
Relativistic particle
Encyclopedia
A relativistic particle is a particle which moves with a relativistic speed
; that is, a speed
comparable to the speed of light
. This is achieved by photon
s to the extent that effects described by special relativity are able to describe those of such particles
themselves. Several approaches exist as a means of describing the motion of single and multiple relativistic particles, with a prominent example being postulations through dirac equation
s of single particle motion.
Mass
ive particles are relativistic when their kinetic energy
is comparable or greater than the energy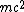 corresponding to their rest mass. (This condition implies that their speed
corresponding to their rest mass. (This condition implies that their speed
is close to the speed of light
.) Such relativistic particles are generated in particle accelerator
s, and are naturally occurring in cosmic radiation. In astrophysics
, jets
of relativistic plasma
are produced by the centers of active galaxies and quasar
s.
A charged relativistic particle crossing the interface of two media with different dielectric constant
s emits transition radiation
. This is exploited in the transition radiation detector
s of high-velocity particles.
Relativistic speed
A Relativistic speed is a speed which is a significant proportion of the speed of light. Therefore scientific analysis must take the consequences of special relativity into account...
; that is, a speed
Speed
In kinematics, the speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity ; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance traveled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as...
comparable to the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
. This is achieved by photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s to the extent that effects described by special relativity are able to describe those of such particles
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle not known to have substructure; that is, it is not known to be made up of smaller particles. If an elementary particle truly has no substructure, then it is one of the basic building blocks of the universe from which...
themselves. Several approaches exist as a means of describing the motion of single and multiple relativistic particles, with a prominent example being postulations through dirac equation
Dirac equation
The Dirac equation is a relativistic quantum mechanical wave equation formulated by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. It provided a description of elementary spin-½ particles, such as electrons, consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and...
s of single particle motion.
Mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
ive particles are relativistic when their kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
is comparable or greater than the energy
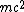 corresponding to their rest mass. (This condition implies that their speed
corresponding to their rest mass. (This condition implies that their speedSpeed
In kinematics, the speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity ; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance traveled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as...
is close to the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
.) Such relativistic particles are generated in particle accelerator
Particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a device that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to high speeds and to contain them in well-defined beams. An ordinary CRT television set is a simple form of accelerator. There are two basic types: electrostatic and oscillating field accelerators.In...
s, and are naturally occurring in cosmic radiation. In astrophysics
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the physics of the universe, including the physical properties of celestial objects, as well as their interactions and behavior...
, jets
Relativistic jet
Relativistic jets are extremely powerful jets of plasma which emerge from presumed massive objects at the centers of some active galaxies, notably radio galaxies and quasars. Their lengths can reach several thousand or even hundreds of thousands of light years...
of relativistic plasma
Relativistic plasma
Relativistic plasmas in physics are plasmas for which relativistic corrections to a particle's mass and velocity are important. Such corrections typically become important when a significant number of electrons reach speeds greater than 0.86c .Such plasmas may be created either by heating a gas to...
are produced by the centers of active galaxies and quasar
Quasar
A quasi-stellar radio source is a very energetic and distant active galactic nucleus. Quasars are extremely luminous and were first identified as being high redshift sources of electromagnetic energy, including radio waves and visible light, that were point-like, similar to stars, rather than...
s.
A charged relativistic particle crossing the interface of two media with different dielectric constant
Dielectric constant
The relative permittivity of a material under given conditions reflects the extent to which it concentrates electrostatic lines of flux. In technical terms, it is the ratio of the amount of electrical energy stored in a material by an applied voltage, relative to that stored in a vacuum...
s emits transition radiation
Transition radiation
Optical Transition radiation is produced by relativistic charged particles when they cross the interface of two media of different dielectric constants. The emitted radiation is the homogeneous difference between the two inhomogeneous solutions of Maxwell's equations of the electric and magnetic...
. This is exploited in the transition radiation detector
Transition radiation detector
A transition radiation detector is a particle detector using the \gamma-dependent threshold of transition radiation in a stratified material. It contains many layers of materials with different indices of refraction. At each interface between materials, the probability of transition radiation...
s of high-velocity particles.
See also
- Special relativitySpecial relativitySpecial relativity is the physical theory of measurement in an inertial frame of reference proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".It generalizes Galileo's...
- Relativistic wave equationsRelativistic wave equationsBefore the creation of quantum field theory, physicists attempted to formulate versions of the Schrödinger equation which were compatible with special relativity...
- Lorentz factorLorentz factorThe Lorentz factor or Lorentz term appears in several equations in special relativity, including time dilation, length contraction, and the relativistic mass formula. Because of its ubiquity, physicists generally represent it with the shorthand symbol γ . It gets its name from its earlier...
- Relativistic mass
- Relativistic plasmaRelativistic plasmaRelativistic plasmas in physics are plasmas for which relativistic corrections to a particle's mass and velocity are important. Such corrections typically become important when a significant number of electrons reach speeds greater than 0.86c .Such plasmas may be created either by heating a gas to...
- Relativistic jetRelativistic jetRelativistic jets are extremely powerful jets of plasma which emerge from presumed massive objects at the centers of some active galaxies, notably radio galaxies and quasars. Their lengths can reach several thousand or even hundreds of thousands of light years...
- Relativistic beamingRelativistic beamingRelativistic beaming is the process by which relativistic effects modify the apparent luminosity of emitting matter that is moving at speeds close to the speed of light...

