
Rechargeable battery
Encyclopedia



Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
or storage battery is a group of one or more electrochemical cell
Electrochemical cell
An electrochemical cell is a device capable of either deriving electrical energy from chemical reactions, or facilitating chemical reactions through the introduction of electrical energy. A common example of an electrochemical cell is a standard 1.5-volt "battery"...
s. They are known as secondary cells because their electrochemical
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place in a solution at the interface of an electron conductor and an ionic conductor , and which involve electron transfer between the electrode and the electrolyte or species in solution.If a chemical reaction is...
reactions
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
are electrically reversible. Rechargeable batteries come in many different shapes and sizes, ranging anything from a button cell to megawatt systems connected to stabilize
Grid energy storage
Grid energy storage refers to the methods used to store electricity on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Electrical energy is stored during times when production exceeds consumption and the stores are used at times when consumption exceeds production...
an electrical distribution network. Several different combinations of chemicals are commonly used, including: lead–acid, nickel cadmium (NiCd), nickel metal hydride (NiMH), lithium ion
Lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery is a family of rechargeable battery types in which lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge, and back when charging. Chemistry, performance, cost, and safety characteristics vary across LIB types...
(Li-ion), and lithium ion polymer
Lithium ion polymer battery
Lithium-ion polymer batteries, polymer lithium ion, or more commonly lithium polymer batteries are rechargeable batteries...
(Li-ion polymer).
Rechargeable batteries have lower total cost of use and environmental impact than disposable batteries. Some rechargeable battery types are available in the same sizes as disposable types. Rechargeable batteries have higher initial cost, but can be recharged very cheaply and used many times.
Usage and applications
Rechargeable batteries are used for automobile startersCar battery
An automotive battery is a type of rechargeable battery that supplies electric energy to an automobile. Usually this refers to an SLI battery to power the starter motor, the lights, and the ignition system of a vehicle’s engine...
, portable consumer devices, light vehicles (such as motorized wheelchairs, golf carts, electric bicycles, and electric forklifts), tools, and uninterruptible power supplies
Uninterruptible power supply
An uninterruptible power supply, also uninterruptible power source, UPS or battery/flywheel backup, is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source, typically mains power, fails...
. Emerging applications in hybrid electric vehicle
Hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
s and electric vehicles
Battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle, or BEV, is a type of electric vehicle that uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs. BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of, or in addition to, internal combustion engines for propulsion.A battery-only electric vehicle or...
are driving the technology to reduce cost and weight and increase lifetime.
Normally, new rechargeable batteries have to be charged before use; newer low self-discharge batteries
Low self-discharge NiMH battery
The low self-discharge nickel-metal hydride battery was introduced in November 2005. These batteries were developed by Sanyo, who called them "eneloop". Subsequently, other manufacturers also offered LSD NiMH....
hold their charge for many months, and are supplied charged to about 70% of their rated capacity.
Grid energy storage
Grid energy storage
Grid energy storage refers to the methods used to store electricity on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Electrical energy is stored during times when production exceeds consumption and the stores are used at times when consumption exceeds production...
applications use rechargeable batteries for load leveling, where they store electric energy for use during peak load periods, and for renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
uses, such as storing power generated from photovoltaic arrays during the day to be used at night. By charging batteries during periods of low demand and returning energy to the grid during periods of high electrical demand, load-leveling helps eliminate the need for expensive peaking power plant
Peaking power plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers," are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity.-Peak hours:...
s and helps amortize
Amortization (business)
In business, amortization refers to spreading payments over multiple periods. The term is used for two separate processes: amortization of loans and amortization of intangible assets.-Amortization of loans:...
the cost of generators over more hours of operation.
The US National Electrical Manufacturers Association
National Electrical Manufacturers Association
is the association of electrical and medical imaging equipment manufacturers. Founded in 1926 and headquartered near Washington, D.C., its approximately manufacture products used in the generation, transmission, distribution, control, and end use of electricity. These products are used in utility,...
has estimated that U.S. demand for rechargeable batteries is growing twice as fast as demand for nonrechargeables.
Charging and discharging
During charging, the positive active material is oxidized, producing electronElectron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s, and the negative material is reduced
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
, consuming electrons. These electrons constitute the current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
flow in the external circuit
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
. The electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
may serve as a simple buffer for ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
flow between the electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s, as in lithium-ion and nickel-cadmium
Nickel-cadmium battery
The nickel–cadmium battery ' is a type of rechargeable battery using nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes....
cells, or it may be an active participant in the electrochemical reaction, as in lead–acid cells.
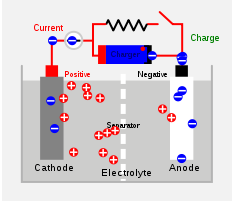


Battery charger
A battery charger is a device used to put energy into a secondary cell or rechargeable battery by forcing an electric current through it.The charge current depends upon the technology and capacity of the battery being charged...
using AC mains electricity
Mains electricity
Mains is the general-purpose alternating current electric power supply. In the US, electric power is referred to by several names including household power, household electricity, powerline, domestic power, wall power, line power, AC power, city power, street power, and grid power...
.
Chargers take from a few minutes (rapid chargers) to several hours to charge a battery. Most batteries are capable of being charged far faster than simple battery chargers are capable of; there are chargers that can charge consumer sizes of NiMH batteries in 15 minutes. Fast charges must have multiple ways of detecting full charge (voltage, temperature, etc.) to stop charging before onset of harmful overcharging.
Rechargeable multi-cell batteries are susceptible to cell damage due to reverse charging if they are fully discharged. Fully integrated battery charger
Battery charger
A battery charger is a device used to put energy into a secondary cell or rechargeable battery by forcing an electric current through it.The charge current depends upon the technology and capacity of the battery being charged...
s that optimize the charging current are available.
Attempting to recharge non-rechargeable batteries with unsuitable equipment may cause battery explosion.
Flow batteries
Flow battery
A flow battery is a form of rechargeable battery in which electrolyte containing one or more dissolved electroactive species flows through an electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy directly to electricity...
, used for specialised applications, are recharged by replacing the electrolyte liquid.
Battery manufacturers' technical notes often refer to VPC; this is volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s per cell
Electrochemical cell
An electrochemical cell is a device capable of either deriving electrical energy from chemical reactions, or facilitating chemical reactions through the introduction of electrical energy. A common example of an electrochemical cell is a standard 1.5-volt "battery"...
, and refers to the individual secondary cells that make up the battery. For example, to charge a 12 V battery (containing 6 cells of 2 V each) at 2.3 VPC requires a voltage of 13.8 V across the battery's terminals.
Non-rechargeable alkaline and zinc–carbon cells output 1.5V when new, but this voltage gradually drops with use. Most NiMH AA and AAA batteries rate their cells at 1.2 V, and can usually be used in equipment designed to use alkaline batteries up to an end-point of 0.9 to 1.2V.
Reverse charging
Subjecting a discharged cell to a current in the direction which tends to discharge it further, rather than charge it, is called reverse charging; this damages cells. Reverse charging can occur under a number of circumstances, the two most common being:- When a battery or cell is connected to a charging circuit the wrong way round.
- When a battery made of several cells connected in series is deeply discharged.
When one cell completely discharges ahead of the rest, the live cells will apply a reverse current to the discharged cell ("cell reversal"). This can happen even to a "weak" cell that is not fully discharged. If the battery drain current is high enough, the weak cell's internal resistance can experience a reverse voltage that is greater than the cell's remaining internal forward voltage. This results in the reversal of the weak cell's polarity while the current is flowing through the cells. This can significantly shorten the life of the affected cell and therefore of the battery. The higher the discharge rate of the battery needs to be, the better matched the cells should be, both in kind of cell and state of charge. In some extreme cases, the reversed cell can begin to emit smoke or catch fire.
In critical applications using Ni-Cad batteries, such as in aircraft, each cell is individually discharged by connecting a load clip across the terminals of each cell, thereby avoiding cell reversal, then charging the cells in series.
Depth of discharge
Depth of discharge (DOD) is normally stated as a percentage of the nominal ampere-hour capacity; 0% DOD means no discharge. Since the usable capacity of a battery system depends on the rate of discharge and the allowable voltage at the end of discharge, the depth of discharge must be qualified to show the way it is to be measured. Due to variations during manufacture and aging, the DOD for complete discharge can change over time or number of charge cycleCharge cycle
A charge cycle is the process of charging a rechargeable battery and discharging it as required into a load. The term is typically used to specify a battery's expected life, as the number of charge cycles affects life more than the mere passage of time...
s. Generally a rechargeable battery system will tolerate more charge/discharge cycles if the DOD is lower on each cycle.
Active components
The active components in a secondary cell are the chemicals that make up the positive and negative active materials, and the electrolyteElectrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
. The positive and negative are made up of different materials, with the positive exhibiting a reduction
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
potential and the negative having an oxidation potential. The sum of these potentials is the standard cell potential or voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
.
In primary cell
Primary cell
A primary cell is any kind of battery in which the electrochemical reaction is not reversible, rendering the cell non-rechargeable. A common example of a primary cell is the disposable battery. Unlike a secondary cell, the reaction cannot be reversed by running a current into the cell; the chemical...
s the positive and negative electrodes are known as the cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
and anode
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
, respectively. Although this convention is sometimes carried through to rechargeable systems — especially with lithium-ion cells, because of their origins in primary lithium cells — this practice can lead to confusion. In rechargeable cells the positive electrode is the cathode on discharge and the anode on charge, and vice versa for the negative electrode.
Table of rechargeable battery types
| Type | Voltagea | Energy densityb | Powerc | Effi.d | E/$e | Disch.f | Cyclesg | Lifeh | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (V) | (MJ/kg) | (Wh/kg) | (Wh/L) | (W/kg) | (%) | (%/month) | (#) | (years) | ||
| Lead–acid | 2.1 | 0.11-0.14 | 30-40 | 60-75 | 180 | 70%-92% | 5-8 | 3%-4% | 500-800 | 5-8 (automotive battery), 20 (stationary) |
| Alkaline Rechargeable alkaline battery Rechargeable alkaline battery is a type of alkaline battery that is rechargeable. The first generation rechargeable alkaline technology was developed by Battery Technologies Inc in Canada and licensed to Pure Energy, EnviroCell, Rayovac, and Grandcell... |
1.5 | 0.31 | 85 | 250 | 50 | -- | 7.7 | <0.3 | 100-1000 | <5 |
| Ni–iron | 1.2 | 0.18 | 50 | 100 | 65% | 5-7.3 | 20%-40% | 50+ | ||
| Ni–cadmium | 1.2 | 0.14-0.22 | 40-60 | 50-150 | 150 | 70%-90% | 1.25-2.5 | 20% | 1500 | |
| NiH2 | 1.5 | 75 | 20,000 | 15+ | ||||||
| NiMH | 1.2 | 0.11-0.29 | 30-80 | 140-300 | 250-1000 | 66% | 2.75 | 30% | 500-1000 | |
| Ni–zinc | 1.7 | 0.22 | 60 | 170 | 900 | 2-3.3 | 100-500 | |||
| Li-ion | 3.6 | 0.58 | 150-250 | 250-360 | 1800 | 80-90% | 2.8-5 | 5%-10% | 1200 | 2-3 |
| Li polymer | 3.7 | 0.47-0.72 | 130-200 | 300 | 3000+ | 99.8% | 2.8-5.0 | 5% | 500~1000 | 2-3 |
| LiFePO4 Lithium iron phosphate battery The lithium iron phosphate battery, also called LFP battery, is a type of rechargeable battery, specifically a lithium-ion battery, which uses LiFePO4 as a cathode material.-History:... |
3.25 | 0.32-0.4 | 80-120 | 170 | 1400 | 93.5% | 0.7-3.0 | 2000+ | >10 | |
| Li sulfur Lithium sulfur battery The lithium–sulfur battery is a rechargeable galvanic cell with a very high energy density. By virtue of the low atomic weight of lithium and moderate weight of sulfur, Li–S batteries are relatively light; about the density of water. They were demonstrated on the longest and highest-altitude... |
2.0 | 0.94-1.44 | 400 | 350 | ~100 | |||||
| Li–titanate | 2.3 | 90 | 4000+ | 87-95%r | 0.5-1.0 | 9000+ | 20+ | |||
| Sodium Ion | 1.7 | 30 | 85% | 3.3 | 5000+ | Still testing | ||||
| Thin film Li Thin film rechargeable lithium battery Thin film lithium ion batteries are similar to lithium-ion batteries, but they are composed of thin materials, some only nanometers or micrometers thick, which allow for the finished battery to be just millimeters thick. They have been developed and advanced primarily within the last decade... |
? | 350 | 959 | ? | ?p | 40000 | ||||
| ZnBr | 75-85 | |||||||||
| V redox Vanadium redox battery The vanadium redox battery is a type of rechargeable flow battery that employs vanadium ions in different oxidation states to store chemical potential energy... |
1.15-1.55 | 25-35 | 80% | 20% | 14,000 | 10(stationary) | ||||
| NaS Sodium-sulfur battery A sodium–sulfur battery or liquid metal battery is a type of molten metal battery constructed from sodium and sulfur . This type of battery has a high energy density, high efficiency of charge/discharge and long cycle life, and is fabricated from inexpensive materials... |
150 | 89%-92% | ||||||||
| Molten salt Molten salt battery Molten salt batteries or liquid sodium battery are a class of primary cell and secondary cell high-temperature electric battery that use molten salts as an electrolyte. They offer both a higher energy density through the proper selection of reactant pairs as well as a higher power density by means... |
2.58 | 70-110 | 160 | 150-220 | 4.54 | 3000+ | 8+ | |||
| Silver zinc (Ag-Zn) Silver-oxide battery A silver oxide battery , not to be confused with a similar but different silver–zinc battery, which is a secondary cell, is a primary cell with relatively very high energy/weight ratio. They are costly due to the high price of silver... |
1.86 | 130 | 240 | |||||||
Notes
For brevity, entries in the table had to be abbreviated. For a full description, please refer to the individual article about each type.
- a Nominal cell voltageVoltageVoltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
in V.
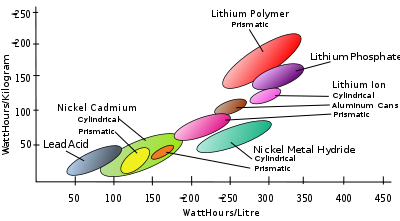
- b Energy densityEnergy densityEnergy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
= energy/weight or energy/size, given in three different units - c Specific powerSpecific powerIn physics and engineering, surface power density or sometimes simply specific power is power per unit area.-Applications:* The intensity of electromagnetic radiation can be expressed in W/m2...
= power/weight in W/kg - d Charge/discharge efficiency in %
- e Energy/consumer price in W·h/US$ (approximately)
- f Self-discharge rate in %/month
- g Cycle durability in number of cycles
- h Time durability in years
- i VRLAVRLAA VRLA battery is a type of low-maintenance lead–acid rechargeable battery. Because of their construction, VRLA batteries do not require regular addition of water to the cells....
or recombinant includes gel batteries and absorbed glass mats - p Pilot production
- r Depending upon charge rate
Common rechargeable battery types
Nickel–cadmium battery (NiCd):Created by Waldemar Jungner
Waldemar Jungner
Ernst Waldemar Jungner, June 19, 1869- August 30, 1924, was a Swedish inventor and engineer. In 1899 he invented the nickel-iron electric storage battery and invented the nickel-cadmium battery.-Literature:...
of Sweden in 1899, it used nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
as electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s. Cadmium is a toxic element, and was banned for most uses by the European Union in 2004. Nickel–cadmium batteries have been almost completely superseded by nickel–metal hydride (NiMH) batteries.
Nickel–metal hydride battery (NiMH):
First commercial types were available in 1989.
These are now a common consumer and industrial type. The battery has a hydrogen-absorbing alloy
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal history...
for the negative electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
instead of cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
.
Lithium-ion battery:
The technology behind lithium-ion battery has not yet fully reached maturity. However, the batteries are the type of choice in many consumer electronics and have one of the best energy-to-mass ratios
Energy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
and a very slow loss of charge when not in use.
Lithium-ion polymer battery
These batteries are light in weight and can be made in any shape desired.
Less common types
Lithium sulfur batteryLithium sulfur battery
The lithium–sulfur battery is a rechargeable galvanic cell with a very high energy density. By virtue of the low atomic weight of lithium and moderate weight of sulfur, Li–S batteries are relatively light; about the density of water. They were demonstrated on the longest and highest-altitude...
: A new battery chemistry developed by Sion Power since 1994. Claims superior energy to weight than current lithium technologies on the market. Also lower material cost may help this product reach the mass market.
Thin film battery
Thin film rechargeable lithium battery
Thin film lithium ion batteries are similar to lithium-ion batteries, but they are composed of thin materials, some only nanometers or micrometers thick, which allow for the finished battery to be just millimeters thick. They have been developed and advanced primarily within the last decade...
(TFB): An emerging refinement of the lithium ion technology by Excellatron. The developers claim a very large increase in recharge cycles, around 40,000 cycles. Higher charge and discharge rates. At least 5C charge rate. Sustained 60C discharge, and 1000C peak discharge rate. And also a significant increase in specific energy, and energy density.
- Also Infinite Power Solutions makes thin film batteries (TFB) for micro-electronic applications, that are flexible, rechargeable, solid-state lithium batteries.
Smart battery: A smart battery has the voltage monitoring circuit built inside. See also: Smart Battery System
Smart Battery System
Smart Battery System is a specification for determining accurate battery capacity readings. It allows operating systems to perform power management operations based on remaining estimated run times. Through this communication, the system also controls the amount the battery is charged. ...
Carbon foam-based lead acid battery: Firefly Energy has developed a carbon foam-based lead acid battery with a reported energy density of 30-40% more than their original 38 W·h/kg, with long life and very high power density.
Potassium-ion battery
Potassium-ion battery
The potassium-ion battery was first invented by the American/Iranian chemist, Ali Eftekhari, in 2004 as an alternative to lithium-ion batteries. The battery uses Prussian blue as the cathode material for its stability, the prototype could be successfully used for millions of cycles...
: This type of rechargeable battery can deliver the best known cycleability, in order of a million cycles, due to the extraordinary electrochemical stability of potassium insertion/extraction materials such as Prussian blue
Prussian blue
Prussian blue is a dark blue pigment with the idealized formula Fe718. Another name for the color Prussian blue is Berlin blue or, in painting, Parisian blue. Turnbull's blue is the same substance but is made from different reagents....
.
Sodium Ion: This type is meant for stationary storage and competes with lead–acid batteries. It aims at a very low total cost ownership per kWh of storage. This is achieved by a long and stable life time. The number of cycles is above 5000 and the battery does not get damage by deep discharge. The energy density is rather low, somewhat lower than lead–acid.
Developments since 2005
In 2007 Yi Cui and colleagues at Stanford UniversityStanford University
The Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University or Stanford, is a private research university on an campus located near Palo Alto, California. It is situated in the northwestern Santa Clara Valley on the San Francisco Peninsula, approximately northwest of San...
's Department of Materials Science and Engineering discovered that using silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
nanowire
Nanowire
A nanowire is a nanostructure, with the diameter of the order of a nanometer . Alternatively, nanowires can be defined as structures that have a thickness or diameter constrained to tens of nanometers or less and an unconstrained length. At these scales, quantum mechanical effects are important —...
s as the anode of a lithium-ion battery increases the volumetric charge density of the anode by up to a factor of 10, the nanowire battery
Nanowire battery
A nanowire battery is a lithium-ion battery invented by a team led by Dr. Yi Cui at Stanford University in 2007. The team's invention consists of a stainless steel anode covered in silicon nanowires, to replace the traditional graphite anode...
.
Another development is the paper-thin flexible self-rechargeable battery combining a thin-film organic solar cell
Solar cell
A solar cell is a solid state electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect....
with an extremely thin and highly flexible lithium-polymer battery, which recharges itself when exposed to light.
Ceramatec, a research and development subcompany of CoorsTek
CoorsTek
CoorsTek, Inc. is a privately owned manufacturer of technical ceramics, semiconductor tooling, plastic tubing, medical devices and other industrial products. CoorsTek’s headquarters and primary factories are located in Golden, Colorado, USA, near the foothills west of Denver. The company is...
, was testing a battery comprising a chunk of solid sodium metal mated to a sulfur compound by a paper-thin ceramic membrane which conducts ions back and forth to generate a current. The company claimed that it could fit about 40 kilowatt hours of energy into a package about the size of a refrigerator, and operate below 90 °C; and that their battery would allow about 3,650 discharge/recharge cycles (or roughly 1 per day for one decade.)
Alternatives
Several alternatives to rechargeable batteries exist or are under development. For uses such as portable radiosClockwork radio
A windup radio or clockwork radio is a radio that is powered by human muscle power rather than batteries or the electrical grid. In the most common arrangement, an internal electrical generator is run by a mainspring, which is wound by a hand crank on the case. Turning the crank winds the spring...
, rechargeable batteries may be replaced by clockwork mechanisms which are wound up by hand, driving dynamos
Electrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
, although this system may be used to charge a battery rather than to operate the radio directly. Flashlight
Flashlight
A flashlight is a hand-held electric-powered light source. Usually the light source is a small incandescent lightbulb or light-emitting diode...
s may be driven by a dynamo directly. For transportation, uninterruptible power supply
Uninterruptible power supply
An uninterruptible power supply, also uninterruptible power source, UPS or battery/flywheel backup, is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source, typically mains power, fails...
systems and laboratories, flywheel energy storage
Flywheel energy storage
Flywheel energy storage works by accelerating a rotor to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy...
systems store energy in a spinning rotor for conversion to electric power when needed; such systems may be used to provide large pulses of power that would otherwise be objectionable on a common electrical grid. Ultracapacitors are also used; an electric screwdriver which charges in 90 seconds and will drive about half as many screws as a device using a rechargeable battery was introduced in 2007, and similar flashlights have been produced.
Ultracapacitors—capacitors of extremely high value—are being developed for transportation, using a large capacitor to store energy instead of the rechargeable battery banks used in hybrid vehicles. One drawback to capacitors compared with batteries is that the terminal voltage drops rapidly; a capacitor that has 25% of its initial energy left in it will have one-half of its initial voltage. Battery systems tend to have a terminal voltage that does not decline rapidly until nearly exhausted. This characteristic complicates the design of power electronics for use with ultracapacitors. However, there are potential benefits in cycle efficiency, lifetime, and weight compared with rechargeable systems. China started using ultracapacitors on two commercial bus routes in 2006; one of them is route 11 in Shanghai
Shanghai
Shanghai is the largest city by population in China and the largest city proper in the world. It is one of the four province-level municipalities in the People's Republic of China, with a total population of over 23 million as of 2010...
.
See Battery (electricity)
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
for comparisons between battery types.
See also
- Automotive battery
- Battery packBattery packA battery pack is a set of any number of identical batteries or individual battery cells. They may be configured in a series, parallel or a mixture of both to deliver the desired voltage, capacity, or power density...
- Battery recyclingBattery recyclingBattery recycling is a recycling activity that aims to reduce the number of batteries being disposed as municipal solid waste. Batteries contain a number of heavy metals and toxic chemicals, their dumping has raised concern over risks of soil contamination and water pollution.-Battery recycling by...
Deep cycle automotive battery manufacturers
- Fuel cellFuel cellA fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
- Potassium-ion batteryPotassium-ion batteryThe potassium-ion battery was first invented by the American/Iranian chemist, Ali Eftekhari, in 2004 as an alternative to lithium-ion batteries. The battery uses Prussian blue as the cathode material for its stability, the prototype could be successfully used for millions of cycles...
- Mercury-containing and Rechargeable Battery Management ActMercury-containing and Rechargeable Battery Management ActIn the United States, the Mercury-Containing and Rechargeable Battery Management Act was signed into law on May 13, 1996...
- Nickel–hydrogen battery
- Power-to-weight ratioPower-to-weight ratioPower-to-weight ratio is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement of actual performance of any engine or power sources...
- Rechargeable electricity storage system
- Service lifeService lifeA product's service life is its expected lifetime, or the acceptable period of use in service. It is the time that any manufactured item can be expected to be 'serviceable' or supported by its manufacturer....
- Smart cardSmart cardA smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card , is any pocket-sized card with embedded integrated circuits. A smart card or microprocessor cards contain volatile memory and microprocessor components. The card is made of plastic, generally polyvinyl chloride, but sometimes acrylonitrile...
- Thin-film battery
- Trickle chargingTrickle chargingTrickle charging, or float charging, means charging a battery at a similar rate as its self-discharging rate, thus maintaining a full capacity battery. Most rechargeable batteries, particularly nickel-cadmium batteries or nickel metal hydride batteries, have a moderate rate of self-discharge,...
- WiTricityWiTricityWiTricity, a portmanteau for "wireless electricity", is a trademark of WiTricity corporation referring to their devices and processes which use a form of wireless energy transfer including resonant energy transfer etc., the ability to provide electrical energy to remote objects without wires using...
External links
- High-performance lithium battery anodes using silicon nanowires
- Scientific American - How Rechargeable Batteries Work
- Battery University – on-line resource that provides practical battery knowledge for engineers, educators, students and battery users alike.

