
Residual gas analyzer
Encyclopedia
A residual gas analyzer (RGA) is a small and usually rugged mass spectrometer, typically designed for process control and contamination monitoring in vacuum systems. Utilizing quadrupole
technology, there exists two implementations, utilizing either an open ion source (OIS) or a closed ion source (CIS). RGAs may be found in high vacuum
applications such as research chambers, surface science
setups, accelerators
, scanning microscopes
, etc. RGAs are used in most cases to monitor the quality of the vacuum and easily detect minute traces of impurities in the low-pressure gas environment. These impurities can be measured down to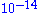 Torr
Torr
levels, possessing sub-ppm detectability in the absence of background interferences.
RGAs would also be used as sensitive in-situ
, helium
leak detectors. With vacuum systems pumped down to lower than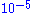 Torr—checking of the integrity of the vacuum seals and the quality of the vacuum—air leaks, virtual leaks and other contaminants at low levels may be detected before a process is initiated.
Torr—checking of the integrity of the vacuum seals and the quality of the vacuum—air leaks, virtual leaks and other contaminants at low levels may be detected before a process is initiated.
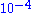 Torr and a maximum detectable partial pressure
Torr and a maximum detectable partial pressure
as low as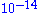 Torr when used in tandem with an electron multiplier
Torr when used in tandem with an electron multiplier
.
OIS RGAs measure residual gas levels without affecting the gas composition of their vacuum environment, though there are performance limitations which include:
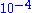 and
and 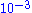 Torr, the problem of ambient and process gases can be significantly reduced by replacing the OIS configuration with a CIS sampling system. Such an ionizer sits on top of the quadrupole mass filter and consists of a short, gas-tight tube with two openings for the entrance of electrons and exit of ions. The ions are formed close to a single extraction plate and exit the ionizer. Electrically insulative alumina rings seal the tube and the biased electrodes from the rest of the quadrupole mass assembly. The ions are produced by electron impact directly at the process pressure. Such design has been applied to gas chromatography mass spectrometry instruments before adaption by quadrupole gas analyzers. Most commercially available CIS systems operate between
Torr, the problem of ambient and process gases can be significantly reduced by replacing the OIS configuration with a CIS sampling system. Such an ionizer sits on top of the quadrupole mass filter and consists of a short, gas-tight tube with two openings for the entrance of electrons and exit of ions. The ions are formed close to a single extraction plate and exit the ionizer. Electrically insulative alumina rings seal the tube and the biased electrodes from the rest of the quadrupole mass assembly. The ions are produced by electron impact directly at the process pressure. Such design has been applied to gas chromatography mass spectrometry instruments before adaption by quadrupole gas analyzers. Most commercially available CIS systems operate between 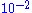 and
and 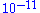 Torr and offer ppm level detectability over the entire mass range for process pressures between
Torr and offer ppm level detectability over the entire mass range for process pressures between 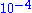 and
and 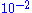 Torr. The upper limit is set by reduction in mean free path
Torr. The upper limit is set by reduction in mean free path
for ion-neutral collisions which takes place at higher pressures, and results in the scattering of ions and reduced sensitivity.
The CIS anode
may be viewed as a high conductance tube connected directly to the process chamber. The pressure in the ionization area is virtually the same as the rest of the chamber. Thus the CIS ionizer produces ions by electron impact directly at the process pressure whilst the rest of the mass analyzer is kept under high pressure. Such direct sampling provides good sensitivity and fast response times.
Quadrupole
A quadrupole or quadrapole is one of a sequence of configurations of—for example—electric charge or current, or gravitational mass that can exist in ideal form, but it is usually just part of a multipole expansion of a more complex structure reflecting various orders of complexity.-Mathematical...
technology, there exists two implementations, utilizing either an open ion source (OIS) or a closed ion source (CIS). RGAs may be found in high vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
applications such as research chambers, surface science
Surface science
Surface science is the study of physical and chemical phenomena that occur at the interface of two phases, including solid–liquid interfaces, solid–gas interfaces, solid–vacuum interfaces, and liquid-gas interfaces. It includes the fields of surface chemistry and surface physics. Some related...
setups, accelerators
Particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a device that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to high speeds and to contain them in well-defined beams. An ordinary CRT television set is a simple form of accelerator. There are two basic types: electrostatic and oscillating field accelerators.In...
, scanning microscopes
Scanning probe microscopy
Scanning Probe Microscopy is a branch of microscopy that forms images of surfaces using a physical probe that scans the specimen. An image of the surface is obtained by mechanically moving the probe in a raster scan of the specimen, line by line, and recording the probe-surface interaction as a...
, etc. RGAs are used in most cases to monitor the quality of the vacuum and easily detect minute traces of impurities in the low-pressure gas environment. These impurities can be measured down to
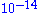 Torr
TorrTorr
The torr is a non-SI unit of pressure with the ratio of 760 to 1 standard atmosphere, chosen to be roughly equal to the fluid pressure exerted by a millimetre of mercury, i.e., a pressure of 1 torr is approximately equal to 1 mmHg...
levels, possessing sub-ppm detectability in the absence of background interferences.
RGAs would also be used as sensitive in-situ
In situ
In situ is a Latin phrase which translated literally as 'In position'. It is used in many different contexts.-Aerospace:In the aerospace industry, equipment on board aircraft must be tested in situ, or in place, to confirm everything functions properly as a system. Individually, each piece may...
, helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
leak detectors. With vacuum systems pumped down to lower than
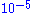 Torr—checking of the integrity of the vacuum seals and the quality of the vacuum—air leaks, virtual leaks and other contaminants at low levels may be detected before a process is initiated.
Torr—checking of the integrity of the vacuum seals and the quality of the vacuum—air leaks, virtual leaks and other contaminants at low levels may be detected before a process is initiated.Open ion source
OIS is the most widely available type of RGA. Cylindrical and axially symmetrical, this kind of ionizer has been around since the early 1950s. The OIS type is usually mounted directly to the vacuum chamber, exposing the filament wire and anode wire cage to the surrounding vacuum chamber, allowing all molecules in the vacuum chamber to move easily through the ion source. With a maximum operating pressure of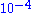 Torr and a maximum detectable partial pressure
Torr and a maximum detectable partial pressurePartial pressure
In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture....
as low as
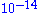 Torr when used in tandem with an electron multiplier
Torr when used in tandem with an electron multiplierElectron multiplier
An electron multiplier is a vacuum-tube structure that multiplies incident charges. In a process called secondary emission, a single electron can, when bombarded on secondary emissive material, induce emission of roughly 1 to 3 electrons...
.
OIS RGAs measure residual gas levels without affecting the gas composition of their vacuum environment, though there are performance limitations which include:
- Outgassing of water from the chamber,
 from the OIS electrodes and most varieties of 300-series stainless steel used in the surrounding vacuum chamber due to the high temperatures of the hot-cathodeHot cathodeIn vacuum tubes, a hot cathode is a cathode electrode which emits electrons due to thermionic emission. In the accelerator community, these are referred to as thermionic cathodes. The heating element is usually an electrical filament...
from the OIS electrodes and most varieties of 300-series stainless steel used in the surrounding vacuum chamber due to the high temperatures of the hot-cathodeHot cathodeIn vacuum tubes, a hot cathode is a cathode electrode which emits electrons due to thermionic emission. In the accelerator community, these are referred to as thermionic cathodes. The heating element is usually an electrical filament...
source (> 1300°C). - Electron Stimulated Desorption (ESD) is noted by peaks observed at 12, 16, 19 and 35 uAtomic mass unitThe unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
rather than by electron-impact ionization of gaseous species, with the effects similar to outgassing effects. This is frequently counteracted by gold-platingGold platingGold plating is a method of depositing a thin layer of gold onto the surface of another metal, most often copper or silver , by chemical or electrochemical plating...
the ionizer which in turn reduces the adsorptionAdsorptionAdsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions, biomolecules or molecules of gas, liquid, or dissolved solids to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. It differs from absorption, in which a fluid permeates or is dissolved by a liquid or solid...
of many gases. Using platinumPlatinumPlatinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal...
-clad molybdenumMolybdenumMolybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores...
ionizers is an alternative.
Closed ion source
With applications requiring measurement of pressures between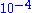 and
and 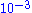 Torr, the problem of ambient and process gases can be significantly reduced by replacing the OIS configuration with a CIS sampling system. Such an ionizer sits on top of the quadrupole mass filter and consists of a short, gas-tight tube with two openings for the entrance of electrons and exit of ions. The ions are formed close to a single extraction plate and exit the ionizer. Electrically insulative alumina rings seal the tube and the biased electrodes from the rest of the quadrupole mass assembly. The ions are produced by electron impact directly at the process pressure. Such design has been applied to gas chromatography mass spectrometry instruments before adaption by quadrupole gas analyzers. Most commercially available CIS systems operate between
Torr, the problem of ambient and process gases can be significantly reduced by replacing the OIS configuration with a CIS sampling system. Such an ionizer sits on top of the quadrupole mass filter and consists of a short, gas-tight tube with two openings for the entrance of electrons and exit of ions. The ions are formed close to a single extraction plate and exit the ionizer. Electrically insulative alumina rings seal the tube and the biased electrodes from the rest of the quadrupole mass assembly. The ions are produced by electron impact directly at the process pressure. Such design has been applied to gas chromatography mass spectrometry instruments before adaption by quadrupole gas analyzers. Most commercially available CIS systems operate between 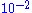 and
and 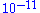 Torr and offer ppm level detectability over the entire mass range for process pressures between
Torr and offer ppm level detectability over the entire mass range for process pressures between 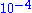 and
and 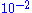 Torr. The upper limit is set by reduction in mean free path
Torr. The upper limit is set by reduction in mean free pathMean free path
In physics, the mean free path is the average distance covered by a moving particle between successive impacts which modify its direction or energy or other particle properties.-Derivation:...
for ion-neutral collisions which takes place at higher pressures, and results in the scattering of ions and reduced sensitivity.
The CIS anode
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
may be viewed as a high conductance tube connected directly to the process chamber. The pressure in the ionization area is virtually the same as the rest of the chamber. Thus the CIS ionizer produces ions by electron impact directly at the process pressure whilst the rest of the mass analyzer is kept under high pressure. Such direct sampling provides good sensitivity and fast response times.

