
Rama's Bridge
Encyclopedia

Tamil language
Tamil is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. It has official status in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and in the Indian union territory of Pondicherry. Tamil is also an official language of Sri Lanka and Singapore...
: , Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
: , ), is a chain of limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
shoal
Shoal
Shoal, shoals or shoaling may mean:* Shoal, a sandbank or reef creating shallow water, especially where it forms a hazard to shipping* Shoal draught , of a boat with shallow draught which can pass over some shoals: see Draft...
s, between Pamban Island
Pamban Island
Pamban Island , also known as Rameswaram Island, is an island located between peninsular India and Sri Lanka. The island is a part of India and is governed by the administration of Ramanathapuram district of the state of Tamil Nadu...
, also known as Rameswaram Island, off the southeastern coast of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu is one of the 28 states of India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory of Pondicherry, and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, and Mannar Island
Mannar Island
Mannar Island, formerly called Manar Island, is part of Mannar District, Sri Lanka. It is linked to the rest of Sri Lanka by a causeway.It has an area of about 50 square kilometres, mainly covered with vegetation and sand.Rama's Bridge or Rama Setu ,[1] is a chain of limestone shoals, between...
, off the northwestern coast of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
. Geological evidence suggests that this bridge is a former land connection between India and Sri Lanka.
The bridge is 18 miles (30 km) long and separates the Gulf of Mannar
Gulf of Mannar
The Gulf of Mannar is a large shallow bay forming part of the Laccadive Sea in the Indian Ocean. It lies between the southeastern tip of India and the west coast of Sri Lanka. A chain of low islands and reefs known as Adam's Bridge, also called Ramsethu, which includes Mannar Island, separates the...
(southwest) from the Palk Strait
Palk Strait
Palk Strait is a strait between the Tamil Nadu state of India and the Mannar district of the Northern Province of the island nation of Sri Lanka. It connects the Bay of Bengal in the northeast with the Palk Bay and thence with the Gulf of Mannar in the southwest. The strait is wide. Several...
(northeast). Some of the sandbanks are dry and the sea in the area is very shallow, being only 3 ft to 30 ft (1 m to 10 m) deep in places, which hinders navigation. It was reportedly passable on foot up to the 15th century until storms deepened the channel: temple records seem to say that Rama’s Bridge was completely above sea level until it broke in a cyclone
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
in 1480 CE.
Name
The bridge was first mentioned in the ancient IndiaIndia
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n Sanskrit epic Ramayana
Ramayana
The Ramayana is an ancient Sanskrit epic. It is ascribed to the Hindu sage Valmiki and forms an important part of the Hindu canon , considered to be itihāsa. The Ramayana is one of the two great epics of India and Nepal, the other being the Mahabharata...
of Valmiki
Valmiki
Valmiki is celebrated as the poet harbinger in Sanskrit literature. He is the author of the epic Ramayana, based on the attribution in the text of the epic itself. He is revered as the Adi Kavi, which means First Poet, for he discovered the first śloka i.e...
. The name Rama's Bridge or Rama Setu (Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
; setu: bridge) refers to the bridge built by the Vanara
Vanara
Vānara popularly refers to a group of ape-like humanoids in the Hindu epic Ramayana who were brave and inquisitive by nature. They possessed supernatural powers and could change their shapes...
(ape men) army of Lord Rama
Rama
Rama or full name Ramachandra is considered to be the seventh avatar of Vishnu in Hinduism, and a king of Ayodhya in ancient Indian...
in Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
mythology, which he used to reach Lanka
Lanka
Sri Lanka is the name given in Hindu mythology to the island fortress capital of the legendary king Ravana in the great Hindu epics, the Ramayana and the Mahabharata...
and rescue his wife Sita
SITA
SITA is a multinational information technology company specialising in providing IT and telecommunication services to the air transport industry...
from the Rakshasa
Rakshasa
A Rakshasa or alternatively rakshas, is a race of mythological humanoid beings or unrighteous spirit in Hindu and Buddhist religion...
king, Ravana
Ravana
' is the primary antagonist character of the Hindu legend, the Ramayana; who is the great king of Lanka. In the classic text, he is mainly depicted negatively, kidnapping Rama's wife Sita, to claim vengeance on Rama and his brother Lakshmana for having cut off the nose of his sister...
. The Ramayana attributes the building of this bridge to Rama
Rama
Rama or full name Ramachandra is considered to be the seventh avatar of Vishnu in Hinduism, and a king of Ayodhya in ancient Indian...
in verse 2-22-76, naming it as Setubandhanam, a name that persists till today.
The sea separating India and Sri Lanka is called Sethusamudram
Sethusamudram
Sethusamudram is the sea that separates Tamil Nadu, India, from Sri Lanka. It encompasses the Gulf of Mannar, the Palk Strait, and a shoal of islands and bays that separate them called Ram Setu...
meaning "Sea of the Bridge". Maps prepared by a Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
cartographer in 1747, available at the Tanjore Saraswathi Mahal Library
Saraswathi Mahal Library
Saraswathi Mahal Library is located in Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India. It is one of the oldest libraries in Asia, and has on display a rare collection of Palm leaf manuscripts and paper written in Tamil, Hindi, English, Telugu, Marathi, and a few other languages indigenous to India. The collection...
show this area as Ramancoil, a colloquial form of the Tamil Raman Kovil (or Rama's Temple). Another map of Mughal
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
India prepared by J. Rennel in 1788 retrieved from the same library called this area as "the area of the Rama Temple", referring to the temple dedicated to Lord Rama at Rameswaram. Many other maps in Schwartzberg's historical atlas and other sources such as travel texts by Marco Polo
Marco Polo
Marco Polo was a Venetian merchant traveler from the Venetian Republic whose travels are recorded in Il Milione, a book which did much to introduce Europeans to Central Asia and China. He learned about trading whilst his father and uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, travelled through Asia and apparently...
call this area by various names such as Sethubandha and Sethubandha Rameswaram.
The western world first encountered it in "historical works in the 9th century" by Ibn Khordadbeh
Ibn Khordadbeh
Abu'l Qasim Ubaid'Allah ibn Khordadbeh , author of the earliest surviving Arabic book of administrative geography, was a Persian geographer and bureaucrat of the 9th century...
in his Book of Roads and Kingdoms
Book of Roads and Kingdoms (ibn Khordadbeh)
The Book of Roads and Kingdoms is a 9th-century geography text by the Persian geographer Ibn Khordadbeh. It maps and describes the major trade routes of the time within the Muslim world, and discusses distant trading regions such as Japan, Korea, and China...
(ca. 850 CE), referring to it is Set Bandhai or "Bridge of the Sea". Later, Alberuni described it. The earliest map that calls this area by the name Adam's bridge was prepared by a British cartographer in 1804, probably referring to an Abrahamic legend, according to which Adam used the bridge to reach a mountain (identified with Adam's Peak
Adam's Peak
Sri Pada , is a tall conical mountain located in central Sri Lanka...
) in Sri Lanka, where he stood repentant on one foot for 1,000 years, leaving a large hollow mark resembling a footprint.
Location
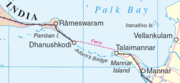
Pamban Island
Pamban Island , also known as Rameswaram Island, is an island located between peninsular India and Sri Lanka. The island is a part of India and is governed by the administration of Ramanathapuram district of the state of Tamil Nadu...
and ends at Sri Lanka's Mannar Island
Mannar Island
Mannar Island, formerly called Manar Island, is part of Mannar District, Sri Lanka. It is linked to the rest of Sri Lanka by a causeway.It has an area of about 50 square kilometres, mainly covered with vegetation and sand.Rama's Bridge or Rama Setu ,[1] is a chain of limestone shoals, between...
. Pamban Island is semi-connected to the Indian mainland by 2 km long Pamban Bridge
Pamban Bridge
The Pamban Bridge is a cantilever bridge on the Palk Strait connects Rameswaram on Pamban Island to mainland India. It refers to both the road bridge and the cantilever railway bridge, though primarily it means the latter. It was India's first sea bridge...
. Mannar Island is connected to mainland Sri Lanka by a causeway. The border between India and Sri Lanka is said to pass across one of the shoals constituting one of the shortest land borders in the world. Adam's bridge and neighbouring areas like Rameswaram, Dhanushkodi, Devipattinam and Thirupullani are mentioned in the context of various legends in Ramayana.
http://www.hinduonnet.com/thehindu/2002/06/15/stories/2002061503750500.htm.
Transportation and navigation

The Pamban Bridge
Pamban Bridge
The Pamban Bridge is a cantilever bridge on the Palk Strait connects Rameswaram on Pamban Island to mainland India. It refers to both the road bridge and the cantilever railway bridge, though primarily it means the latter. It was India's first sea bridge...
crossing the Pamban channel links Pamban Island with mainland India. It refers to both: a road bridge and a cantilever railway bridge. Small boats would go below the 2065 m long road bridge and the railway bridge would open up.
The problem in navigation exists because big ships can't travel in the shallow waters of the Pamban channel. Dredging in this channel would cost more than dredging a channel in the Rama Setu area, where the waters are comparatively deep and lesser earth would have to be dredged. Hence, in 2001, the Government of India approved a multi-million dollar Sethusamudram Shipping Canal Project that aims to create a ship channel across the Palk Bay cutting across Rama Setu. Various organizations have opposed the project based on religious, economic and environmental grounds and have sought the implementation of one of the alternative alignments considered during the earlier stages of the discussion.
A ferry
Ferry
A ferry is a form of transportation, usually a boat, but sometimes a ship, used to carry primarily passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo as well, across a body of water. Most ferries operate on regular, frequent, return services...
service linked Dhanushkodi in India with Talaimannar
Talaimannar
Talaimannar is a settlement in Sri Lanka located on the northwestern coast of Mannar Island.- Transport :Prior to the severe destructions by a cyclone in December 1964, it was the terminus of a ferry service to India across the very shallow Palk Bay...
in Sri Lanka. The service was part of the Indo-Ceylon Railway service during the British Rule. One could buy a railway ticket from Chennai
Chennai
Chennai , formerly known as Madras or Madarasapatinam , is the capital city of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, located on the Coromandel Coast off the Bay of Bengal. Chennai is the fourth most populous metropolitan area and the sixth most populous city in India...
to Colombo
Colombo
Colombo is the largest city of Sri Lanka. It is located on the west coast of the island and adjacent to Sri Jayawardenapura Kotte, the capital of Sri Lanka. Colombo is often referred to as the capital of the country, since Sri Jayawardenapura Kotte is a satellite city of Colombo...
, whereby people traveled by rail from Chennai to Pamban island, go by ferry to Talaimannar, and then go again by rail to Colombo. in 1964, a cyclone
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
completely destroyed Dhanushkodi, a train about to enter the station, the tracks and the pier and heavily damaged the shores of Palk Bay and Palk Strait. Dhanushkodi was not rebuilt and the train then finished at Rameswaram. There was a small ferry service from there to Talaimannar, but it has been suspended around 1982 because of the fighting between Sri Lankan government forces and the separatist LTTE
Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam
The Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam was a separatist militant organization formerly based in northern Sri Lanka. Founded in May 1976 by Vellupillai Prabhakaran, it waged a violent secessionist and nationalist campaign to create an independent state in the north and east of Sri Lanka for Tamil...
.
Geological evolution

According to V. Ram Mohan of the Centre of Natural Hazards and Disaster Studies of the University of Madras "reconstruction of the geological evolution of the island chain is a challenging task and has to be carried out based on circumstantial evidence". The lack of comprehensive field studies explains many of the uncertainties regarding the nature and origin of Adam's Bridge, which essentially consists of a series of parallel ledges of sandstone and conglomerates that are hard at the surface and grows coarse and soft as it descends to sandy banks.
Studies have variously described the structure as a chain of shoal
Shoal
Shoal, shoals or shoaling may mean:* Shoal, a sandbank or reef creating shallow water, especially where it forms a hazard to shipping* Shoal draught , of a boat with shallow draught which can pass over some shoals: see Draft...
s, coral reefs, a ridge formed in the region owing to thinning of the earth's crust, a double tombolo
Tombolo
A tombolo, from the Italian tombolo, derived from the Latin tumulus, meaning 'mound,' and sometimes translated as ayre , is a deposition landform in which an island is attached to the mainland by a narrow piece of land such as a spit or bar. Once attached, the island is then known as a tied island...
, a sand spit
Spit (landform)
A spit or sandspit is a deposition landform found off coasts. At one end, spits connect to land, and extend into the sea. A spit is a type of bar or beach that develops where a re-entrant occurs, such as at cove's headlands, by the process of longshore drift...
, or barrier islands. It has been reported that this bridge was formerly the world's largest tombolo
Tombolo
A tombolo, from the Italian tombolo, derived from the Latin tumulus, meaning 'mound,' and sometimes translated as ayre , is a deposition landform in which an island is attached to the mainland by a narrow piece of land such as a spit or bar. Once attached, the island is then known as a tied island...
before it was split into a chain of shoals by the rise in mean sea level few thousand years ago.
Based on satellite remote sensing data, but without actual field verification, Marine and Water Resources Group of Space Application Centre (SAC) of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) states that Adam's Bridge comprises 103 small patch reefs lying in a linear pattern with reef crest (flattened, emergent – especially during low tides – or nearly emergent segment of a reef), sand cays (accumulations of loose coral sands and beach rock) and intermittent deep channels. The coral reefs are designated by the different studies variously as ribbon and atoll reefs.
The geological process that gave rise to this structure has also been attributed to crustal downwarping, block faulting, and mantle plume activity by one study while another theory attributes it to continuous sand deposition and the natural process of sedimentation leading to the formation of a chain of barrier islands related to rising sea levels. Another theory affirms that the origin and linearity of the Adam's bridge may be due to the old shoreline – implying that the two landmasses of India and Sri Lanka were once connected – from where coral reefs evolved.
Another study explains the origin the structure due to longshore drift
Longshore drift
Longshore drift consists of the transportation of sediments along a coast at an angle to the shoreline, which is dependent on prevailing wind direction, swash and backwash. This process occurs in the littoral zone, and in or within close proximity to the surf zone...
ing currents which moved in an anticlockwise direction in the north and clockwise direction in the south of Rameswaram and Talaimannar. The sand was supposedly dumped in a linear pattern along the current shadow zone between Dhanushkodi and Talaimannar with later accumulation of corals over these linear sand bodies. In a diametrically opposing view, another group of geologists propose crustal thinning theory, block faulting and a ridge formed in the region owing to thinning and asserts that development of this ridge augmented the coral growth in the region and in turn coral cover acted as a `sand trapper'.
The tombolo model affirms a constant sediment source and a strong unidirectional or bi-directional (monsoonal) longshore current. One study tentatively concludes that there is insufficient evidence to indicate eustatic emergence and that the raised reef in south India probably results from a local uplift. Other studies also conclude that during periods of lowered sea level over the last 100,000 years, Adam's Bridge has provided an intermittent land connection between India and Sri Lanka, which according to famous ornithologists Sidney Dillon Ripley
Sidney Dillon Ripley
Sidney Dillon Ripley was an American ornithologist and wildlife conservationist. He served as Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution from 1964-1984.-Biography:...
and Bruce Beehler
Bruce Beehler
Dr. Bruce Beehler is an ornithologist and vice-president of Conservation International's Melanesia Center for Biodiversity Conservation ....
supports the vicariance model
Allopatric speciation
Allopatric speciation or geographic speciation is speciation that occurs when biological populations of the same species become isolated due to geographical changes such as mountain building or social changes such as emigration...
for speciation in some birds of the Indian Subcontinent.
Age
Geological Survey of India (GSI) carried out a special programme called “Project Rameswaram” that concluded that age data of corals indicate that the Rameswaram island has evolved since 125,000 years ago. Radiocarbon dating of samples in this study suggests that the domain between Rameswaram and Talaimannar may have thus been exposed sometime between 18,000 and 7,000 years ago. Thermoluminescence dating by GSI concludes that the sand dunes of Dhanushkodi to Adam's bridge started forming only about 500–600 years ago.Investigation by Centre for Remote Sensing (CRS) of Bharathidasan University
Bharathidasan University
Bharathidasan University is a university in the city of Tiruchirapalli, Tamil Nadu state, India. It has affiliated colleges in districts of the state, including Nagapattinam, Perambalur, Pudukkottai, Thanjavur, Tiruvarur and Tiruchirapalli. It is a recognised university, supported by the...
, Tiruchi, led by Professor S.M. Ramasamy dates the structure to 3,500 years. In the same study, carbon dating of some ancient beaches between Thiruthuraipoondi and Kodiyakarai shows the Thiruthuraipoondi beach dates back to 6,000 years and Kodiyakarai around 1,100 years ago. Another study suggests that the appearance of the reefs and other evidence indicate their recency, and a coral sample gives a radiocarbon age of 4020±160 years BP
Before Present
Before Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
Early surveys and dredging efforts

James Rennell
Major James Rennell, FRS was an English geographer, historian and a pioneer of oceanography.-Early life:Rennell was born near Chudleigh in Devon...
, who surveyed the region as a young officer in the late eighteenth century, suggested that a "navigable passage could be maintained by dredging the strait of Ramisseram [sic]". However little notice was given to his proposal, perhaps because it came from "so young and unknown an officer", and the idea was only revived 60 years later.
In 1823, Sir Arthur Cotton
Arthur Cotton
General Sir Arthur Thomas Cotton KCSI was a British general and irrigation engineer.Cotton devoted his life to the construction of irrigation and navigation canals throughout the British Empire in India, however, his dream was only partially realized, but he is still honored in parts of rural...
(then an Ensign
Ensign
An ensign is a national flag when used at sea, in vexillology, or a distinguishing token, emblem, or badge, such as a symbol of office in heraldry...
), was trusted with the responsibility of surveying the Pamban channel, which separates the Indian mainland from the island of Rameswaram and forms the first link of Ram Setu. Geological evidence indicates that this was at one point bridged by a land connection, and some temple records suggest that the connection was broken by violent storms in 1480. Cotton suggested that the channel be dredge
Dredge
Dredging is an excavation activity or operation usually carried out at least partly underwater, in shallow seas or fresh water areas with the purpose of gathering up bottom sediments and disposing of them at a different location...
d to enable passage of ships, but nothing was done till 1828, when some rocks were blasted and removed under the direction of Major Sim.
A more detailed marine survey of Ram Setu was undertaken in 1837 by Lieutenants F. T. Powell, Ethersey, Grieve and Christopher along with draughtsman Felix Jones, and operations to dredge the channel were recommenced the next year. However these, and subsequent efforts in the 19th century, did not succeed in keeping the passage navigable for any vessels except those with a light draft.
Sethusamudram shipping canal project
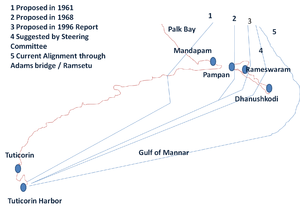
In 2001, the Government of India
Government of India
The Government of India, officially known as the Union Government, and also known as the Central Government, was established by the Constitution of India, and is the governing authority of the union of 28 states and seven union territories, collectively called the Republic of India...
approved a multi-million dollar Sethusamudram Shipping Canal Project
Sethusamudram Shipping Canal Project
Sethusamudram Ship Channel Project proposes linking the Palk Bay and the Gulf of Mannar between India and Sri Lanka by creating a shipping channel through the shallow sea sometimes called Setu Samudram, and through the chain of islands variously known as Ramar Palam , ram sethu and Adam's Bridge...
that aims to create a ship channel across the Palk Strait
Palk Strait
Palk Strait is a strait between the Tamil Nadu state of India and the Mannar district of the Northern Province of the island nation of Sri Lanka. It connects the Bay of Bengal in the northeast with the Palk Bay and thence with the Gulf of Mannar in the southwest. The strait is wide. Several...
by dredging the shallow ocean floor near Dhanushkodi. The channel is expected to cut over 400 km (nearly 30 hours of shipping time) off the voyage around the island of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
. This proposed channel's current alignment requires dredging through Rama's Bridge.
Political parties including the Bharatiya Janata Party
Bharatiya Janata Party
The Bharatiya Janata Party ,; translation: Indian People's Party) is one of the two major political parties in India, the other being the Indian National Congress. Established in 1980, it is India's second largest political party in terms of representation in the parliament...
(BJP), All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam is a state political party in the states of Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry, India. The party was founded by M. G. Ramachandran and is now headed by J. Jayalalithaa. The party headquarters is in Royapettah, Chennai, and was gifted to the party in 1986 by its...
(AIADMK), Rashtriya Janata Dal
Rashtriya Janata Dal
The Rashtriya Janata Dal is a political party in India, based in the state of Bihar. The party was founded in 1997 by Laloo Prasad Yadav. The party came about as a result of Lalu Prasad Yadav, ex-president of Janata Dal, being evicted by Sharad Yadav, the then president, on corruption charges ...
(RJD), Janata Dal (Secular)
Janata Dal (Secular)
The Janata Dal is a Centre-left ಕನ್ನಡ: ಜನತಾ ದಳIndian political party led by former Prime Minister of India H.D. Deve Gowda.The party recognized as state party in the states of Karnataka and Kerala . It was formed in July 1999 by the split of Janata Dal party. It has political presence mainly in...
(JD(S)) and some Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
organizations oppose dredging through the shoal on religious grounds — Rama's Bridge being popularly identified as the causeway described in the Ramayana
Ramayana
The Ramayana is an ancient Sanskrit epic. It is ascribed to the Hindu sage Valmiki and forms an important part of the Hindu canon , considered to be itihāsa. The Ramayana is one of the two great epics of India and Nepal, the other being the Mahabharata...
— and suggest using an alternate alignment for the channel that avoids damage to Adam's Bridge. The state and central government have opposed such changes, with Union Shipping Minister T R Baalu, who belongs to the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam
Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam is a state political party in the states of Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry, India. It is a Dravidian party founded by C. N. Annadurai as a breakaway faction from the Dravidar Kazhagam headed by Periyar...
and a strong supporter of the project, saying the current proposal was well scrutinised for economic viability and environmental sustainability and that there were no other environmentally feasible alternatives.
Opposition to dredging through this causeway also stems from concerns over its impact on the area's ecology and marine wealth, potential loss of thorium
Thorium
Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder....
deposits in the area, and increased risk of damage due to tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
s. Some organizations are completely opposing this project on economical and environmental grounds and claim proper scientific studies were not conducted before undertaking this project.
Controversies
Certain historical inscriptions, old travel guides, old dictionary references and some old maps have been said to reinforce a religious and geographical belief that this is an ancient bridge.(see RamayanaRamayana
The Ramayana is an ancient Sanskrit epic. It is ascribed to the Hindu sage Valmiki and forms an important part of the Hindu canon , considered to be itihāsa. The Ramayana is one of the two great epics of India and Nepal, the other being the Mahabharata...
). In 2007 the Sri Lankan Tourism Development Authority sought to promote religious tourism from Hindu piligrims in India by including the phenomenon as one of the points on its "Ramayana Trail", celebrating the legend of Prince Rama. Sri Lankan historians condemn the undertaking as "a gross distortion of Sri Lankan history". Vaishnava News Network and some other U.S.-based news services suggested that they had discovered the remains of the bridge built by Rama and his Vanara
Vanara
Vānara popularly refers to a group of ape-like humanoids in the Hindu epic Ramayana who were brave and inquisitive by nature. They possessed supernatural powers and could change their shapes...
army that is referred to in the Ramayana
Ramayana
The Ramayana is an ancient Sanskrit epic. It is ascribed to the Hindu sage Valmiki and forms an important part of the Hindu canon , considered to be itihāsa. The Ramayana is one of the two great epics of India and Nepal, the other being the Mahabharata...
, and that it was not a natural formation, basing their claim on 2002 NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
satellite footage. NASA distanced itself from the claims saying that what had been captured was nothing more than a 30-km-long, naturally occurring chain of sandbanks. It also clarified that, "The images reproduced on the websites may well be ours, but their interpretation is certainly not ours. [...] Remote sensing images or photographs from orbit cannot provide direct information about the origin or age of a chain of islands, and certainly cannot determine whether humans were involved in producing any of the patterns seen."
A team from the Centre for Remote Sensing (CRS) of Bharathidasan University
Bharathidasan University
Bharathidasan University is a university in the city of Tiruchirapalli, Tamil Nadu state, India. It has affiliated colleges in districts of the state, including Nagapattinam, Perambalur, Pudukkottai, Thanjavur, Tiruvarur and Tiruchirapalli. It is a recognised university, supported by the...
, Tiruchi led by Professor S.M. Ramasamy in 2003 said "the land/beaches were formed between Ramanathapuram and Pamban because of the long shore drifting currents which moved in an anti-clockwise direction in the north and clockwise direction in the south of Rameswaram and Talaimannar about 3,500 years ago." and, "as the carbon dating of the beaches roughly matches the dates of Ramayana, its link to the epic needs to be explored". A former director of the Geological Survey of India
Geological Survey of India
Geological Survey of India , established in 1851 is a government organization in India which is an attached office to the Ministry of Mines of Union Government of India for conducting geological surveys and studies. It is one of the oldest of such organizations in the world and the second oldest...
, S. Badrinarayanan, claims that such a natural formation would be impossible. He justifies the same by the presence of a loose sand layer under corals for the entire stretch. Corals normally form above rocks. He feels that thorough analysis was not conducted by the Geological Survey of India before undertaking the SSCP project. Government of India, in an affidavit in the Supreme Court of India
Supreme Court of India
The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial forum and final court of appeal as established by Part V, Chapter IV of the Constitution of India...
, said that there is no historical proof of the bridge being built by Rama. In connection with the canal project, the Madras High Court
Madras High Court
The Madras High Court is a senior court located at Chennai , in India. The court buildings, which are believed to be the second largest judicial complex in the world, are located near the beach, in one of the city's major business districts....
in its verdict stated that the Rama Sethu is a man-made structure.
Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
belief is that the bridge was created by Shri Rama
Rama
Rama or full name Ramachandra is considered to be the seventh avatar of Vishnu in Hinduism, and a king of Ayodhya in ancient Indian...
and Shri Lakshman
Lakshmana
Lakshmana was the brother and close companion of Rama, and himself a hero in the famous epic Ramayana...
with the assistance of Lord Hanuman and the 'monkey army' to reach Lanka
Lanka
Sri Lanka is the name given in Hindu mythology to the island fortress capital of the legendary king Ravana in the great Hindu epics, the Ramayana and the Mahabharata...
in order to find Shri Rama's wife Sita
SITA
SITA is a multinational information technology company specialising in providing IT and telecommunication services to the air transport industry...
who was kidnapped by Ravana
Ravana
' is the primary antagonist character of the Hindu legend, the Ramayana; who is the great king of Lanka. In the classic text, he is mainly depicted negatively, kidnapping Rama's wife Sita, to claim vengeance on Rama and his brother Lakshmana for having cut off the nose of his sister...
. A 2007 publication of the National Remote Sensing Agency said that the structure "may be man-made", contradicting the report from the Archaeological Survey of India which found no evidence for it being man-made. In a 2008 court case, a spokesman for the government stated "So where is the Setu? We are not destroying any bridge. There is no bridge. It was not a man-made structure. It may be a superman-made structure, but the same superman had destroyed it. That is why for centuries nobody mentioned anything about it. It (Ram Setu) has become an object of worship only recently,".
See also
- Pamban channel
- RamayanaRamayanaThe Ramayana is an ancient Sanskrit epic. It is ascribed to the Hindu sage Valmiki and forms an important part of the Hindu canon , considered to be itihāsa. The Ramayana is one of the two great epics of India and Nepal, the other being the Mahabharata...
- Rama Setu (Ramayana)
- Lord Rama
- Kumari KandamKumari KandamKumari Kandam is the name of a supposed sunken landmass referred to in existing ancient Tamil literature...
- Bimini RoadBimini RoadThe Bimini Road, sometimes called the Bimini Wall, is an underwater rock formation near North Bimini island in the Bahamas. The Road consists of a -long northeast-southwest linear feature composed of roughly rectangular to subrectangular limestone blocks....

