
Power supply rejection ratio
Encyclopedia
In electronics, power supply rejection ratio or PSRR is a term widely used in the electronic amplifier
(especially operational amplifier
) or voltage regulator
datasheets; used to describe the amount of noise
from a power supply
that a particular device can reject.
s. An ideal op-amp would have infinite PSRR. The output voltage will depend on the feedback circuit, as is the case of regular input offset voltages. But testing is not confined to DC
(zero frequency); often an operational amplifier will also have its PSRR given at various frequencies (in which case the ratio is one of RMS
amplitudes of sinewaves present at a power supply compared with the output, with gain taken into account).
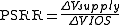
For example: an amplifier with a PSRR of 100 dB in a circuit to give 40 dB closed-loop gain
would allow about 1 millivolt of power supply ripple to be superimposed on the output for every 1 volt
of ripple in the supply. This is because
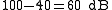 .
.
And since thats 60 dB of rejection, the sign is negative so:
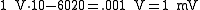
Note:
Electronic amplifier
An electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude...
(especially operational amplifier
Operational amplifier
An operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output...
) or voltage regulator
Voltage regulator
A voltage regulator is an electrical regulator designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. A voltage regulator may be a simple "feed-forward" design or may include negative feedback control loops. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components...
datasheets; used to describe the amount of noise
Noise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
from a power supply
Power supply
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
that a particular device can reject.
Definition
The PSRR is defined as the ratio of the change in supply voltage to the equivalent (differential) input voltage it produces in the op-amp, often expressed in decibelDecibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s. An ideal op-amp would have infinite PSRR. The output voltage will depend on the feedback circuit, as is the case of regular input offset voltages. But testing is not confined to DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
(zero frequency); often an operational amplifier will also have its PSRR given at various frequencies (in which case the ratio is one of RMS
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
amplitudes of sinewaves present at a power supply compared with the output, with gain taken into account).
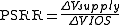
For example: an amplifier with a PSRR of 100 dB in a circuit to give 40 dB closed-loop gain
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
would allow about 1 millivolt of power supply ripple to be superimposed on the output for every 1 volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
of ripple in the supply. This is because
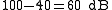 .
.And since thats 60 dB of rejection, the sign is negative so:
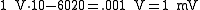
Note:
- The PSRR doesn't necessarily have the same poles as A(s), the open-loop gain of the op-amp, but generally tends to also worsen with increasing frequency (e.g. http://focus.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/opa2277.pdf).
- For amplifiers with both positive and negative power supplies (with respect to earth, as op-amps often have), the PSRR for each supply voltage may be separately specified (sometimes written: PSRR+ and PSRR-), but normally the PSRR is tested with opposite polarity signals applied to both supply rails at the same time (otherwise the common-mode rejection ratioCommon-mode rejection ratioThe common-mode rejection ratio of a differential amplifier is the tendency of the devices to reject the input signals common to both input leads...
(CMRR) will affect the measurement of the PSRR). - For voltage regulators the PSRR is occasionally quoted (confusingly; to refer to output voltage change ratios), but often the concept is transferred to other terms relating changes in output voltage to input: Ripple Rejection (RR) for low frequencies, Line Transient Response for high frequencies, and Line Regulation for DC.
- Sometimes kSVR (or simply SVR) is used to denote the Power Supply Rejection Ratio (e.g. http://focus.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/tl071.pdf)

