Roman ring
Encyclopedia
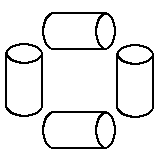
A Roman ring, in theoretical physics
, is a configuration of wormhole
s where for each individual wormhole the time
difference across its mouths is such that it may not allow a closed timelike curve
(CTC), or 'closed-time loop'. If these wormholes and their mouths are arranged in a suitable configuration, a closed time loop will be again possible.
For example, an Earth
-Moon
wormhole whose far end is 0.5 seconds in the "past
" will not violate causality
, since information
sent to the far end via the wormhole and back through normal space will still arrive back on Earth (-0.5 + 1) = 0.5 seconds after it was transmitted; but an additional wormhole in the other direction will allow information to arrive back on Earth 1 second before it was transmitted.
Semiclassical
approaches to incorporating quantum effects into general relativity seem to show that the chronology protection conjecture
postulated by physicist Stephen Hawking
fails to prevent the formation of such rings, although some experts such as Matt Visser
feel that there are reasons to think the semiclassical approach is unreliable here, and that a full theory of quantum gravity
will likely uphold chronology protection.

Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, is a configuration of wormhole
Wormhole
In physics, a wormhole is a hypothetical topological feature of spacetime that would be, fundamentally, a "shortcut" through spacetime. For a simple visual explanation of a wormhole, consider spacetime visualized as a two-dimensional surface. If this surface is folded along a third dimension, it...
s where for each individual wormhole the time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
difference across its mouths is such that it may not allow a closed timelike curve
Closed timelike curve
In mathematical physics, a closed timelike curve is a worldline in a Lorentzian manifold, of a material particle in spacetime that is "closed," returning to its starting point...
(CTC), or 'closed-time loop'. If these wormholes and their mouths are arranged in a suitable configuration, a closed time loop will be again possible.
For example, an Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
-Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
wormhole whose far end is 0.5 seconds in the "past
Relativity of simultaneity
In physics, the relativity of simultaneity is the concept that simultaneity–whether two events occur at the same time–is not absolute, but depends on the observer's reference frame. According to the special theory of relativity, it is impossible to say in an absolute sense whether two events occur...
" will not violate causality
Causality
Causality is the relationship between an event and a second event , where the second event is understood as a consequence of the first....
, since information
Information
Information in its most restricted technical sense is a message or collection of messages that consists of an ordered sequence of symbols, or it is the meaning that can be interpreted from such a message or collection of messages. Information can be recorded or transmitted. It can be recorded as...
sent to the far end via the wormhole and back through normal space will still arrive back on Earth (-0.5 + 1) = 0.5 seconds after it was transmitted; but an additional wormhole in the other direction will allow information to arrive back on Earth 1 second before it was transmitted.
Semiclassical
Semiclassical gravity
Semiclassical gravity is the approximation to the theory of quantum gravity in which one treats matter fields as being quantum and the gravitational field as being classical....
approaches to incorporating quantum effects into general relativity seem to show that the chronology protection conjecture
Chronology protection conjecture
The chronology protection conjecture is a conjecture by the physicist Professor Stephen Hawking that the laws of physics are such as to prevent time travel on all but sub-microscopic scales. Mathematically, the permissibility of time travel is represented by the existence of closed timelike curves...
postulated by physicist Stephen Hawking
Stephen Hawking
Stephen William Hawking, CH, CBE, FRS, FRSA is an English theoretical physicist and cosmologist, whose scientific books and public appearances have made him an academic celebrity...
fails to prevent the formation of such rings, although some experts such as Matt Visser
Matt Visser
Matt Visser is a mathematics Professor at Victoria University of Wellington.Some of his research interests include General Relativity, Quantum Field Theory and Cosmology....
feel that there are reasons to think the semiclassical approach is unreliable here, and that a full theory of quantum gravity
Quantum gravity
Quantum gravity is the field of theoretical physics which attempts to develop scientific models that unify quantum mechanics with general relativity...
will likely uphold chronology protection.




