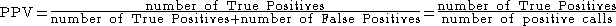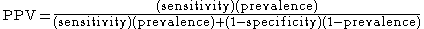Positive predictive value
Encyclopedia
In statistics
and diagnostic testing, the positive predictive value, or precision rate is the proportion of subjects with positive test results who are correctly diagnosed. It is a critical measure of the performance of a diagnostic method, as it reflects the probability that a positive test reflects the underlying condition being tested for. Its value does however depend on the prevalence
of the outcome of interest, which may be unknown for a particular target population. The PPV can be derived using Bayes' theorem
.
Although sometimes used synonymously, a positive predictive value generally refers to what is established by control groups, while a post-test probability
rather refers to a probability for an individual. Still, if the individual's pre-test probability of the target condition is the same as the prevalence in the control group used to establish the positive predictive value, the two are numerically equal.
where a "true positive" is the event that the test makes a positive prediction, and the subject has a positive result under the gold standard, and a "false positive" is the event that the test makes a positive prediction, and the subject has a negative result under the gold standard.
The following diagram illustrates how the positive predictive value, negative predictive value
, sensitivity
, and specificity
are related.
Note that the positive and negative predictive values can only be estimated using data from a cross-sectional study
or other population-based study in which valid prevalence
estimates may be obtained. In contrast, the sensitivity and specificity can be estimated from case-control studies.
If the prevalence, sensitivity, and specificity are known, the positive predictive value can be obtained from the following identity:
(FOB) screen test is used in 2030 people to look for bowel cancer:
The small positive predictive value (PPV = 10%) indicates that many of the positive results from this testing procedure are false positives. Thus it will be necessary to follow up any positive result with a more reliable test to obtain a more accurate assessment as to whether cancer is present. Nevertheless, such a test may be useful if it is inexpensive and convenient.
To overcome this problem, NPV and PPV should only be used if the ratio of the number of patients in the disease group and the number of patients in the healthy control group used to establish the NPV and PPV is equivalent to the prevalence of the diseases in the studied population, or, in case two disease groups are compared, if the ratio of the number of patients in disease group 1 and the number of patients in disease group 2 is equivalent to the ratio of the prevalences of the two diseases studied. Otherwise, positive and negative likehood ratios
are more accurate than NPV and PPV, because likelihood ratios do not depend on prevalence.
When an individual being tested has a different pre-test probability of having a condition than the control groups used to establish the PPV and NPV, the PPV and NPV are generally distinguished from the positive and negative post-test probabilities, with the PPV and NPV referring to the ones established by the control groups, and the post-test probabilities referring to the ones for the tested individual (as estimated, for example, by likehood ratios
). Preferably, in such cases, a large group of equivalent individuals should be studied, in order to establish separate positive and negative predictive values for use of the test in such individuals.
An example is the microbiological throat swab used in patients with a sore throat. Usually publications stating PPV of a throat swab are reporting on the probability that this bacteria is present in the throat, rather than that the patient is ill from the bacteria found. If presence of this bacteria always resulted in a sore throat, then the PPV would be very useful. However the bacteria may colonise individuals in a harmless way and never result in infection or disease. Sore throats occurring in these individuals is caused by other agents such as a virus. In this situation the gold standard used in the evaluation study represents only the presence of bacteria (that might be harmless) but not a causal bacterial sore throat illness. It can be proven that this problem will affect positive predictive value far more than negative predictive value. To evaluate diagnostic tests where the gold standard looks only at potential causes of disease, one may use an extension of the predictive value termed the Etiologic Predictive Value.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
and diagnostic testing, the positive predictive value, or precision rate is the proportion of subjects with positive test results who are correctly diagnosed. It is a critical measure of the performance of a diagnostic method, as it reflects the probability that a positive test reflects the underlying condition being tested for. Its value does however depend on the prevalence
Prevalence
In epidemiology, the prevalence of a health-related state in a statistical population is defined as the total number of cases of the risk factor in the population at a given time, or the total number of cases in the population, divided by the number of individuals in the population...
of the outcome of interest, which may be unknown for a particular target population. The PPV can be derived using Bayes' theorem
Bayes' theorem
In probability theory and applications, Bayes' theorem relates the conditional probabilities P and P. It is commonly used in science and engineering. The theorem is named for Thomas Bayes ....
.
Although sometimes used synonymously, a positive predictive value generally refers to what is established by control groups, while a post-test probability
Pre- and post-test probability
Pre-test probability and post-test probability are the subjective probabilities of the presence of a condition before and after a diagnostic test, respectively...
rather refers to a probability for an individual. Still, if the individual's pre-test probability of the target condition is the same as the prevalence in the control group used to establish the positive predictive value, the two are numerically equal.
Definition
The Positive Predictive Value is defined aswhere a "true positive" is the event that the test makes a positive prediction, and the subject has a positive result under the gold standard, and a "false positive" is the event that the test makes a positive prediction, and the subject has a negative result under the gold standard.
The following diagram illustrates how the positive predictive value, negative predictive value
Negative predictive value
In statistics and diagnostic testing, the negative predictive value is a summary statistic used to describe the performance of a diagnostic testing procedure. It is defined as the proportion of subjects with a negative test result who are correctly diagnosed. A high NPV means that when the test...
, sensitivity
Sensitivity
Stimulus|Sensitivity may refer to:* Sensitivity , the ability to react to a stimulus* Sensitivity , the strength of physical or emotional reaction in people* Sensitivity , variations in process dynamics and control systems...
, and specificity
Specificity
Specificity may refer to:* Being specific * Specificity , the proportion of negatives in a binary classification test which are correctly identified...
are related.
Note that the positive and negative predictive values can only be estimated using data from a cross-sectional study
Cross-sectional study
Cross-sectional studies form a class of research methods that involve observation of all of a population, or a representative subset, at one specific point in time...
or other population-based study in which valid prevalence
Prevalence
In epidemiology, the prevalence of a health-related state in a statistical population is defined as the total number of cases of the risk factor in the population at a given time, or the total number of cases in the population, divided by the number of individuals in the population...
estimates may be obtained. In contrast, the sensitivity and specificity can be estimated from case-control studies.
If the prevalence, sensitivity, and specificity are known, the positive predictive value can be obtained from the following identity:
Worked example
Suppose the fecal occult bloodFecal occult blood
Fecal occult blood refers to blood in the feces that is not visibly apparent. A fecal occult blood test checks for hidden blood in the stool...
(FOB) screen test is used in 2030 people to look for bowel cancer:
The small positive predictive value (PPV = 10%) indicates that many of the positive results from this testing procedure are false positives. Thus it will be necessary to follow up any positive result with a more reliable test to obtain a more accurate assessment as to whether cancer is present. Nevertheless, such a test may be useful if it is inexpensive and convenient.
Other individual factors
Note that the PPV is not intrinsic to the test—it depends also on the prevalence http://www.ipathology.com/ipathology/effect-of-disease-prevale.html. PPV is directly proportional to the prevalence of the disease or condition. In the above example, if the group of people tested had included a higher proportion of people with bowel cancer, then the PPV would probably come out higher and the NPV lower. If everybody in the group had bowel cancer, the PPV would be 100% and the NPV 0%.To overcome this problem, NPV and PPV should only be used if the ratio of the number of patients in the disease group and the number of patients in the healthy control group used to establish the NPV and PPV is equivalent to the prevalence of the diseases in the studied population, or, in case two disease groups are compared, if the ratio of the number of patients in disease group 1 and the number of patients in disease group 2 is equivalent to the ratio of the prevalences of the two diseases studied. Otherwise, positive and negative likehood ratios
Likelihood ratios in diagnostic testing
In evidence-based medicine, likelihood ratios are used for assessing the value of performing a diagnostic test. They use the sensitivity and specificity of the test to determine whether a test result usefully changes the probability that a condition exists.-Calculation:Two versions of the...
are more accurate than NPV and PPV, because likelihood ratios do not depend on prevalence.
When an individual being tested has a different pre-test probability of having a condition than the control groups used to establish the PPV and NPV, the PPV and NPV are generally distinguished from the positive and negative post-test probabilities, with the PPV and NPV referring to the ones established by the control groups, and the post-test probabilities referring to the ones for the tested individual (as estimated, for example, by likehood ratios
Likelihood ratios in diagnostic testing
In evidence-based medicine, likelihood ratios are used for assessing the value of performing a diagnostic test. They use the sensitivity and specificity of the test to determine whether a test result usefully changes the probability that a condition exists.-Calculation:Two versions of the...
). Preferably, in such cases, a large group of equivalent individuals should be studied, in order to establish separate positive and negative predictive values for use of the test in such individuals.
Different target conditions
PPV is used to indicate the probability that in case of a positive test, that the patient really has the specified disease. However there may be more than one cause for a disease and any single potential cause may not always result in the overt disease seen in a patient. There is potential to mixup related target conditions of PPV and NPV, such as interpreting the PPV or NPV of a test as having a disease, when that PPV or NPV value actually refers only to a predisposition of having that disease.An example is the microbiological throat swab used in patients with a sore throat. Usually publications stating PPV of a throat swab are reporting on the probability that this bacteria is present in the throat, rather than that the patient is ill from the bacteria found. If presence of this bacteria always resulted in a sore throat, then the PPV would be very useful. However the bacteria may colonise individuals in a harmless way and never result in infection or disease. Sore throats occurring in these individuals is caused by other agents such as a virus. In this situation the gold standard used in the evaluation study represents only the presence of bacteria (that might be harmless) but not a causal bacterial sore throat illness. It can be proven that this problem will affect positive predictive value far more than negative predictive value. To evaluate diagnostic tests where the gold standard looks only at potential causes of disease, one may use an extension of the predictive value termed the Etiologic Predictive Value.
See also
- Binary classificationBinary classificationBinary classification is the task of classifying the members of a given set of objects into two groups on the basis of whether they have some property or not. Some typical binary classification tasks are...
- Sensitivity and specificitySensitivity and specificitySensitivity and specificity are statistical measures of the performance of a binary classification test, also known in statistics as classification function. Sensitivity measures the proportion of actual positives which are correctly identified as such Sensitivity and specificity are statistical...
- Negative predictive valueNegative predictive valueIn statistics and diagnostic testing, the negative predictive value is a summary statistic used to describe the performance of a diagnostic testing procedure. It is defined as the proportion of subjects with a negative test result who are correctly diagnosed. A high NPV means that when the test...
- False discovery rateFalse discovery rateFalse discovery rate control is a statistical method used in multiple hypothesis testing to correct for multiple comparisons. In a list of rejected hypotheses, FDR controls the expected proportion of incorrectly rejected null hypotheses...
- Relevance (information retrieval)Relevance (information retrieval)In information science and information retrieval, relevance denotes how well a retrieved document or set of documents meets the information need of the user.-Types:...
- Receiver-operator characteristic
- Gain (information retrieval)Gain (information retrieval)The gain, also called improvement over random can be specified for a classifier and is an important measure to describe the performance of it.- Definition :...