
Rent's Rule
Encyclopedia
Rent's rule pertains to the organization of computing logic, specifically the relationship between the number of external signal connections to a logic block (i.e., the number of "pins") with the number of logic gates in the logic block, and has been applied to circuits ranging from small digital circuits to mainframe computers.
employee, found a remarkable trend
between the number of pins (terminals T) at the boundaries of
integrated circuit
designs at IBM
and the number of internal components (g),
such as logic gates or standard cells. On a plot, these datapoints
plot, these datapoints
were on a straight line, implying a power-law relation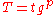 where
where
t and p are constants (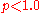 , and generally
, and generally 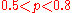 ).
).
Rent disclosed his findings in IBM
-internal memoranda, but the relation was described
in 1971 by Landman and Russo. They performed a hierarchical circuit partitioning
in such a way that at each hierarchical level (top-down) the least number of
interconnections had to be cut to partition the circuit (in more or less equal parts).
At each partitioning step, they noted the number of terminals and the
number of components in each partition and then partitioned the sub-partitions further.
They found the power law rule applied to the resulting T versus g plot and named it
"Rent's rule".
It is crucial to recognise that Rent's rule is an empirical result based on observations of existing designs, and therefore it is less applicable to the analysis of non-traditional circuit architectures. Having said that, it does provide a useful framework with which to compare similar architectures.
for homogeneous systems and pointed out that the amount of optimization
achieved in placement
is reflected by the parameter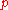 ,
,
the "Rent exponent", which also depends on the circuit topology. In particular, values
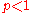 correspond to a greater fraction of short interconnects.
correspond to a greater fraction of short interconnects.
The constant in Rent's rule can be viewed as the average number
in Rent's rule can be viewed as the average number
of terminals required by a single logic block since
when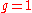 .
.
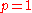 .
.
Larger values are impossible since the maximum number of terminals
for any region containing g logic components in a homogeneous system is
given by . Lower bounds on p depend on the interconnection
. Lower bounds on p depend on the interconnection
topology since it is generally impossible to make all wires short.
This lower bound is often called the "intrinsic Rent exponent",
is often called the "intrinsic Rent exponent",
a notion first introduced by Hagen et al. It can be used to characterize
optimal placements and also measure the interconnection complexity
of a circuit. Higher (intrinsic) Rent exponent values correspond
to a higher topological complexity. One extreme example ( )
)
is a long chain of logic blocks, while a clique has .
.
In realistic 2D circuits,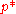 ranges from 0.5 for
ranges from 0.5 for
highly-regular circuits (such as SRAM
)
to 0.75 for random logic.
System performance analysis tools such as BACPAC
typically use Rent's rule to calculate expected wiring lengths and wiring demands.
as used in min-cut placement. For every partition, count
the number of terminals connected to the partition and
compare it to the number of logic blocks in the partition.
Rent's exponent can then be found by fitting these datapoints
on a log-log plot, resulting in an exponent p'.
For optimally partitioned circuits,
but this is no longer the case for practical (heuristic)
partitioning approaches. For partitioning-based placement
algorithms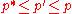 .
.
"far end", i.e., for partitions with a large number of blocks, which is
known as "Region II" of Rent's Rule. A similar deviation exists at
for small partitions, and has been found by Stroobandt who called it Region III.
employee, Donath, discovered that Rent's rule can be used
to estimate the average wirelength and the wirelength distribution
in VLSI chips.
This motivated the System Level Interconnect Prediction
workshop, founded in 1999, and an entire community working
on wirelength prediction (see a survey by Stroobandt). The resulting
wirelength estimates have been improved significantly since
then and are now used for "technology exploration."
The use of Rent's rule allows to perform such estimates a priori
(i.e., before actual placement) and thus predict the properties
of future technologies (clock frequencies, number of routing layers needed,
area, power) based on limited information about future circuits and
technologies.
A comprehensive overview of work based on Rent's rule has been published by Stroobandt.
E.F. Rent's discovery and first publications
In the 1960's, E.F. Rent, an IBMIBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
employee, found a remarkable trend
between the number of pins (terminals T) at the boundaries of
integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
designs at IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
and the number of internal components (g),
such as logic gates or standard cells. On a
 plot, these datapoints
plot, these datapointswere on a straight line, implying a power-law relation
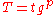 where
wheret and p are constants (
 , and generally
, and generally 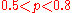 ).
).Rent disclosed his findings in IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
-internal memoranda, but the relation was described
in 1971 by Landman and Russo. They performed a hierarchical circuit partitioning
in such a way that at each hierarchical level (top-down) the least number of
interconnections had to be cut to partition the circuit (in more or less equal parts).
At each partitioning step, they noted the number of terminals and the
number of components in each partition and then partitioned the sub-partitions further.
They found the power law rule applied to the resulting T versus g plot and named it
"Rent's rule".
It is crucial to recognise that Rent's rule is an empirical result based on observations of existing designs, and therefore it is less applicable to the analysis of non-traditional circuit architectures. Having said that, it does provide a useful framework with which to compare similar architectures.
Theoretical basis
Christie and Stroobandt later derived Rent's rule theoreticallyfor homogeneous systems and pointed out that the amount of optimization
achieved in placement
Placement (EDA)
Placement is an essential step in electronic design automation - the portion of the physical design flow that assigns exact locations for various circuitcomponents within the chip’s core area...
is reflected by the parameter
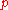 ,
,the "Rent exponent", which also depends on the circuit topology. In particular, values
 correspond to a greater fraction of short interconnects.
correspond to a greater fraction of short interconnects.The constant
 in Rent's rule can be viewed as the average number
in Rent's rule can be viewed as the average numberof terminals required by a single logic block since

when
 .
.Special cases and applications
Random arrangement of logic blocks typically have .
.Larger values are impossible since the maximum number of terminals
for any region containing g logic components in a homogeneous system is
given by
 . Lower bounds on p depend on the interconnection
. Lower bounds on p depend on the interconnectiontopology since it is generally impossible to make all wires short.
This lower bound
 is often called the "intrinsic Rent exponent",
is often called the "intrinsic Rent exponent",a notion first introduced by Hagen et al. It can be used to characterize
optimal placements and also measure the interconnection complexity
of a circuit. Higher (intrinsic) Rent exponent values correspond
to a higher topological complexity. One extreme example (
 )
)is a long chain of logic blocks, while a clique has
 .
.In realistic 2D circuits,
 ranges from 0.5 for
ranges from 0.5 forhighly-regular circuits (such as SRAM
Static random access memory
Static random-access memory is a type of semiconductor memory where the word static indicates that, unlike dynamic RAM , it does not need to be periodically refreshed, as SRAM uses bistable latching circuitry to store each bit...
)
to 0.75 for random logic.
System performance analysis tools such as BACPAC
BACPAC
BACPAC, or the Berkeley Advanced Chip Performance Calculator, is a software program to explore the effect of changes in IC technology. The use enters a set of fairly fundamental properites of the technology and the program estimates the system level performance of an IC built with these assumptions...
typically use Rent's rule to calculate expected wiring lengths and wiring demands.
Estimating Rent's exponent
To estimate Rent's exponent, one can use top-down partitioning,as used in min-cut placement. For every partition, count
the number of terminals connected to the partition and
compare it to the number of logic blocks in the partition.
Rent's exponent can then be found by fitting these datapoints
on a log-log plot, resulting in an exponent p'.
For optimally partitioned circuits,

but this is no longer the case for practical (heuristic)
partitioning approaches. For partitioning-based placement
algorithms
 .
.Region II of Rent's rule
Landman and Russo found a deviation of Rent's rule near the"far end", i.e., for partitions with a large number of blocks, which is
known as "Region II" of Rent's Rule. A similar deviation exists at
for small partitions, and has been found by Stroobandt who called it Region III.
Rentian wirelength estimation
Another IBMIBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
employee, Donath, discovered that Rent's rule can be used
to estimate the average wirelength and the wirelength distribution
in VLSI chips.
This motivated the System Level Interconnect Prediction
workshop, founded in 1999, and an entire community working
on wirelength prediction (see a survey by Stroobandt). The resulting
wirelength estimates have been improved significantly since
then and are now used for "technology exploration."
The use of Rent's rule allows to perform such estimates a priori
(i.e., before actual placement) and thus predict the properties
of future technologies (clock frequencies, number of routing layers needed,
area, power) based on limited information about future circuits and
technologies.
A comprehensive overview of work based on Rent's rule has been published by Stroobandt.

