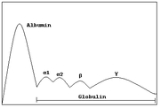
Protein electrophoresis
Overview
Gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge and or size and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge...
(in short gel electrophoresis, PAGE, or SDS-electrophoresis, free flow electrophoresis, electrofocusing, isotachophoresis
Isotachophoresis
Isotachophoresis is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate charged particles. It is a further development of electrophoresis. It is a powerful separation technique using a discontinuous electrical field to create sharp boundaries between the sample constituents.In conventional...
, affinity electrophoresis
Affinity electrophoresis
Affinity electrophoresis is a general name for many analytical methods used in biochemistry and biotechnology. Both qualitative and quantitative information may be obtained through affinity electrophoresis. The methods include the so-called mobility shift electrophoresis, charge shift...
, immunoelectrophoresis
Immunoelectrophoresis
Immunoelectrophoresis is a general name for a number of biochemical methods for separation and characterization of proteins based on electrophoresis and reaction with antibodies. All variants of immunoelectrophoresis require immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies reacting with the proteins to be...
, counterelectrophoresis, and capillary electrophoresis
Capillary electrophoresis
Capillary electrophoresis , also known as capillary zone electrophoresis , can be used to separate ionic species by their charge and frictional forces and hydrodynamic radius. In traditional electrophoresis, electrically charged analytes move in a conductive liquid medium under the influence of an...
). Each method has many variations with individual advantages and limitations.
Unanswered Questions

