
Power electronics
Encyclopedia
Power electronics is the application of solid-state electronics for the control and conversion of electric power.
The first very high power electronic devices were mercury arc valve
s. In modern systems the conversion is performed with semiconductor
switching devices such as diode
s, thyristors and transistors. In contrast to electronic systems concerned with transmission and processing of signals and data, in power electronics substantial amounts of electrical energy are processed. An AC/DC
converter (rectifier
) is the most typical power electronics device found in many consumer electronic devices, e.g. television
sets, personal computer
s, battery charger
s, etc. The power range is typically from tens of watt
s to several hundred watts. In industry
the most common application is the variable speed drive (VSD) that is used to control an induction motor
. The power range of VSDs start from a few hundred watts and end at tens of megawatts.
The power conversion systems can be classified according to the type of the input and output power
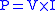 ). From this, one can see that the losses of a power device are at a minimum when the voltage across it is zero (the device is in the On-State) or when no current flows through it (Off-State). Therefore, a power electronic converter is built around one (or more) device operating in switching mode (either On or Off). With such a structure, the energy is transferred from the input of the converter to its output by bursts.
). From this, one can see that the losses of a power device are at a minimum when the voltage across it is zero (the device is in the On-State) or when no current flows through it (Off-State). Therefore, a power electronic converter is built around one (or more) device operating in switching mode (either On or Off). With such a structure, the energy is transferred from the input of the converter to its output by bursts.
Introduction
Power electronic converters can be found wherever there is a need to modify a form of electrical energy (i.e. change its voltage, current or frequency). The power range of these converters is from some milliwatts (as in a mobile phone) to hundreds of megawatts (e.g. in a HVDC transmission system). With "classical" electronics, electrical currents and voltage are used to carry information, whereas with power electronics, they carry power. Thus, the main metric of power electronics becomes the efficiency.The first very high power electronic devices were mercury arc valve
Mercury arc valve
A mercury-arc valve is a type of electrical rectifier used for converting high-voltage or high-current alternating current into direct current . Rectifiers of this type were used to provide power for industrial motors, electric railways, streetcars, and electric locomotives, as well as for...
s. In modern systems the conversion is performed with semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
switching devices such as diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
s, thyristors and transistors. In contrast to electronic systems concerned with transmission and processing of signals and data, in power electronics substantial amounts of electrical energy are processed. An AC/DC
AC/DC (electricity)
The description AC/DC refers to equipment designed to be operate on either alternating current or direct current . This term typically describes certain types of vacuum tube radio or television receivers. AC/DC equipment was necessary because in the early days of vacuum tubes, some regions were...
converter (rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
) is the most typical power electronics device found in many consumer electronic devices, e.g. television
Television
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
sets, personal computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
s, battery charger
Battery charger
A battery charger is a device used to put energy into a secondary cell or rechargeable battery by forcing an electric current through it.The charge current depends upon the technology and capacity of the battery being charged...
s, etc. The power range is typically from tens of watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s to several hundred watts. In industry
Industry
Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,...
the most common application is the variable speed drive (VSD) that is used to control an induction motor
Induction motor
An induction or asynchronous motor is a type of AC motor where power is supplied to the rotor by means of electromagnetic induction. These motors are widely used in industrial drives, particularly polyphase induction motors, because they are robust and have no brushes...
. The power range of VSDs start from a few hundred watts and end at tens of megawatts.
The power conversion systems can be classified according to the type of the input and output power
- AC to DC (rectifierRectifierA rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
) - DC to AC (inverterInverter (electrical)An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current ; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits....
) - DC to DC (DC to DC converterDC to DC converterA DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit which converts a source of direct current from one voltage level to another. It is a class of power converter.- Usage :...
) - AC to AC (AC to AC converterAC/AC converterA solid-state AC/AC converter converts an AC waveform such as the mains supply, to another AC waveform, where the output voltage and frequency can be set arbitrarily.AC/AC converters can be categorized into* Converters with a DC-link.* Cycloconverters...
)
Switching
As efficiency is at a premium in a power electronic converter, the losses that a power electronic device generates should be as low as possible. The instantaneous dissipated power of a device is equal to the product of the voltage across the device and the current through it (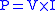 ). From this, one can see that the losses of a power device are at a minimum when the voltage across it is zero (the device is in the On-State) or when no current flows through it (Off-State). Therefore, a power electronic converter is built around one (or more) device operating in switching mode (either On or Off). With such a structure, the energy is transferred from the input of the converter to its output by bursts.
). From this, one can see that the losses of a power device are at a minimum when the voltage across it is zero (the device is in the On-State) or when no current flows through it (Off-State). Therefore, a power electronic converter is built around one (or more) device operating in switching mode (either On or Off). With such a structure, the energy is transferred from the input of the converter to its output by bursts.Applications
Power electronic systems are found in virtually every electronic device. For example:- DC/DC converters are used in most mobile devices (mobile phones, PDA etc.) to maintain the voltage at a fixed value whatever the voltage level of the battery is. These converters are also used for electronic isolation and power factorPower factorThe power factor of an AC electric power system is defined as the ratio of the real power flowing to the load over the apparent power in the circuit, and is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1 . Real power is the capacity of the circuit for performing work in a particular time...
correction. - AC/DC converters (rectifierRectifierA rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
s) are used every time an electronic device is connected to the mains (computer, television etc.). These may simply change AC to DC or can also change the voltage level as part of their operation. - AC/AC converters are used to change either the voltage level or the frequency (international power adapters, light dimmer). In power distribution networks AC/AC converters may be used to exchange power between utility frequencyUtility frequencyThe utility frequency, line frequency or mains frequency is the frequency at which alternating current is transmitted from a power plant to the end-user. In most parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas it is typically 60 Hz...
50 Hz and 60 Hz power grids. - DC/AC converters (invertersInverter (electrical)An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current ; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits....
) are used primarily in UPSUninterruptible power supplyAn uninterruptible power supply, also uninterruptible power source, UPS or battery/flywheel backup, is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source, typically mains power, fails...
or renewable energy systemsRenewable Energy SystemsThe RES Group is a UK-based renewable energy project developer. Its core business is to develop, construct and operate large-scale, grid-connected renewable energy projects worldwide. As part of the Sir Robert McAlpine group, RES is active in the wind, biomass and solar energy sectors...
or emergency lighting systemsEmergency lightAn emergency light is a battery-backed lighting device that comes on automatically when a building experiences a power outage. Emergency lights are standard in new commercial and high occupancy residential buildings, such as college dormitories...
. When mains power is available, it will charge the DC battery. If the mains fails, an inverter will be used to produce AC electricity at mains voltage from the DC battery.

