Reflow soldering
Encyclopedia
Reflow soldering is a process in which a solder paste
(a sticky mixture of powdered solder
and flux
) is used to temporarily attach one or several electrical components to their contact pad
s, after which the entire assembly is subjected to controlled heat, which melts the solder, permanently connecting the joint. Heating may be accomplished by passing the assembly through a reflow oven
or under an infrared lamp
or by soldering individual joints with a hot air pencil.
Reflow soldering is the most common method of attaching surface mount components to a circuit board. The goal of the reflow process is to melt the solder and heat the adjoining surfaces, without overheating and damaging the electrical components. In the conventional reflow soldering process, there are usually four stages, called "zones", each having a distinct thermal profile: preheat, thermal soak (often shortened to just soak), reflow, and cooling.
or cracking can occur. Solder paste can also have a spattering effect. The preheat section is where the solvent in the paste begins to evaporate, and if the rise rate (or temperature level) is too low, evaporation of flux volatiles is incomplete.
), where the flux components begin oxide
reduction on component leads and pads. Too high or too low a temperature can lead to solder spattering or balling as well as oxidation of the paste, the attachment pads and the component terminations. Similarly, fluxes may not fully activate if the temperature is too low. At the end of the soak zone a thermal equilibrium
of the entire assembly is desired just before the reflow zone. A soak profile is suggested to decrease any delta T between components of varying sizes or if the PCB assembly is very large. A soak profile is also recommended to diminish voiding in area array type packages.
s of SMT
components as well as foster intermetallic growth. Conversely, a temperature that isn’t hot enough may prevent the paste from reflowing adequately.
Time above liquidus (TAL), or time above reflow, measures how long the solder is a liquid. The flux reduces surface tension at the juncture of the metals to accomplish metallurgical bonding, allowing the individual solder powder spheres to combine. If the profile time exceeds the manufacturer’s specification, the result may be premature flux activation or consumption, effectively “drying” the paste before formation of the solder joint. An insufficient time/temperature relationship causes a decrease in the flux’s cleaning action, resulting in poor wetting
, inadequate removal of the solvent and flux, and possibly defective solder joints. Experts usually recommend the shortest TAL possible, however, most pastes specify a minimum TAL of 30 seconds, although there appears to be no clear reason for that specific time. One possibility is that there are places on the PCB that are not measured during profiling, and therefore, setting the minimum allowable time to 30 seconds reduces the chances of an unmeasured area not reflowing. A high minimum reflow time also provides a margin of safety against oven temperature changes. The wetting time ideally stays below 60 seconds above liquidus. Additional time above liquidus may cause excessive intermetallic growth, which can lead to joint brittleness. The board and components may also be damaged at extended times over liquidus, and most components have a well-defined time limit for how long they may be exposed to temperatures over a given maximum. Too little time above liquidus may trap solvents and flux and create the potential for cold or dull joints as well as solder voids.
is certain to melt (as opposed to merely soften). If cooled below this temperature, the solder will not flow. Warmed above it once more, the solder will flow again—hence "re-flow".
Modern circuit assembly techniques that use reflow soldering do not necessarily allow the solder to flow more than once. They guarantee that the granulated solder contained in the solder paste surpasses the reflow temperature of the solder involved.
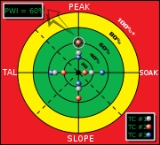
.svg.png) In the electronics manufacturing industry, a statistical measure, known as the Process Window Index
In the electronics manufacturing industry, a statistical measure, known as the Process Window Index
(PWI) is used to quantify the robustness of a thermal process. PWI helps measure how well a process "fits" into a user-defined process limit known as the Specification Limit.
Each thermal profile is ranked on how it "fits" in a process window (the specification or tolerance limit). The center of the process window is defined as zero, and the extreme edge of the process window as 99%. A PWI greater than or equal to 100% indicates that the profile does not process the product within specification. A PWI of 99% indicates that the profile processes the product within specification, but runs at the edge of the process window. A PWI of 60% indicates a profile uses 60% of the process specification. By using PWI values, manufacturers can determine how much of the process window a particular thermal profile uses. A lower PWI value indicates a more robust profile.
For maximum efficiency, separate PWI values are computed for peak, slope, reflow, and soak processes of a thermal profile. To avoid the possibility of thermal shock
affecting the output, the steepest slope in the thermal profile must be determined and leveled. Manufacturers use custom-built software to accurately determine and decrease the steepness of the slope. In addition, the software also automatically recalibrates the PWI values for the peak, slope, reflow, and soak processes. By setting PWI values, engineers can ensure that the reflow soldering work does not overheat or cool too quickly.
Solder paste
Solder paste sometimes refers to soldering flux that does not contain solder.Solder paste is used to connect the leads of integrated chip packages to attachment points in the circuit patterns on a printed circuit board...
(a sticky mixture of powdered solder
Solder
Solder is a fusible metal alloy used to join together metal workpieces and having a melting point below that of the workpiece.Soft solder is what is most often thought of when solder or soldering are mentioned and it typically has a melting range of . It is commonly used in electronics and...
and flux
Flux (metallurgy)
In metallurgy, a flux , is a chemical cleaning agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time...
) is used to temporarily attach one or several electrical components to their contact pad
Contact pad
Contact pads are designated surface areas of a printed circuit board or die of an integrated circuit. Possibilities to contact to pads include soldering, wirebonding, Flip chip mounting, or probe needles....
s, after which the entire assembly is subjected to controlled heat, which melts the solder, permanently connecting the joint. Heating may be accomplished by passing the assembly through a reflow oven
Reflow oven
A reflow oven is a machine used primarily for reflow soldering of surface mount electronic components to printed circuit boards .- Infrared and convection ovens :...
or under an infrared lamp
Infrared heater
An infrared heater is a body with a higher temperature which transfers energy to a body with a lower temperature through electromagnetic radiation. Depending on the temperature of the emitting body, the wavelength of the infrared radiation ranges from 780 nm to 1 mm. The relationship...
or by soldering individual joints with a hot air pencil.
Reflow soldering is the most common method of attaching surface mount components to a circuit board. The goal of the reflow process is to melt the solder and heat the adjoining surfaces, without overheating and damaging the electrical components. In the conventional reflow soldering process, there are usually four stages, called "zones", each having a distinct thermal profile: preheat, thermal soak (often shortened to just soak), reflow, and cooling.
Preheat zone
Maximum slope is a temperature/time relationship that measures how fast the temperature on the printed circuit board changes. The preheat zone is often the lengthiest of the zones and often establishes the ramp-rate. The ramp–up rate is usually somewhere between 1.0 °C and 3.0 °C per second, often falling between 2.0 °C and 3.0 °C (4 °F to 5 °F) per second. If the rate exceeds the maximum slope, potential damage to components from thermal shockThermal shock
Thermal shock is the name given to cracking as a result of rapid temperature change. Glass and ceramic objects are particularly vulnerable to this form of failure, due to their low toughness, low thermal conductivity, and high thermal expansion coefficients...
or cracking can occur. Solder paste can also have a spattering effect. The preheat section is where the solvent in the paste begins to evaporate, and if the rise rate (or temperature level) is too low, evaporation of flux volatiles is incomplete.
Thermal soak zone
The second section, thermal soak, is typically a 60 to 120 second exposure for removal of solder paste volatiles and activation of the fluxes (see fluxFlux (metallurgy)
In metallurgy, a flux , is a chemical cleaning agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time...
), where the flux components begin oxide
Oxide
An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom in its chemical formula. Metal oxides typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2....
reduction on component leads and pads. Too high or too low a temperature can lead to solder spattering or balling as well as oxidation of the paste, the attachment pads and the component terminations. Similarly, fluxes may not fully activate if the temperature is too low. At the end of the soak zone a thermal equilibrium
Thermal equilibrium
Thermal equilibrium is a theoretical physical concept, used especially in theoretical texts, that means that all temperatures of interest are unchanging in time and uniform in space...
of the entire assembly is desired just before the reflow zone. A soak profile is suggested to decrease any delta T between components of varying sizes or if the PCB assembly is very large. A soak profile is also recommended to diminish voiding in area array type packages.
Reflow zone
The third section, the reflow zone, is also referred to as the “time above reflow” or “time above liquidus” (TAL), and is the part of the process where the maximum temperature is reached. An important consideration is peak temperature, which is the maximum allowable temperature of the entire process. A common peak temperature is 20-40°C above liquidus. This limit is determined by the component on the assembly with the lowest tolerance for high temperatures (The component most susceptible to thermal damage). A standard guideline is to subtract 5 °C from the maximum temperature that the most vulnerable component can sustain to arrive at the maximum temperature for process. It is important to monitor the process temperature to keep it from exceeding this limit. Additionally, high temperatures (beyond 260 °C) may cause damage to the internal dieDie (integrated circuit)
A die in the context of integrated circuits is a small block of semiconducting material, on which a given functional circuit is fabricated.Typically, integrated circuits are produced in large batches on a single wafer of electronic-grade silicon or other semiconductor through processes such as...
s of SMT
Surface-mount technology
Surface mount technology is a method for constructing electronic circuits in which the components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards . An electronic device so made is called a surface mount device...
components as well as foster intermetallic growth. Conversely, a temperature that isn’t hot enough may prevent the paste from reflowing adequately.
Time above liquidus (TAL), or time above reflow, measures how long the solder is a liquid. The flux reduces surface tension at the juncture of the metals to accomplish metallurgical bonding, allowing the individual solder powder spheres to combine. If the profile time exceeds the manufacturer’s specification, the result may be premature flux activation or consumption, effectively “drying” the paste before formation of the solder joint. An insufficient time/temperature relationship causes a decrease in the flux’s cleaning action, resulting in poor wetting
Wetting
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface, resulting from intermolecular interactions when the two are brought together. The degree of wetting is determined by a force balance between adhesive and cohesive forces.Wetting is important in the bonding or adherence of...
, inadequate removal of the solvent and flux, and possibly defective solder joints. Experts usually recommend the shortest TAL possible, however, most pastes specify a minimum TAL of 30 seconds, although there appears to be no clear reason for that specific time. One possibility is that there are places on the PCB that are not measured during profiling, and therefore, setting the minimum allowable time to 30 seconds reduces the chances of an unmeasured area not reflowing. A high minimum reflow time also provides a margin of safety against oven temperature changes. The wetting time ideally stays below 60 seconds above liquidus. Additional time above liquidus may cause excessive intermetallic growth, which can lead to joint brittleness. The board and components may also be damaged at extended times over liquidus, and most components have a well-defined time limit for how long they may be exposed to temperatures over a given maximum. Too little time above liquidus may trap solvents and flux and create the potential for cold or dull joints as well as solder voids.
Cooling zone
The last zone is a cooling zone to gradually cool the processed board and solidify the solder joints. Proper cooling inhibits excess intermetallic formation or thermal shock to the components. Typical temperatures in the cooling zone range from 30–100 °C (86–212 °F). A fast cooling rate is chosen to create a fine grain structure that is most mechanically sound. Unlike the maximum ramp-up rate, the ramp–down rate is often ignored. It may be that the ramp rate is less critical above certain temperatures, however, the maximum allowable slope for any component should apply whether the component is heating up or cooling down. A cooling rate of 4°C/s is commonly suggested. It is a parameter to consider when analyzing process results.Etymology
The term "reflow" is used to refer to the temperature above which a solid mass of solder alloyAlloy
An alloy is a mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal history...
is certain to melt (as opposed to merely soften). If cooled below this temperature, the solder will not flow. Warmed above it once more, the solder will flow again—hence "re-flow".
Modern circuit assembly techniques that use reflow soldering do not necessarily allow the solder to flow more than once. They guarantee that the granulated solder contained in the solder paste surpasses the reflow temperature of the solder involved.
Thermal profiling
.svg.png)
Process Window Index
Process Window Index is a statistical measure that quantifies the robustness of a manufacturing process which involves heating and cooling, known as a thermal process...
(PWI) is used to quantify the robustness of a thermal process. PWI helps measure how well a process "fits" into a user-defined process limit known as the Specification Limit.
Each thermal profile is ranked on how it "fits" in a process window (the specification or tolerance limit). The center of the process window is defined as zero, and the extreme edge of the process window as 99%. A PWI greater than or equal to 100% indicates that the profile does not process the product within specification. A PWI of 99% indicates that the profile processes the product within specification, but runs at the edge of the process window. A PWI of 60% indicates a profile uses 60% of the process specification. By using PWI values, manufacturers can determine how much of the process window a particular thermal profile uses. A lower PWI value indicates a more robust profile.
For maximum efficiency, separate PWI values are computed for peak, slope, reflow, and soak processes of a thermal profile. To avoid the possibility of thermal shock
Thermal shock
Thermal shock is the name given to cracking as a result of rapid temperature change. Glass and ceramic objects are particularly vulnerable to this form of failure, due to their low toughness, low thermal conductivity, and high thermal expansion coefficients...
affecting the output, the steepest slope in the thermal profile must be determined and leveled. Manufacturers use custom-built software to accurately determine and decrease the steepness of the slope. In addition, the software also automatically recalibrates the PWI values for the peak, slope, reflow, and soak processes. By setting PWI values, engineers can ensure that the reflow soldering work does not overheat or cool too quickly.
See also
- Wave solderingWave solderingWave soldering is a large-scale soldering process by which electronic components are soldered to a printed circuit board to form an electronic assembly. The name is derived from the use of waves of molten solder to attach metal components to the PCB...
- Reflow ovenReflow ovenA reflow oven is a machine used primarily for reflow soldering of surface mount electronic components to printed circuit boards .- Infrared and convection ovens :...
- Restriction of Hazardous Substances DirectiveRestriction of Hazardous Substances DirectiveThe Directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment 2002/95/EC was adopted in February 2003 by the European Union. The RoHS directive took effect on 1 July 2006, and is required to be enforced and become law in each member state...
(RoHS) - Thermal profilingThermal profilingA thermal profile is a complex set of time-temperature data typically associated with an objected heat up and cool down. The thermal profile is often measured along a variety of dimensions such as slope, soak, time above liquidus , and peak....

