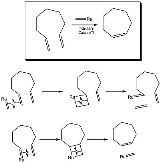
Ring-closing metathesis
Overview
Olefin metathesis
Olefin metathesis or transalkylidenation is an organic reaction that entails redistribution of alkylene fragments by the scission of carbon - carbon double bonds in olefins . Its advantages include the creation of fewer sideproducts and hazardous wastes. Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R...
that allows the closing of previously hard to make rings (7-8 member rings in particular). RCM is simply an intramolecular olefin metathesis with a Grubbs' catalyst
Grubbs' catalyst
Grubbs' Catalyst is a transition metal carbene complex named after Robert H. Grubbs, the chemist who first synthesized it. There are two generations of the catalyst, as shown on the right. In contrast to other olefin metathesis catalysts, Grubbs' Catalysts tolerate other functional groups in the...
, yielding the cycloalkene
Cycloalkene
A cycloalkene or cycloolefin is a type of alkene hydrocarbon which contains a closed ring of carbon atoms, but has no aromatic character. Some cycloalkenes, such as cyclobutene and cyclopentene, can be used as monomers to produce polymer chains. Unless the rings are very large, cycloalkenes are...
and a volatile alkene, in this example ethene.
Many metathesis reactions with ruthenium
Ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most chemicals. The Russian scientist Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element...
catalysts are hampered by unwanted isomerization of the newly formed double bond and it is believed that ruthenium hydrides are responsible that form as a side reaction.

