
Roy's identity
Encyclopedia
Roy's identityRoy's identity (named for French
economist
Rene Roy
) is a major result in microeconomics
having applications in consumer
choice and the theory of the firm
. The lemma relates the ordinary (Marshallian) demand function to the derivatives of the indirect utility function
. Specifically, where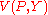 is the indirect utility function, then the Marshallian demand function for good
is the indirect utility function, then the Marshallian demand function for good 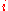 can be calculated as:
can be calculated as:
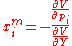
in order to get a Marshallian demand function
for an individual and a good (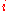 ) from some indirect utility function.
) from some indirect utility function.
The first step is to consider the trivial identity obtained by substituting the expenditure function
for wealth
or income
 in the indirect utility function
in the indirect utility function
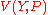 , at a utility of
, at a utility of  :
:
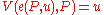
This says that the indirect utility function evaluated in such a way that minimizes the cost for achieving a certain utility given a set of prices (a vector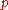 ) is equal to that utility when evaluated at those prices.
) is equal to that utility when evaluated at those prices.
Taking the derivative of both sides of this equation with respect to the price of a single good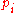 (with the utility level held constant) gives:
(with the utility level held constant) gives:
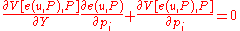 .
.
Rearranging gives the desired result:
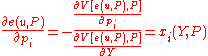
The indirect utility function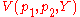 is the maximand of the constrained optimization problem characterized by the following Lagrangian:
is the maximand of the constrained optimization problem characterized by the following Lagrangian:
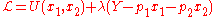
By the envelope Theorem, the derivatives of the maximand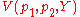 with respect to the parameters can be computed as such:
with respect to the parameters can be computed as such:
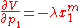
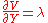
where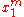 is the maximizer (i.e. the Marshallian demand function for good 1). Simple arithmetic then gives Roy's Identity:
is the maximizer (i.e. the Marshallian demand function for good 1). Simple arithmetic then gives Roy's Identity:
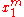
of a good for some consumer from the indirect utility function of that consumer. It is also fundamental in deriving the Slutsky equation
.
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
economist
Economist
An economist is a professional in the social science discipline of economics. The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy...
Rene Roy
Rene Roy
René François Joseph Roy was a French economist. He is primarily recognized for the contribution now known as Roy's identity.-References:...
) is a major result in microeconomics
Microeconomics
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of how the individual modern household and firms make decisions to allocate limited resources. Typically, it applies to markets where goods or services are being bought and sold...
having applications in consumer
Consumer
Consumer is a broad label for any individuals or households that use goods generated within the economy. The concept of a consumer occurs in different contexts, so that the usage and significance of the term may vary.-Economics and marketing:...
choice and the theory of the firm
Theory of the firm
The theory of the firm consists of a number of economic theories that describe the nature of the firm, company, or corporation, including its existence, behavior, structure, and relationship to the market.-Overview:...
. The lemma relates the ordinary (Marshallian) demand function to the derivatives of the indirect utility function
Indirect utility function
In economics, a consumer's indirect utility functionv gives the consumer's maximal utility when faced with a price level p and an amount of income w. It represents the consumer's preferences over market conditions....
. Specifically, where
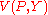 is the indirect utility function, then the Marshallian demand function for good
is the indirect utility function, then the Marshallian demand function for good 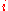 can be calculated as:
can be calculated as: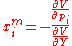
Derivation of Roy's identity
Roy's identity reformulates Shephard's lemmaShephard's lemma
Shephard's lemma is a major result in microeconomics having applications in the theory of the firm and in consumer choice. The lemma states that if indifference curves of the expenditure or cost function are convex, then the cost minimizing point of a given good with price p_i is unique...
in order to get a Marshallian demand function
Marshallian demand function
In microeconomics, a consumer's Marshallian demand function specifies what the consumer would buy in each price and wealth situation, assuming it perfectly solves the utility maximization problem...
for an individual and a good (
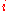 ) from some indirect utility function.
) from some indirect utility function.The first step is to consider the trivial identity obtained by substituting the expenditure function
Expenditure function
In microeconomics, the expenditure function describes the minimum amount of money an individual needs to achieve some level of utility, given a utility function and prices....
for wealth
Wealth
Wealth is the abundance of valuable resources or material possessions. The word wealth is derived from the old English wela, which is from an Indo-European word stem...
or income
Income
Income is the consumption and savings opportunity gained by an entity within a specified time frame, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. However, for households and individuals, "income is the sum of all the wages, salaries, profits, interests payments, rents and other forms of earnings...
 in the indirect utility function
in the indirect utility functionIndirect utility function
In economics, a consumer's indirect utility functionv gives the consumer's maximal utility when faced with a price level p and an amount of income w. It represents the consumer's preferences over market conditions....
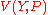 , at a utility of
, at a utility of  :
: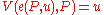
This says that the indirect utility function evaluated in such a way that minimizes the cost for achieving a certain utility given a set of prices (a vector
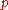 ) is equal to that utility when evaluated at those prices.
) is equal to that utility when evaluated at those prices.Taking the derivative of both sides of this equation with respect to the price of a single good
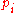 (with the utility level held constant) gives:
(with the utility level held constant) gives: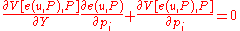 .
.Rearranging gives the desired result:
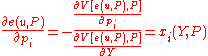
Alternative Proof for the Differentiable Case
There is a simpler proof of Roy's Identity, stated for the two-good case for simplicity.The indirect utility function
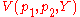 is the maximand of the constrained optimization problem characterized by the following Lagrangian:
is the maximand of the constrained optimization problem characterized by the following Lagrangian: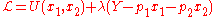
By the envelope Theorem, the derivatives of the maximand
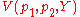 with respect to the parameters can be computed as such:
with respect to the parameters can be computed as such: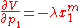
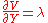
where
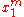 is the maximizer (i.e. the Marshallian demand function for good 1). Simple arithmetic then gives Roy's Identity:
is the maximizer (i.e. the Marshallian demand function for good 1). Simple arithmetic then gives Roy's Identity: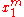
Application
This gives a method of deriving the Marshallian demand functionMarshallian demand function
In microeconomics, a consumer's Marshallian demand function specifies what the consumer would buy in each price and wealth situation, assuming it perfectly solves the utility maximization problem...
of a good for some consumer from the indirect utility function of that consumer. It is also fundamental in deriving the Slutsky equation
Slutsky equation
The Slutsky equation in economics, named after Eugen Slutsky , relates changes in Marshallian demand to changes in Hicksian demand...
.

