
Porosimetry
Encyclopedia
Porosimetry is an analytical technique
used to determine various quantifiable aspects of a material's porous
nature, such as pore diameter, total pore volume, surface area
, and bulk
and absolute densities
.
The technique involves the intrusion of a non-wetting
liquid (often mercury
) at high pressure
into a material through the use of a porosimeter. The pore size can be determined based on the external pressure needed to force the liquid into a pore against the opposing force of the liquid's surface tension
.
A force balance equation known as Washburn's equation
for the above material having cylindrical
pores is given as:
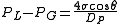
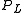 = pressure of liquid
= pressure of liquid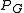 = pressure of gas
= pressure of gas = surface tension of liquid
= surface tension of liquid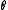 = contact angle
= contact angle
of intrusion liquid = pore diameter
= pore diameter
Since the technique is usually done under vacuum
, the gas pressure begins at zero. The contact angle
of mercury
with most solids is between 135° and 142°, so an average of 140° can be taken without much error. The surface tension
of mercury at 20 °C under vacuum is 480 mN/m
. With the various substitutions, the equation becomes:

As pressure increases, so does the cumulative pore volume. From the cumulative pore volume, one can find the pressure and pore diameter where 50% of the total volume has been added to give the median pore diameter.
Measurement
Measurement is the process or the result of determining the ratio of a physical quantity, such as a length, time, temperature etc., to a unit of measurement, such as the metre, second or degree Celsius...
used to determine various quantifiable aspects of a material's porous
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0–1, or as a percentage between 0–100%...
nature, such as pore diameter, total pore volume, surface area
Surface area
Surface area is the measure of how much exposed area a solid object has, expressed in square units. Mathematical description of the surface area is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of a curve. For polyhedra the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces...
, and bulk
Bulk density
Bulk density is a property of powders, granules and other "divided" solids, especially used in reference to mineral components , chemical substances, ingredients, foodstuff or any other masses of corpuscular or particulate matter. It is defined as the mass of many particles of the material...
and absolute densities
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
.
The technique involves the intrusion of a non-wetting
Wetting
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface, resulting from intermolecular interactions when the two are brought together. The degree of wetting is determined by a force balance between adhesive and cohesive forces.Wetting is important in the bonding or adherence of...
liquid (often mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
) at high pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
into a material through the use of a porosimeter. The pore size can be determined based on the external pressure needed to force the liquid into a pore against the opposing force of the liquid's surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
.
A force balance equation known as Washburn's equation
Washburn's equation
In physics, the Washburn's equation describes capillary flow in a bundle of parallel cylindrical tubes; it is extended with some issues also to imbibition into porous materials...
for the above material having cylindrical
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder is one of the most basic curvilinear geometric shapes, the surface formed by the points at a fixed distance from a given line segment, the axis of the cylinder. The solid enclosed by this surface and by two planes perpendicular to the axis is also called a cylinder...
pores is given as:
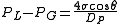
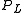 = pressure of liquid
= pressure of liquid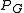 = pressure of gas
= pressure of gas = surface tension of liquid
= surface tension of liquid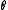 = contact angle
= contact angleContact angle
The contact angle is the angle at which a liquid/vapor interface meets a solid surface. The contact angle is specific for any given system and is determined by the interactions across the three interfaces. Most often the concept is illustrated with a small liquid droplet resting on a flat...
of intrusion liquid
 = pore diameter
= pore diameterSince the technique is usually done under vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
, the gas pressure begins at zero. The contact angle
Contact angle
The contact angle is the angle at which a liquid/vapor interface meets a solid surface. The contact angle is specific for any given system and is determined by the interactions across the three interfaces. Most often the concept is illustrated with a small liquid droplet resting on a flat...
of mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
with most solids is between 135° and 142°, so an average of 140° can be taken without much error. The surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
of mercury at 20 °C under vacuum is 480 mN/m
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
. With the various substitutions, the equation becomes:

As pressure increases, so does the cumulative pore volume. From the cumulative pore volume, one can find the pressure and pore diameter where 50% of the total volume has been added to give the median pore diameter.

