
Powdery mildew
Encyclopedia

Fungus
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds , as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteria...
disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of fungi in the order Erysiphales
Erysiphales
Erysiphales are an order of ascomycete fungi. The order contains one family, Erysiphaceae. Many of them cause plant diseases called powdery mildew.-Systematics:The order contains one family , 28 genera and approximately 100 species...
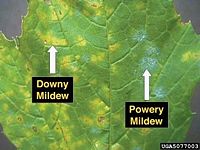
. It is one of the easier diseases to spot, as its symptoms are quite distinctive. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems. The lower leaves are the most affected, but the mildew can appear on any above-ground part of the plant. As the disease progresses, the spots get larger and denser as large numbers of asexual spore
Spore
In biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
s are formed, and the mildew may spread up and down the length of the plant.
Powdery mildews of various plants
Powdery mildew of grape

Uncinula necator
Uncinula necator is a fungus that causes powdery mildew of grape. It is a common pathogen of Vitis species, including the wine grape, Vitis vinifera. The fungus is believed to have originated in North America. European varieties of Vitis vinifera are more or less susceptible to this fungus...
(or Uncinula necator) causes powdery mildew of grapes. It produces common odors such as 1-octen-3-one and (Z)-1,5-octadien-3-one.
Summary:
Blumeria graminisBlumeria graminis
Blumeria graminis is a fungus that causes powdery mildew on grasses, including cereals . It is the only species in the genus Blumeria. It has also been called Erysiphe graminis and Oidium monilioides or Oidium tritici.-Systematics:Previously B...
f. sp. tritici, causes powdery mildew of wheat. Powdery mildew of wheat is relatively easy to diagnose due to the characteristic little white spots of cotton like mycelia. These can appear on the upper and lower epidermis of the leaves. As the disease progresses they become a light tan color. Blumeria graminis
Blumeria graminis
Blumeria graminis is a fungus that causes powdery mildew on grasses, including cereals . It is the only species in the genus Blumeria. It has also been called Erysiphe graminis and Oidium monilioides or Oidium tritici.-Systematics:Previously B...
f. sp. tritici is an obligate parasite which means it only grows on living tissue. Though present throughout wheat growing regions, it especially favors the eastern seaboard of the United States as well as coastal regions of the United Kingdom.
Hosts and Symptoms:
Triticum sp. (wheat) is the only host of Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici. Signs on the foliage of wheat are white, powdery mycelium and conidia. As the disease progresses, the patches turn gray and small dark black or brown cleistothecia form in the mycelium mass. Symptoms progress from lower to upper leaves. Symptoms of powdery mildew are chlorotic areas surrounding the infected areas. The lower leaf surface corresponding to the mycelial mat will also show chlorosis. Lower leaves are commonly the most infected because of higher humidity around them.Disease Cycle:
Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici has a polycyclic life cycle typical of its phylum, Ascomycota. Powdery mildew of wheat overwinters as cleistothecia dormant in plant debris. Under warmer conditions, however, the fungus can overwinter as conidia or mycelium on living host plants. It can persist between seasons most likely as ascospores in wheat debris left in the field. Ascospores are produced from the cleistothecia and are wind dispersed during the growing season. These spores, as well as conidia, serve as the primary inoculum. Neither spore requires free water to germinate, only high relative humidity.. Wheat powdery mildew thrives in cool humid conditions and cloudy weather increases chances of disease.When conidia land on a wheat leaf’s hydrophobic surface cuticle, they release proteins which facilitate active transport of lightweight substances between leaf and fungus even before germination. This process helps Blumeria recognize that it is on the correct host and directs growth of the germ tube.
Both ascospores and conidia germinate directly with a germ tube. Conidia can recognize the host plant and within one minute of initial contact, the direction of germ tube growth is determined. The development of appressoria then begins infection following the growth of a germ tube. After initial infection, the fungus produces haustoria inside of the wheat cells and mycelium grows on the plant’s outer surface. Powdery mildew of wheat produces conidia during the growing season as often as every 7 to 10 days. These conidia function as secondary inoculum as growth and reproduction repeat throughout the growing season.
Environment:
Powdery mildew of wheat thrives in cool, humid climates and proliferates in cloudy weather conditions. The pathogen can also be an issue in drier climates if wheat fields are irrigated. Ideal temperatures for growth and reproduction of the pathogen are between 60 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit with growth ceasing above 77 degrees Fahrenheit. Dense, genetically similar plantings provide opportune conditions for growth of powdery mildew.Management:
Controlling the disease involves eliminating conducive conditions as much as possible by altering planting density and carefully timing applications and rates of nitrogenNitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
. Since nitrogen fertilizer
Fertilizer
Fertilizer is any organic or inorganic material of natural or synthetic origin that is added to a soil to supply one or more plant nutrients essential to the growth of plants. A recent assessment found that about 40 to 60% of crop yields are attributable to commercial fertilizer use...
s encourage dense leafy growth, nitrogen should be applied at precise rates, less than 70 pounds per acre, to control decrease severity. Crop rotation with non-host plants is another way to keep mildew infection to a minimum, however the aerial nature of conidia and ascospore
Ascospore
An ascospore is a spore contained in an ascus or that was produced inside an ascus. This kind of spore is specific to fungi classified as ascomycetes ....
dispersal makes it of limited use. Wheat powdery mildew can also be controlled by eliminating the presence of volunteer wheat in agricultural fields as well as tilling under crop residues.
Chemical control is possible with fungicides such as triademefon and propiconazole
Propiconazole
Propiconazole is a triazole fungicide, also known as a DMI, or demethylation inhibiting fungicide due to its binding with and inhibiting the 14-alpha demethylase enzyme from demethylating a precursor to ergosterol. Without this demethylation step, the ergosterols are not incorporated into the...
. Another chemical treatment involves treating wheat with a silicon solution or calcium silicate slag. Silicon helps the plant cells defend against fungal attack by degrading haustoria and by producing callose and papilla. With silicon treatment, epidermal cells are less susceptible to powdery mildew of wheat.
The most effective way to control wheat powdery mildew is through genetic resistance, using R genes (resistance genes) to prevent infection. There are at least 25 loci on the wheat genome that encode resistance to powdery mildew. If the particular variety of wheat has only one loci for resistance, the pathogen may be controlled only for a couple years. If, however, the variety of wheat has multiple loci for resistance, the crop may be protected for around 15 years. Because finding these loci can be difficult and time consuming, molecular markers are used to facilitate combining resistant genomes. One organization working towards identifying these molecular markers is the Coordinated Agricultural Project for Wheat. With these markers established, researchers will then be able to determine the most effective combination of resistance genes.
Importance:
Powdery mildew can be found in all wheat growing areas of the United States but usually will be most severe in the east and southeast. It is more common in areas with a humid or semi-arid environment where wheat is grown. Powdery mildew has become a more important disease in some areas because of increased application of nitrogen fertilizer, which favors the development of the fungus. Severe symptoms of powdery mildew can cause stunting of wheat. If unmanaged, this disease can reduce yields significantly by reducing photosynthetic areas and causes non-seed producing tillers. Powdery mildew causes reduced kernel size and lower yields. The sooner powdery mildew begins to develop and how high on the plant it develops by flowering the larger the yield loss. Yield Losses up to 45 percent have been shown in Ohio on susceptible varieties when plants are infected early and weather favors disease.Powdery mildew of onions
The fungus causing powdery mildew of onions is Leveillula tauricaLeveillula taurica
Leveillula taurica is a plant pathogen.- External links :* *...
(also known by its anamorph name, Oidiopsis taurica). It also infects the artichoke
Artichoke
-Plants:* Globe artichoke, a partially edible perennial thistle originating in southern Europe around the Mediterranean* Jerusalem artichoke, a species of sunflower with an edible tuber...
.
Powdery mildew of apples and pears
Podosphaera leucotrichaPodosphaera leucotricha
Podosphaera leucotricha is a plant pathogen.- External links :* *...
is a fungus that can cause powdery mildew of apple
Apple
The apple is the pomaceous fruit of the apple tree, species Malus domestica in the rose family . It is one of the most widely cultivated tree fruits, and the most widely known of the many members of genus Malus that are used by humans. Apple grow on small, deciduous trees that blossom in the spring...
s and pear
Pear
The pear is any of several tree species of genus Pyrus and also the name of the pomaceous fruit of these trees. Several species of pear are valued by humans for their edible fruit, but the fruit of other species is small, hard, and astringent....
s.
Powdery mildew of gourds and melons
Podosphaera fuscaPodosphaera fusca
Podosphaera fusca is a plant pathogen. It is the principal cause of powdery mildew in melons and gourds.- External links :* *...
is a fungus that can cause powdery mildew of Curcurbits
Cucurbitaceae
The plant family Cucurbitaceae consists of various squashes, melons, and gourds, including crops such as cucumber, pumpkins, luffas, and watermelons...
: cucumbers, squashes (including pumpkins), luffas, melons and watermelons.
Powdery mildew in lilacs
Microsphaera syringae is a fungus that can cause powdery mildew in lilacLilac
Syringa is a genus of about 20–25 species of flowering woody plants in the olive family , native to woodland and scrub from southeastern Europe to eastern Asia, and widely and commonly cultivated in temperate areas elsewhere....
.
Powdery mildew in strawberry
Podosphaera aphanis is the cause of powdery mildew in strawberries and other Rosaceae like Geum rivale (the Water Avens)Powdery mildew on tree leaves
Sawadaea tulasneiSawadaea tulasnei
Sawadaea tulasnei is a form of Powdery mildew is a species of fungus in the family Erysiphaceae.This fungus attacks the leaves of the Acer platanoides in North America, and in Great Britain and/or Ireland, Acer palmatum .-Synonyms:*Erysiphe varium Fr. 1822*Uncinula aceris var...
is a fungus that causes powdery mildew on tree leaves.
This fungus attacks the leaves of the Acer platanoides (Norway Maple) in North America, and in Great Britain and/or Ireland, Acer palmatum
Acer palmatum
Acer palmatum, called Japanese Maple or Smooth Japanese Maple is a species of woody plant native to Japan, North Korea, South Korea, China, eastern Mongolia, and southeast Russia. Many different cultivars of this maple have been selected and they are grown worldwide for their attractive leaf...
(also known as the Japanese Maple or Smooth Japanese Maple).
Reproduction
Powdery mildew fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction is via chasmothecia (formerly cleistothecium), a type of ascocarpAscocarp
An ascocarp, or ascoma , is the fruiting body of an ascomycete fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and may contain millions of asci, each of which typically contains eight ascospores...
. Within each ascocarp are several asci
Ascus
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. On average, asci normally contain eight ascospores, produced by a meiotic cell division followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can number one , two, four, or multiples...
. Over time, ascospores mature and are released to initiate new infections. Conditions necessary for spore maturation differ among species.
See also
- ErysiphalesErysiphalesErysiphales are an order of ascomycete fungi. The order contains one family, Erysiphaceae. Many of them cause plant diseases called powdery mildew.-Systematics:The order contains one family , 28 genera and approximately 100 species...
- Oidium (genus)Oidium (genus)Oidium is a genus of Deuteromycetes, where traditionally most anamorphs of the order Erysiphales are included. Most of them are plant pathogens causing different forms of powdery mildew, for example:*Oidium alphitoides Oidium is a genus of Deuteromycetes, where traditionally most anamorphs of the...
- Powdery mildew (barley)Powdery mildew (barley)Powdery mildew is a fungal disease of barley caused by Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei. The disease has a worldwide distribution and is most damaging in cool, wet climates...

