
Rotary converter
Encyclopedia

Electrical machine
An electrical machine is the generic name for a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy, converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, or changes alternating current from one voltage level to a different voltage level....
which acts as a mechanical rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
or inverter
Inverter (electrical)
An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current ; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits....
. It was used to convert AC
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
to DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
or DC to AC power before the advent of chemical or solid state
Solid state (electronics)
Solid-state electronics are those circuits or devices built entirely from solid materials and in which the electrons, or other charge carriers, are confined entirely within the solid material...
power rectification. They were commonly used to provide DC power for commercial, industrial and railway electrification from an AC power source.
Principles of operation
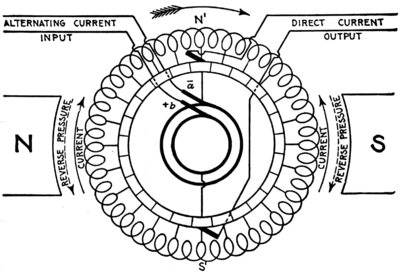

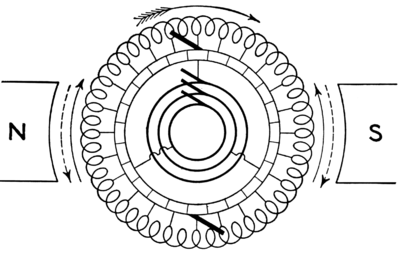
Motor-generator
A motor-generator is a device for converting electrical power to another form. Motor-generator sets are used to convert frequency, voltage, or phase of power. They may also be used to isolate electrical loads from the electrical power supply line...
where the two machines share a single rotating armature
Armature (electrical engineering)
In electrical engineering, an armature generally refers to one of the two principal electrical components of an electromechanical machine–generally in a motor or generator, but it may also mean the pole piece of a permanent magnet or electromagnet, or the moving iron part of a solenoid or relay....
and set of field coil
Field coil
A field coil is a component of an electro-magnetic machine, typically a rotating electrical machine such as a motor or generator. A current-carrying coil is used to generate a magnetic field....
s. The basic construction of the rotary converter consists of a DC generator (dynamo) with a set of slip ring
Slip ring
A slip ring is a method of making an electrical connection through a rotating assembly. Slip rings, also called rotary electrical interfaces, rotating electrical connectors, collectors, swivels, or electrical rotary joints, are commonly found in electric motors, electrical generators for AC...
s tapped into its rotor windings at evenly spaced intervals. When a dynamo is spun the electric currents in its rotor windings alternate as it rotates in the magnetic field of the stationary field windings. This alternating current is rectified by means of a commutator
Commutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary electrical switch in certain types of electric motors or electrical generators that periodically reverses the current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. In a motor, it applies power to the best location on the rotor, and in a generator, picks off power...
which allows DC current to be extracted from the rotor. This principle is taken advantage of by energizing the same rotor windings with AC power which causes the machine to act as a synchronous AC motor. The rotation of the energized coils excites the stationary field windings producing part of the DC current. The other part is AC current from the slip rings which is directly rectified into DC by the commutator. This makes the rotary converter a hybrid dynamo and mechanical rectifier. When used in this way it is referred to as a synchronous rotary converter or simply a synchronous converter. The AC slip rings also allow the machine to act as an alternator. The device can be reversed and DC applied to the field and commutator windings to spin the machine and produce AC power. When operated as a DC to AC machine it is referred to as an inverted rotary converter.
One way to envision what is happening in an AC-to-DC rotary converter is to imagine a rotary reversing switch that is being driven at a speed that is synchronous with the power line. Such a switch could rectify
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
the AC input waveform with no magnetic components at all save those driving the switch. The rotary converter is somewhat more complex than this trivial case because it delivers near-DC rather than the pulsating DC that would result from just the reversing switch, but the analogy may be helpful in understanding how the rotary converter avoids transforming all of the energy from electrical to mechanical and back to electrical.
The advantage of the rotary converter over the discrete motor-generator set is that the rotary converter avoids converting all of the power flow into mechanical energy and then back into electrical energy; some of the electrical energy instead flows directly from input to output, allowing the rotary converter to be much smaller and lighter than a motor-generator set of an equivalent power-handling capability. The advantages of a motor-generator set include adjustable voltage regulation which can compensate for voltage drop in the supply network; it also provided complete power isolation, harmonics isolation, greater surge and transient protection, and sag (brownout) protection through increased momentum.
In this first illustration of a single-phase to direct-current rotary converter, it may be used five different ways:
- If the coil is rotated, alternating currents can be taken from the collector rings, and it is called an alternatorAlternatorAn alternator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current.Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field but linear alternators are occasionally used...
. - if the coil is rotated, direct current can be taken from the commutator, and it is called a dynamoDynamo- Engineering :* Dynamo, a magnetic device originally used as an electric generator* Dynamo theory, a theory relating to magnetic fields of celestial bodies* Solar dynamo, the physical process that generates the Sun's magnetic field- Software :...
. - If the coil is rotated, two separate currents can be taken from the armature, one providing direct current and the other providing alternating current. Such a machine is called a double current generator.
- If a direct current is applied to the commutator, the coil will begin to rotate as a commutated electric motorBrushed DC electric motorA brushed DC motor is an internally commutated electric motor designed to be run from a direct current power source.-Simple two-pole DC motor:The following graphics illustrate a simple, two-pole, brushed, DC motor.DC Motor Rotation...
and an alternating current can be taken out of the collector rings. This is called an inverted rotary converter (see InverterInverter (electrical)An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current ; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits....
). - If the machine is brought up to synchronous speed by external means and if the direction of the current through the armature has the correct relationship to the field coils, then the coil will continue to rotate in sychronism with the alternating current as a synchronous motorSynchronous motorA synchronous electric motor is an AC motor distinguished by a rotor spinning with coils passing magnets at the same rate as the power supply frequency and resulting rotating magnetic field which drives it....
. A direct current can be taken from the commutator. When used this way, it is called a rotary converter.
Applications

Railway electrification system
A railway electrification system supplies electrical energy to railway locomotives and multiple units as well as trams so that they can operate without having an on-board prime mover. There are several different electrification systems in use throughout the world...
, where utility power was supplied as alternating current (AC
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
) but the trains were designed to work on direct current (DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
). Before the invention of mercury arc rectifiers and high-power semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
s, this conversion could only be accomplished using motor-generator
Motor-generator
A motor-generator is a device for converting electrical power to another form. Motor-generator sets are used to convert frequency, voltage, or phase of power. They may also be used to isolate electrical loads from the electrical power supply line...
s or rotary converters.
Most machinery and appliances were operated by DC power at the turn of the century which was provided by rotary converter substations for residential, commercial and industrial consumption. Rotary converters provided high current DC power for industrial electrochemical
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place in a solution at the interface of an electron conductor and an ionic conductor , and which involve electron transfer between the electrode and the electrolyte or species in solution.If a chemical reaction is...
processes such as electroplating
Electroplating
Electroplating is a plating process in which metal ions in a solution are moved by an electric field to coat an electrode. The process uses electrical current to reduce cations of a desired material from a solution and coat a conductive object with a thin layer of the material, such as a metal...
. Steel mill
Steel mill
A steel mill or steelworks is an industrial plant for the manufacture of steel.Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. It is produced in a two-stage process. First, iron ore is reduced or smelted with coke and limestone in a blast furnace, producing molten iron which is either cast into pig iron or...
s needed large amounts of on site DC power for their main roll drive motors.
Obsolescence
AC to DC synchronous rotary converters were made obsolete by mercury arc rectifiersMercury arc valve
A mercury-arc valve is a type of electrical rectifier used for converting high-voltage or high-current alternating current into direct current . Rectifiers of this type were used to provide power for industrial motors, electric railways, streetcars, and electric locomotives, as well as for...
in the 1930s and later on by semiconductor rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
s in the 1960s. Some of the original New York City MTA railway substations using synchronous rotary converters operated until 1999. Compared to the rotary converter, the mercury arc and semiconductor rectifiers did not need daily maintenance, manual synchronizing for parallel operation, skilled personnel and they provided clean DC power. This enabled the new substations to be unmanned, only requiring periodic visits from a technician for inspection and maintenance. AC replaced DC in most applications and eventually the need for local DC substations diminished along with the need for rotary converters. Many DC customers converted to AC power, and on-site solid-state DC rectifiers were used to power the remaining DC equipment from the AC supply.
Self-balancing dynamo
The self-balancing dynamo is of similar construction to the single- and two-phase rotary converter. It was commonly used to create a completely balanced three-wire 120/240-volt DC electrical supply. The AC extracted from the slip rings was fed into a transformer with a single center-tapped winding. The center-tapped winding forms the DC neutral wire. It needed to be driven by a mechanical power source, such as a steam engine, diesel engine, or electric motor. It could be considered a rotary converter used as a double current generator; the AC current was used to balance the DC neutral wire.See also
- Cascade converterCascade converterA Cascade Converter is a type of motor-generator which was patented in 1902 by J. L. la Cour and O. S. Bragstad.It consists of an induction motor driving a dynamo through a shaft...
- Motor-generatorMotor-generatorA motor-generator is a device for converting electrical power to another form. Motor-generator sets are used to convert frequency, voltage, or phase of power. They may also be used to isolate electrical loads from the electrical power supply line...
- Rotary phase converterRotary phase converterA rotary phase converter, abbreviated RPC, is an electrical machine that produces three-phase electric power from single-phase electric power. This allows three phase loads to run using generator or utility-supplied single-phase electric power....
- Frequency converter
- Three-phaseThree-phase electric powerThree-phase electric power is a common method of alternating-current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system and is the most common method used by grids worldwide to transfer power. It is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads...
- Rotary converter plantRotary converter plantA rotary converter plant is a facility at which one form of electricity is converted into another form of electricity by using a combination of an electric motor and an electric generator. The installed combinations of motors and generators at a plant determine the possible type of conversion...
- Traction current converter plantTraction current converter plantA traction substation or traction current converter plant is an electrical substation that converts electric power from the form provided by the electrical power industry for public utility service to an appropriate voltage, current type and frequency to supply railways, trams and/or trolleybuses...

