterlogging or water logging may refer to:* Waterlogging , saturation of the soil by groundwater sufficient to prevent or hinder agriculture...
and soil salinity can be automatically accounted for. The method can gradually decrease:
- The amount of irrigationIrrigationIrrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
water applied when the water table becomes shallower depending on the kind of crop (paddy rice and non-rice) - The fraction of irrigated land when the available irrigationIrrigationIrrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
water is scarce; - The fraction of irrigated land when the soil salinity increases; for this purpose, the salinity is given a stochasticStochasticStochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
interpretation; - The groundwaterGroundwaterGroundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock...
abstraction by pumping from wellsWater wellA water well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, boring or drilling to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The well water is drawn by an electric submersible pump, a trash pump, a vertical turbine pump, a handpump or a mechanical pump...
when the water table drops.
The farmers' responses influence the water and salt balances, which, in turn, slows down the process of water logging and salinization. Ultimately a new equilibrium situation will arise.
The user can also introduce farmers' responses by manually changing the relevant input data. Perhaps it will be useful first to study the automatic farmers' responses and their effect first and thereafter decide what the farmers' responses will be in the view of the user.
Annual input changes
The program runs either with fixed input data for the number of years determined by the user. This option can be used to predict future developments based on long-term average input values, e.g. rainfall, as it will be difficult to assess the future values of the input data year by year.The program also offers the possibility to follow historic records with annually changing input values (e.g. rainfall, irrigation, cropping rotations), the calculations must be made year by year. If this possibility is chosen, the program creates a transfer file by which the final conditions of the previous year (e.g. water table and salinity) are automatically used as the initial conditions for the subsequent period. This facility makes it also possible to use various generated rainfall sequences drawn randomly from a known rainfall probability distribution and to obtain a stochastic prediction of the resulting output parameters.
Some input parameters should not be changed, like the nodal network relations, the system geometry
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, the thickness of the soil layers, and the total porosity
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0–1, or as a percentage between 0–100%...
, otherwise illogical jumps occur in the water and salt balances. These parameters are also stored in the transfer file, so that any impermissible change is overruled by the transfer data. In some cases of incorrect changes, the program will stop and request the user to adjust the input.
Output data


Cumulative frequency analysis
Cumulative frequency analysis is the applcation of estimation theory to exceedance probability . The complement, the non-exceedance probability concerns the frequency of occurrence of values of a phenomenon staying below a reference value. The phenomenon may be time or space dependent...
in the output. The figure was made with the CumFreq program http://www.waterlog.info/cumfreq.htm .
The output data are filed in the form of tables that can be inspected directly, through the user menu, that calls selected groups of data either for a certain polygon
Polygon
In geometry a polygon is a flat shape consisting of straight lines that are joined to form a closed chain orcircuit.A polygon is traditionally a plane figure that is bounded by a closed path, composed of a finite sequence of straight line segments...
over time, or for a certain season over the polygons.
Also, the program has the facility to store the selected data in a spreadsheet
Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application that simulates a paper accounting worksheet. It displays multiple cells usually in a two-dimensional matrix or grid consisting of rows and columns. Each cell contains alphanumeric text, numeric values or formulas...
format for further analysis and for import into a mapping program.
A user interface to assist with the production of maps of output parameters is still in development.
Different users may wish to establish different cause-effect relationships. The program offers only a limited number of standard graphics
Graphics
Graphics are visual presentations on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, computer screen, paper, or stone to brand, inform, illustrate, or entertain. Examples are photographs, drawings, Line Art, graphs, diagrams, typography, numbers, symbols, geometric designs, maps, engineering drawings,or...
, as it is not possible to foresee all different uses that may be made. This is the reason why the possibility for further analysis through spreadsheet programs was created.
Although the computations need many iterations, all the end results can be checked by hand using the equations presented in the manual.
External links & download location
- Free download location of SahysMod software from : http://www.waterlog.info/software.htm or from : http://www.waterlog.info/sahysmod.htm

