
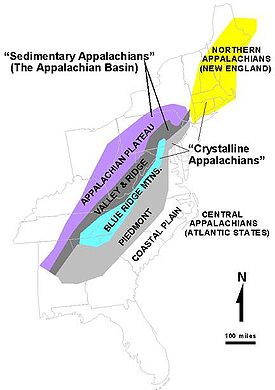
Ridge-and-valley Appalachians
Encyclopedia

Physiographic regions of the world
The physiographic regions of the world are a means of defining the Earth's landforms into distinct regions based upon classic 1916 three-tiered approach defining divisions, provinces, and sections...
of the larger Appalachian
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
division and are also a belt within the Appalachian Mountains
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
extending from southeastern New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
through northwestern New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
, westward into Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
and southward into Maryland
Maryland
Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
, West Virginia
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian and Southeastern regions of the United States, bordered by Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Ohio to the northwest, Pennsylvania to the northeast and Maryland to the east...
, Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
, Tennessee
Tennessee
Tennessee is a U.S. state located in the Southeastern United States. It has a population of 6,346,105, making it the nation's 17th-largest state by population, and covers , making it the 36th-largest by total land area...
, Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
and Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
. They form a broad arc between the Blue Ridge Mountains
Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. This province consists of northern and southern physiographic regions, which divide near the Roanoke River gap. The mountain range is located in the eastern United States, starting at its southern-most...
and the Appalachian Plateau
Appalachian Plateau
The Appalachian Plateau is the western part of the Appalachian mountains, stretching from New York and Alabama. The plateau is a second level United States physiographic region....
physiographic province (the Allegheny
Allegheny Plateau
The Allegheny Plateau is a large dissected plateau area in western and central New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Ohio...
and Cumberland
Cumberland Plateau
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and western West Virginia, part of Tennessee, and a small portion of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia . The terms "Allegheny Plateau" and the "Cumberland Plateau" both refer to the...
Plateaus).
These mountains are characterized by long, even ridge
Ridge
A ridge is a geological feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for some distance. Ridges are usually termed hills or mountains as well, depending on size. There are several main types of ridges:...
s, with long, continuous valley
Valley
In geology, a valley or dale is a depression with predominant extent in one direction. A very deep river valley may be called a canyon or gorge.The terms U-shaped and V-shaped are descriptive terms of geography to characterize the form of valleys...
s in between. From a great enough altitude, they almost look like corduroy
Corduroy
Corduroy is a textile composed of twisted fibers that, when woven, lie parallel to one another to form the cloth's distinct pattern, a "cord." Modern corduroy is most commonly composed of tufted cords, sometimes exhibiting a channel between the tufts...
, except that the widths of the valleys are somewhat variable and ridges sometimes meet in a vee.
The ridge and valley system presents an important obstacle to east-west land travel
Transport
Transport or transportation is the movement of people, cattle, animals and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, rail, road, water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations...
even with today's technology and was a nearly insurmountable barrier to railroads crossing the range and especially to underfunded migrants traveling west to settle the Ohio Country
Ohio Country
The Ohio Country was the name used in the 18th century for the regions of North America west of the Appalachian Mountains and in the region of the upper Ohio River south of Lake Erie...
, Northwest Territory
Northwest Territory
The Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, more commonly known as the Northwest Territory, was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 13, 1787, until March 1, 1803, when the southeastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of Ohio...
and Oregon Country
Oregon Country
The Oregon Country was a predominantly American term referring to a disputed ownership region of the Pacific Northwest of North America. The region was occupied by British and French Canadian fur traders from before 1810, and American settlers from the mid-1830s, with its coastal areas north from...
, before the days of motorized transportation. In the era when animal power dominated transportation there was no safe way to cross east-west in the middle of the range, only nearer its extremes save for the presence of a few rough passages
Military road
A military road is a type of road built by the United States Army. They are used mostly by soldiers, government officials, and sometimes the public. Most military roads are not accessible by public vehicles, however, some are designated as state highways that maintains it. Some military roads are...
opened mid-range during the colonial era such as Braddock's Road and Forbes Road
Forbes Road
The Forbes Road was a historic military roadway in what was then British America, that was constructed in 1758 from Carlisle, Pennsylvania, to the French Fort Duquesne at the junction of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers in what is now downtown Pittsburgh...
, later improved into America's first National Roads (respectively Cumberland Road, Lincoln Highway
Lincoln Highway
The Lincoln Highway was the first road across the United States of America.Conceived and promoted by entrepreneur Carl G. Fisher, the Lincoln Highway spanned coast-to-coast from Times Square in New York City to Lincoln Park in San Francisco, originally through 13 states: New York, New Jersey,...
or designated U.S. 40
U.S. Route 40
U.S. Route 40 is an east–west United States highway. As with most routes whose numbers end in a zero, U.S. 40 once traversed the entire United States. It is one of the original 1920s U.S. Highways, and its first termini were San Francisco, California, and Atlantic City, New Jersey...
and U.S. 30
U.S. Route 30
U.S. Route 30 is an east–west main route of the system of United States Numbered Highways, with the highway traveling across the northern tier of the country. It is the third longest U.S. route, after U.S. Route 20 and U.S. Route 6. The western end of the highway is at Astoria, Oregon; the...
in later years).
Geography
The two great mountain ranges constituting the middle portion of the Ridge and Valley Province are the AllegheniesAllegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range , also spelled Alleghany, Allegany and, informally, the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the eastern United States and Canada...
and the Cumberlands
Cumberland Mountains
The Cumberland Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern section of the Appalachian Mountains. They are located in southern West Virginia, western Virginia, eastern edges of Kentucky, and eastern middle Tennessee, including the Crab Orchard Mountains...
.
The eastern head of the Ridge and Valley region is marked by the Great Appalachian Valley
Great Appalachian Valley
The Great Valley, also called the Great Appalachian Valley or Great Valley Region, is one of the major landform features of eastern North America. It is a gigantic trough — a chain of valley lowlands — and the central feature of the Appalachian Mountain system...
, which lies just west of the Blue Ridge
Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. This province consists of northern and southern physiographic regions, which divide near the Roanoke River gap. The mountain range is located in the eastern United States, starting at its southern-most...
. The western side of the Ridge and Valley region is marked by steep escarpments such as the Allegheny Front
Allegheny Front
The Allegheny Front is the major southeast- or east-facing escarpment in the Allegheny Mountains in southern Pennsylvania, western Maryland, and eastern West Virginia, USA. The Allegheny Front delineates the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians to its east from the Appalachian Plateau to its west...
, the Cumberland Mountains
Cumberland Mountains
The Cumberland Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern section of the Appalachian Mountains. They are located in southern West Virginia, western Virginia, eastern edges of Kentucky, and eastern middle Tennessee, including the Crab Orchard Mountains...
, and Walden Ridge
Walden Ridge
Walden Ridge is a mountain ridge and escarpment located in Tennessee, in the United States. It marks the eastern edge of the Cumberland Plateau and is generally considered part of it. Walden Ridge is about long, running generally north-south...
.
Geology
Alleghenian orogeny
The Alleghenian orogeny or Appalachian orogeny is one of the geological mountain-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Mountains. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 1957....
(Stanley, 421-2). Here, strata have been folded westward, and forced over massive thrust faults; there is little metamorphism
Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is the transformation of an existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat and pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change...
, and no igneous intrusion.(Stanley, 421-2) The ridges represent the edges of the erosion-resistant strata, and the valleys portray the absence of the more erodible
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
strata. Smaller streams have developed their valleys following the lines of the more easily eroded strata. But a few major rivers, such as the Delaware River
Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river on the Atlantic coast of the United States.A Dutch expedition led by Henry Hudson in 1609 first mapped the river. The river was christened the South River in the New Netherland colony that followed, in contrast to the North River, as the Hudson River was then...
, the Susquehanna River
Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River is a river located in the northeastern United States. At long, it is the longest river on the American east coast that drains into the Atlantic Ocean, and with its watershed it is the 16th largest river in the United States, and the longest river in the continental United...
, and the Potomac River
Potomac River
The Potomac River flows into the Chesapeake Bay, located along the mid-Atlantic coast of the United States. The river is approximately long, with a drainage area of about 14,700 square miles...
are evidently older than the present mountains, having cut water gap
Water gap
A water gap is an opening or notch which flowing water has carved through a mountain range. Water gaps often offer a practical route for road and rail transport to cross mountain ridges.- Geology :...
s that are perpendicular to hard strata ridges. The evidence point to a wearing down of the entire region (the original mountains) to a low level with little relief, so that major rivers were flowing in unconsolidated sediments that were unaffected by the underlying rock structure. Then the region was uplifted slowly enough that the rivers were able to maintain their course, cutting through the ridges as they developed.
Valleys may be synclinal
Syncline
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold, with younger layers closer to the center of the structure. A synclinorium is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold, termed a synformal syncline In structural geology, a syncline is a fold, with younger...
valleys or anticlinal
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up. Therefore if age relationships In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is...
valleys.
These mountains are at their highest development in central Pennsylvania, a phenomenon termed the Pennsylvania climax.
Significant ridges (from north to south)
| Name | State |
|---|---|
| Shawangunk Ridge Shawangunk Ridge The Shawangunk Ridge , also known as the Shawangunk Mountains or The Gunks, is a ridge of bedrock in Ulster County, Sullivan County and Orange County in the state of New York, extending from the northernmost point of New Jersey to the Catskill Mountains.The ridgetop, which widens considerably at... | New York |
| Kittatinny Mountains Kittatinny Mountains The Kittatinny Mountains are a long ridge traversing across northwestern New Jersey running in a northeast-southwest axis. It is the first major ridge in the far northeastern extension of the Ridge and Valley province of the Appalachian Mountains... | New Jersey |
| Bald Eagle Mountain Bald Eagle Mountain Bald Eagle Mountain, once known locally as Muncy Mountain, is a stratigraphic ridge in central Pennsylvania, United States, running east of the Allegheny Front and northwest of Mount Nittany. It lies along the southeast side of Bald Eagle Creek, and south of the West Branch Susquehanna River, and... | Pennsylvania |
| Blue Mountain Blue Mountain (Pennsylvania) Blue Mountain is a ridge that forms the eastern edge of the Appalachian mountain range in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. It cuts across the eastern half of the state from New Jersey to Maryland, providing a distinct boundary between a number of Pennsylvania's geographical and cultural regions... | Pennsylvania |
| Jacks Mountain Jacks Mountain Jacks Mountain is a stratigraphic ridge in central Pennsylvania, United States, trending southeast of the Stone Mountain ridge and Jacks Mountain Anticline. The ridge line separates Kishacoquillas Valley from the Ferguson and Dry Valleys... | Pennsylvania |
| Nittany Mountain | Pennsylvania |
| Tuscarora Mountain Tuscarora Mountain Tuscoarora Mountain is a mountain ridge of the Appalachian Mountains in the Ridge and Valley province in central Pennsylvania. It reaches its highest point on Big Mountain at 2,458 feet above sea level.... | Pennsylvania |
| Tussey Mountain Tussey Mountain ]Tussey Mountain is a stratigraphic ridge in central Pennsylvania, United States, trending east of the Bald Eagle, Brush, Dunning and Evitts Mountain ridges... | Pennsylvania |
| Wills Mountain Wills Mountain Wills Mountain is a quartzite-capped ridge in the Ridge and Valley physiographic province of the Appalachian Mountains in Pennsylvania and Maryland, USA, extending from near Bedford, Pennsylvania to near Cumberland, Maryland... | Pennsylvania and Maryland |
| Sideling Hill Sideling Hill Sideling Hill is a long, steep, narrow mountain ridge in the Ridge-and-Valley physiographic province of the Appalachian Mountains, located in Washington County in western Maryland and adjacent West Virginia and Pennsylvania, USA... | West Virginia, Maryland, and Pennsylvania |
| Cacapon Mountain Cacapon Mountain Cacapon Mountain runs northwest through Morgan and Hampshire counties in West Virginia's Eastern Panhandle, rising to its greatest elevation of 2,618 feet above sea-level at High Point. Cacapon Mountain is a folded mountain ridge, belonging to the Appalachian Ridge and Valley Province. Cacapon... | West Virginia |
| Knobly Mountain Knobly Mountain Knobly Mountain is a part of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, located east of New Creek Mountain in Mineral and Grant counties, West Virginia, in the United States.... | West Virginia |
| Mill Creek Mountain Mill Creek Mountain Mill Creek Mountain is a continuous mountain ridge that runs northeast through Hampshire and Hardy counties in the Eastern Panhandle region of the U.S. state of West Virginia. Rising to its greatest elevation of 2,648 feet above sea-level at High Knob, Mill Creek is a folded mountain ridge,... | West Virginia |
| New Creek Mountain New Creek Mountain New Creek Mountain is a mountain ridge of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians in Grant and Mineral counties in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The mountain is named for New Creek which rises and flows along its western flanks. It is part of the Wills Mountain Anticline, with Knobly Mountain along... | West Virginia |
| North Fork Mountain North Fork Mountain North Fork Mountain is a quartzite-capped mountain ridge in the Ridge and Valley physiographic province of the Allegheny Mountains of eastern West Virginia, USA... | West Virginia |
| Patterson Creek Mountain Patterson Creek Mountain Patterson Creek Mountain is a mountain ridge that forms the border between Mineral and Hampshire counties and Grant and Hardy Counties in West Virginia's Eastern Panhandle. The mountain's namesake, Patterson Creek, parallels its western flank... | West Virginia |
| Sleepy Creek Mountain Sleepy Creek Mountain Sleepy Creek Mountain forms the border between Morgan and Berkeley Counties. Together with Third Hill Mountain, the two mountains contain between them Sleepy Creek Lake and the Sleepy Creek Wildlife Management Area... | West Virginia |
| South Branch Mountain South Branch Mountain South Branch Mountain is a mountain ridge that runs southwest to northeast through Hampshire and Hardy counties in the Eastern Panhandle of the U.S. state of West Virginia, rising to its greatest elevation of 3,028 feet above sea-level in the Nathaniel Mountain Wildlife Management Area... | West Virginia |
| Spruce Knob Spruce Knob Spruce Knob, at , is the highest point in the state of West Virginia and the summit of Spruce Mountain, the tallest mountain in the Alleghenies.-Overview:... | West Virginia |
| Allegheny Mountain Allegheny Mountain (West Virginia-Virginia) Allegheny Mountain is a major mountain ridge in the southern range of the Allegheny Mountains, part of the Appalachian Mountains... | Virginia and West Virginia |
| Great North Mountain Great North Mountain Great North Mountain is a long mountain range within the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians in the U.S. states of Virginia and West Virginia. The range is located west of the Shenandoah Valley and Massanutten Mountain in Virginia, and east of the Allegheny Mountains and Cacapon River in West... | Virginia and West Virginia |
| North Mountain North Mountain (Virginia-West Virginia) North Mountain is a mountain ridge within the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians in the U.S. states of Virginia and West Virginia.-Geography:North Mountain spans from the Potomac River in the north to the community of Green Spring in Frederick County, Virginia in the south. The ridge is divided into... | Virginia and West Virginia |
| Massanutten Mountain Massanutten Mountain Massanutten Mountain is a synclinal ridge in the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, located in the U.S. state of Virginia.-Geography:The mountain bisects the Shenandoah Valley just east of Strasburg in Shenandoah County in the north, to its highest peak east of Harrisonburg in Rockingham County in the... | Virginia |
| Pine Mountain Pine Mountain (ridge) Pine Mountain is a ridge in the Appalachian Mountains running through Kentucky, Virginia and Tennessee. It extends about 125 miles from near Jellico, Tennessee, to a location near Elkhorn City, Kentucky. The highest point is 3,273 feet above sea level, east of Whitesburg, Kentucky... | Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee |
| Clinch Mountain Clinch Mountain Clinch Mountain is a mountain ridge in the U.S. states of Tennessee and Virginia, lying in the ridge-and-valley section of the Appalachian Mountains... | Tennessee and Virginia |
| Powell Mountain Powell Mountain (Virginia) Powell Mountain is a mountain ridge of the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians of the Appalachian Mountains. It is a long and narrow ridge, running northeast to southwest, from about Norton, Virginia to near Tazewell, Tennessee... | Tennessee and Virginia |
| Bays Mountain Bays Mountain Bays Mountain is a ridge of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, located in eastern Tennessee. It runs southwest to northeast, from just south of Knoxville to Kingsport.Its southern segment is relatively low in elevation... | Tennessee |
| Lookout Mountain | Tennessee, Alabama, and Georgia |
| Red Mountain Red Mountain, Birmingham, Alabama Red Mountain is a long ridge running southwest-northeast and dividing Jones Valley from Shades Valley south of Birmingham, Alabama. It is part of the Ridge-and-Valley region of the Appalachian mountains... | Alabama |
See also
- Geology of the AppalachiansGeology of the AppalachiansThe geology of the Appalachians dates back to more than 480 million years ago. A look at rocks exposed in today's Appalachian Mountains reveals elongate belts of folded and thrust faulted marine sedimentary rocks, volcanic rocks and slivers of ancient ocean floor - strong evidence that these rocks...
- Allegheny FrontAllegheny FrontThe Allegheny Front is the major southeast- or east-facing escarpment in the Allegheny Mountains in southern Pennsylvania, western Maryland, and eastern West Virginia, USA. The Allegheny Front delineates the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians to its east from the Appalachian Plateau to its west...
- Eastern Continental DivideEastern Continental DivideThe Eastern Continental Divide, in conjunction with other continental divides of North America, demarcates two watersheds of the Atlantic Ocean: the Gulf of Mexico watershed and the Atlantic Seaboard watershed. Prior to 1760, the divide represented the boundary between British and French colonial...
- Tennessee Valley DivideTennessee Valley DivideThe Tennessee Valley Divide is the eastern and southern boundary of the drainage basin of the Tennessee River and its tributaries.The Tennessee Valley Divide begins near the northeasternmost source of the Tennessee River, in the vicinity of Bluefield, West Virginia. From there, the divide...

