Regular economy
Encyclopedia
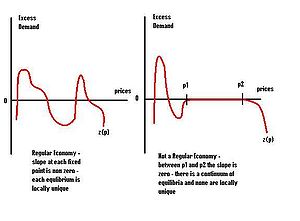
A regular economy is an economy characterized by an excess demand function which has the property that its slope at any equilibrium price vector is non-zero. In other words, if we graph the excess demand function against prices, then the excess demand function "cuts" the x-axis assuring that each equilibrium is locally unique. Local uniqueness in turn permits the use of comparative statics - an analysis of how the economy responds to external shocks - as long as these shocks are not too large.
An important result due to Debreu
(1970) states that almost any economy, defined by an initial distribution of consumer's endowments, is regular. In technical terms, the set of nonregular economies is of Lebesgue measure
zero.
Combined with the index theorem this result implies that almost any economy will have a finite (and odd) number of equilibria.
An important result due to Debreu
Gerard Debreu
Gérard Debreu was a French economist and mathematician, who also came to have United States citizenship. Best known as a professor of economics at the University of California, Berkeley, where he began work in 1962, he won the 1983 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics.-Biography:His father was the...
(1970) states that almost any economy, defined by an initial distribution of consumer's endowments, is regular. In technical terms, the set of nonregular economies is of Lebesgue measure
Lebesgue measure
In measure theory, the Lebesgue measure, named after French mathematician Henri Lebesgue, is the standard way of assigning a measure to subsets of n-dimensional Euclidean space. For n = 1, 2, or 3, it coincides with the standard measure of length, area, or volume. In general, it is also called...
zero.
Combined with the index theorem this result implies that almost any economy will have a finite (and odd) number of equilibria.


