Reflux
Overview
- This article is about using reflux in chemical engineering and chemistry. For the reflux of stomach acids, see articles on heartburnHeartburnHeartburn, also known as pyrosis or acid indigestion is a burning sensation in the chest, just behind the breastbone or in the epigastrium...
, gastroesophageal reflux diseaseGastroesophageal reflux diseaseGastroesophageal reflux disease , gastro-oesophageal reflux disease , gastric reflux disease, or acid reflux disease is chronic symptoms or mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from the stomach into the esophagus...
, and laryngopharyngeal refluxLaryngopharyngeal refluxLaryngopharyngeal reflux , also extraesophageal reflux disease refers to retrograde flow of gastric contents to the upper aero-digestive tract, which causes a variety of symptoms, such as cough, hoarseness, and asthma, among others.Although heartburn is a primary symptom among people with...
. For the reflux of bile into the stomach and esophagus, see biliary refluxBiliary refluxBiliary reflux or duodenogastric reflux is a condition that occurs when biliary fluid flows upward from the duodenum into the stomach and esophagus....
. For the reflux of urineUrineUrine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
, see vesicoureteral refluxVesicoureteral refluxVesicoureteral reflux is an abnormal movement of urine from the bladder into ureters or kidneys. Urine normally travels from the kidneys via the ureters to the bladder...
.
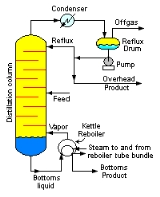
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillation
Distillation
Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in volatilities of components in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process, and not a chemical reaction....
s.

