
Proca action
Encyclopedia
In physics
, in the area of field theory, the Proca action describes a mass
ive spin
-1 field
of mass m in Minkowski spacetime. The field involved is a real vector field
A. The Lagrangian density is given by:
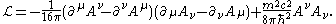
The above presumes the metric signature
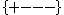 . Here,
. Here,  is the speed of light
is the speed of light
and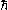 is the reduced Planck constant. In the dimensionless units
is the reduced Planck constant. In the dimensionless units
commonly employed in theoretical physics, these may both be taken to be one.
The Euler-Lagrange equation
of motion for this case, also called the Proca equation, is:
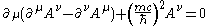
which is equivalent to the conjunction of
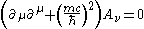
with

which is the Lorenz gauge condition
. The Proca equation is closely related to the Klein-Gordon equation
.
The Proca action is the gauge-fixed version of the Stueckelberg action via the Higgs mechanism
. Quantizing the Proca action requires the use of second class constraints
.
The Proca action is named after Romanian physicist Alexandru Proca
.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, in the area of field theory, the Proca action describes a mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
ive spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
-1 field
Field (physics)
In physics, a field is a physical quantity associated with each point of spacetime. A field can be classified as a scalar field, a vector field, a spinor field, or a tensor field according to whether the value of the field at each point is a scalar, a vector, a spinor or, more generally, a tensor,...
of mass m in Minkowski spacetime. The field involved is a real vector field
Vector field
In vector calculus, a vector field is an assignmentof a vector to each point in a subset of Euclidean space. A vector field in the plane for instance can be visualized as an arrow, with a given magnitude and direction, attached to each point in the plane...
A. The Lagrangian density is given by:
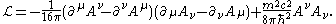
The above presumes the metric signature
Metric signature
The signature of a metric tensor is the number of positive and negative eigenvalues of the metric. That is, the corresponding real symmetric matrix is diagonalised, and the diagonal entries of each sign counted...
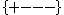 . Here,
. Here,  is the speed of light
is the speed of lightSpeed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
and
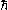 is the reduced Planck constant. In the dimensionless units
is the reduced Planck constant. In the dimensionless unitsNatural units
In physics, natural units are physical units of measurement based only on universal physical constants. For example the elementary charge e is a natural unit of electric charge, or the speed of light c is a natural unit of speed...
commonly employed in theoretical physics, these may both be taken to be one.
The Euler-Lagrange equation
Euler-Lagrange equation
In calculus of variations, the Euler–Lagrange equation, Euler's equation, or Lagrange's equation, is a differential equation whose solutions are the functions for which a given functional is stationary...
of motion for this case, also called the Proca equation, is:
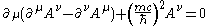
which is equivalent to the conjunction of
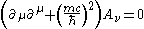
with

which is the Lorenz gauge condition
Lorenz gauge condition
In electromagnetism, the Lorenz gauge or Lorenz gauge condition is a partial gauge fixing of the electromagnetic vector potential. The condition is that \partial_\mu A^\mu=0...
. The Proca equation is closely related to the Klein-Gordon equation
Klein-Gordon equation
The Klein–Gordon equation is a relativistic version of the Schrödinger equation....
.
The Proca action is the gauge-fixed version of the Stueckelberg action via the Higgs mechanism
Higgs mechanism
In particle physics, the Higgs mechanism is the process in which gauge bosons in a gauge theory can acquire non-vanishing masses through absorption of Nambu-Goldstone bosons arising in spontaneous symmetry breaking....
. Quantizing the Proca action requires the use of second class constraints
Second class constraints
In a constrained Hamiltonian system, a dynamical quantity is second class if its Poisson bracket with at least one constraint is nonvanishing...
.
The Proca action is named after Romanian physicist Alexandru Proca
Alexandru Proca
Alexandru Proca was a Romanian physicist who studied and worked in France. He developed the vector meson theory of nuclear forces and the relativistic quantum field equations that bear his name for the massive, vector spin-1 mesons...
.

