
Root hair
Encyclopedia
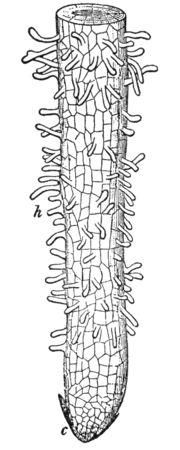
Rhizoid
Rhizoids are thread-like growths from the base or bottom of a plant, found mainly in lower groups such as algae, fungi, bryophytes and pteridophytes, that function like roots of higher plants ....
of a vascular plant
Vascular plant
Vascular plants are those plants that have lignified tissues for conducting water, minerals, and photosynthetic products through the plant. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, Equisetum, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms...
, is a tubular outgrowth of a trichoblast, a hair-forming cell on the epidermis
Epidermis (botany)
The epidermis is a single-layered group of cells that covers plants' leaves, flowers, roots and stems. It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The epidermis serves several functions, it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds,...
of a plant root. That is, root hairs are lateral extensions of a single cell and only rarely branched, thus invisible to the naked eye. They are found only in the region of maturation of the root. Just prior to the root hair cell development, there is a point of elevated phosphorylase activity.
Function
The functions of the root hairs are to collect large amounts of water, nutrients and minerals in the soil. This allows for transportation to ultimately aid in photosynthesis.Formation
Root hair cells are outgrowths at a tip of the plants roots Root hair cells vary between 5 and 17 micrometres in diameter, and 80 to 1,500 micrometres in length. They are found only in the zone of maturation, and not the zone of elongation, possibly because any root hairs that arise are sheared off as the root elongates and moves through the soil.Importance
Root hairs form an important surface over which plants absorb most of their water and nutrients. They are also directly involved in the formation of root nodules in legumeFabaceae
The Fabaceae or Leguminosae, commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, is a large and economically important family of flowering plants. The group is the third largest land plant family, behind only the Orchidaceae and Asteraceae, with 730 genera and over 19,400 species...
plants
They have a large surface area,this makes absorbing both water and minerals more efficient using osmosis. Also, root hair cells secrete acid (H+ from malic acid
Malic acid
Malic acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH2CHOHCO2H. It is a dicarboxylic acid which is made by all living organisms, contributes to the pleasantly sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms , though only the L-isomer exists...
which exchanges and helps solubilize the minerals into ionic form, making the ions easier to take up.
Survival
Root hair cells can survive for 2 to 3 weeks and then die off. At the same time new root hair cells are continually being formed at the tip of the root. This way, the root hair coverage stays the same. When a new root hair cell grows, it excretes a poison so that the other cells in close proximity to it are unable to grow one of these hairs. This ensures equal and efficient distribution of the actual hairs on these cells.It is, therefore, understandable that re-potting must be done with care, because the root hair cells are pulled off for the most part. This is why planting-out leaves the plant withered for some time.

