
Quantum concentration
Encyclopedia
The quantum concentration nQ is the particle concentration
(i.e. the number of particles per unit volume) of a system where the interparticle distance
is equal to the thermal de Broglie wavelength or equivalently when the wavefunction
s of the particles are touching but not overlapping.
Quantum effects become appreciable when the particle concentration is greater than or equal to the quantum concentration, which is defined as: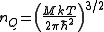
As the quantum concentration depends on temperature, high temperatures will put most systems in the classical limit unless they have a very high density e.g. a White dwarf
.
Particle density
The particle density or true density of a particulate solid or powder, is the density of the particles that make up the powder, in contrast to the bulk density, which measures the average density of a large volume of the powder in a specific medium .The particle density is a relatively well-defined...
(i.e. the number of particles per unit volume) of a system where the interparticle distance
Mean inter-particle distance
Mean inter-particle distance is the mean distance between microscopic particles in a macroscopic body.-Ambiguity:...
is equal to the thermal de Broglie wavelength or equivalently when the wavefunction
Wavefunction
Not to be confused with the related concept of the Wave equationA wave function or wavefunction is a probability amplitude in quantum mechanics describing the quantum state of a particle and how it behaves. Typically, its values are complex numbers and, for a single particle, it is a function of...
s of the particles are touching but not overlapping.
Quantum effects become appreciable when the particle concentration is greater than or equal to the quantum concentration, which is defined as:
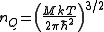
- where:
- M is the mass of the particles in the system
- k is the Boltzmann constant
- T is the temperature as measured in kelvinKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s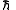 is the reduced Planck constantPlanck constantThe Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
is the reduced Planck constantPlanck constantThe Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
As the quantum concentration depends on temperature, high temperatures will put most systems in the classical limit unless they have a very high density e.g. a White dwarf
White dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
.

