
Pompeian Styles
Encyclopedia
The Pompeian Styles are four periods which are distinguished in ancient Roman mural painting. They were originally delineated and described by the German archaeologist August Mau
, 1840 – 1909, from the excavation of wall paintings at Pompeii
, which is one of the largest group of surviving examples of Roman frescoes.
The wall painting styles have allowed art historians to delineate the various phases of interior decoration in the centuries leading up to the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD, which both destroyed the city and preserved the paintings, and between stylistic shifts in Roman art
. In the succession of styles, there is a reiteration of stylistic themes. The paintings also tell a great deal about the prosperity of the area and specific tastes during the times.
The main purpose of these frescoes was to reduce the claustrophobic interiors of Roman rooms, which were windowless and dark. The paintings, full of color and life, brightened up the interior and made the room feel more spacious.
 The First style, also referred to as structural, incrustation or masonry style, was most popular from 200 BC
The First style, also referred to as structural, incrustation or masonry style, was most popular from 200 BC
until 80 BC
. It is characterized by the simulation
of marble (marble veneering), with other simulated elements (e.g. suspended alabaster
discs in vertical lines, 'wooden' beams in yellow and 'pillars' and 'cornices' in white), and the use of vivid colour, both being a sign of wealth. This style was a replica of that found in the Ptolemaic palaces of the near east, where the walls were inset with real stones and marbles, and also reflects the spread of Hellenistic culture as Rome interacted and conquered other Greek and Hellenistic states in this period. Mural reproductions of Greek paintings are also found. This style divided the wall into various, multi-colored patterns that took the place of extremely expensive cut stone. The First Style was also used with other styles for decorating the lower sections of walls that were not seen as much as the higher levels.
An example would be the wall painting in the Samnite House in Herculaneum (late 2nd century BC).
 The Second style, architectural style, or 'illusionism' dominated the 1st century BC, where walls were decorated with architectural features and trompe l'oeil
The Second style, architectural style, or 'illusionism' dominated the 1st century BC, where walls were decorated with architectural features and trompe l'oeil
(trick of the eye) compositions. Early on, elements of this style are reminiscent of the First Style, but this slowly starts to be substituted element by element. This technique consists of highlighting elements to pass them off as three-dimensional realities - columns for example, dividing the wall-space into zones - and was a method widely used by the Romans.
It is characterized by use of relative perspective (not precise linear perspective because this style involves mathematical concepts and scientific proportions like that of the Renaissance) to create trompe l'oeil in wall paintings. The picture plane was pushed farther back into the wall by painted architectonic features such as Ionic columns or stage platforms. These wall paintings counteracted the claustrophobic nature of the small, windowless rooms of Roman houses.
Images and landscapes began to be introduced to the first style around 90 BC, and gained ground from 70 BC onwards, along with illusionistic and architectonic motives. Decoration had to give the greatest possible impression of depth. Imitations of images appeared, at first in the higher section, then (after 50 BC) in the background of landscapes which provided a stage for mythological stories, theatrical masks, or decorations.
During the reign of Augustus
, the style evolved. False architectural elements opened up wide expanses with which to paint artistic compositions. A structure inspired by stage sets developed, whereby one large central tableau is flanked by two smaller ones. In this style, the illusionistic tendency continued, with a 'breaking up' of walls with painted architectural elements or scenes. The landscape elements eventually took over to cover the entire wall, with no framing device, so it looked to the viewer as if he or she was merely looking out of a room onto a real scene. Basically, the more developed Second Style was the antithesis of the First Style. Instead on confining and strengthening the walls, the goal was to break down the wall to show scenes of nature and the outside world. Much of the depth of the mature Second Style comes from the use of aerial (atmospheric) perspective that blurred the appearance of objects further away. Thus, the foreground is rather precise while the background is somewhat indistinctly purple, blue, and gray.
One of the most recognized and unique pieces representing the Second Style is the Dionysiac mystery frieze in the Villa of the Mysteries. This work depicts the Dionysian Cult that was made mostly women. In the scene, however,one boy is depicted.
Fashionable particularly from the 40s BC onwards, it began to wane in the final decades BC.
An example is the architectural painting at the Villa Boscoreale
at Boscoreale
(c. 40 BC).
-0 BC] as a reaction to the austerity of the previous period. It leaves room for more figurative and colorful decoration, with an overall more ornamental feeling, and often presents great finesse in execution. This style is typically noted as simplistically elegant.
Its main characteristic was departure from illusionistic devices, although these (along with figural representation) later crept back into this style. It obeyed strict rules of symmetry dictated by the central element, dividing the wall into 3 horizontal and 3-5 vertical zones. The vertical zones would be divided up by geometric motifs or bases, or slender columns of foliage hung around candelabra
. Delicate motifs of birds or semi-fantastical animals appeared in the background. Plants and characteristically Egyptian animals were often introduced, part of the Egyptomania in Roman art after Augustus's defeat of Cleopatra and annexation of Egypt in 30 BC.
These paintings were decorated with delicate linear fantasies, predominantly monochromatic, that replaced the three-dimensional worlds of the Second Style. An example is the Villa of Livia
in Prima Porta (c. 30-20 BC). Also included in this style are paintings similar to the one found in Cubiculum 15 of the Villa of Agrippa Postumus
in Boscotrecase
(ca. 10 BC). These involve a delicate architectural frame over a blank, monochromatic background with only a small scene located in the middle, like a tiny floating landscape.
It was found in Rome
until 40
AD and in the Pompeii area until 60
AD.
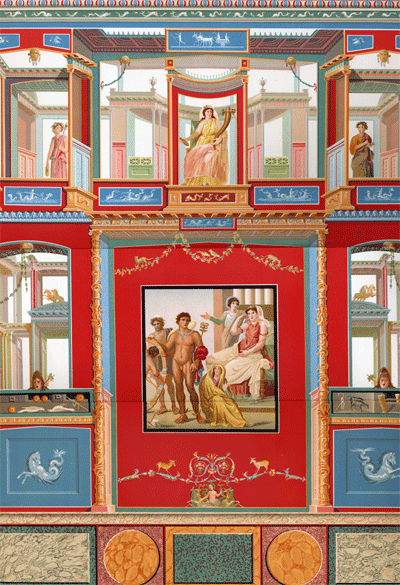 Characterized as a baroque
Characterized as a baroque
reaction to the Third Style's mannerism, the Fourth Style in Roman wall painting (ca. 60–79 AD) is generally less ornamented than its predecessor. The style was, however, much more complex. It revives large-scale narrative painting and panoramic vistas while retaining the architectural details of the Second and First Styles. In the Julio-Claudian phase (ca. 20–54 AD), a textile like quality dominates and tendrils seem to connect all the elements on the wall. The colors warm up once again, and they are used to advantage in the depiction of scenes drawn from mythology.
The overall feeling of the walls typically formed a mosaic of framed pictures that took up entire walls. The lower zones of these walls tended to be composed of the First Style. Panels were also used with floral designs on the walls. A prime example of the Fourth Style is the Ixion Room in the House of Vetti in Pompeii. One of the largest contributions seen in the Fourth Style is the advancement of still life with intense space and light. Shading was very important in the Roman still life. This style was never truly seen again until 17th and 18th centuries with the Dutch.
August Mau
August Mau was a prominent German art historian and archaeologist who worked with the Deutsches Archäologisches Institut while studying and classifying the Roman paintings at Pompeii, which was destroyed with the town of Herculaneum by volcanic eruption in 79 AD...
, 1840 – 1909, from the excavation of wall paintings at Pompeii
Pompeii
The city of Pompeii is a partially buried Roman town-city near modern Naples in the Italian region of Campania, in the territory of the comune of Pompei. Along with Herculaneum, Pompeii was destroyed and completely buried during a long catastrophic eruption of the volcano Mount Vesuvius spanning...
, which is one of the largest group of surviving examples of Roman frescoes.
The wall painting styles have allowed art historians to delineate the various phases of interior decoration in the centuries leading up to the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD, which both destroyed the city and preserved the paintings, and between stylistic shifts in Roman art
Roman art
Roman art has the visual arts made in Ancient Rome, and in the territories of the Roman Empire. Major forms of Roman art are architecture, painting, sculpture and mosaic work...
. In the succession of styles, there is a reiteration of stylistic themes. The paintings also tell a great deal about the prosperity of the area and specific tastes during the times.
The main purpose of these frescoes was to reduce the claustrophobic interiors of Roman rooms, which were windowless and dark. The paintings, full of color and life, brightened up the interior and made the room feel more spacious.
First Style

200 BC
Year 200 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Maximus and Cotta...
until 80 BC
80 BC
Year 80 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sulla and Metellus...
. It is characterized by the simulation
Trompe l'oeil
Trompe-l'œil, which can also be spelled without the hyphen in English as trompe l'oeil, is an art technique involving extremely realistic imagery in order to create the optical illusion that the depicted objects appear in three dimensions.-History in painting:Although the phrase has its origin in...
of marble (marble veneering), with other simulated elements (e.g. suspended alabaster
Alabaster
Alabaster is a name applied to varieties of two distinct minerals, when used as a material: gypsum and calcite . The former is the alabaster of the present day; generally, the latter is the alabaster of the ancients...
discs in vertical lines, 'wooden' beams in yellow and 'pillars' and 'cornices' in white), and the use of vivid colour, both being a sign of wealth. This style was a replica of that found in the Ptolemaic palaces of the near east, where the walls were inset with real stones and marbles, and also reflects the spread of Hellenistic culture as Rome interacted and conquered other Greek and Hellenistic states in this period. Mural reproductions of Greek paintings are also found. This style divided the wall into various, multi-colored patterns that took the place of extremely expensive cut stone. The First Style was also used with other styles for decorating the lower sections of walls that were not seen as much as the higher levels.
An example would be the wall painting in the Samnite House in Herculaneum (late 2nd century BC).
Second Style

Trompe l'oeil
Trompe-l'œil, which can also be spelled without the hyphen in English as trompe l'oeil, is an art technique involving extremely realistic imagery in order to create the optical illusion that the depicted objects appear in three dimensions.-History in painting:Although the phrase has its origin in...
(trick of the eye) compositions. Early on, elements of this style are reminiscent of the First Style, but this slowly starts to be substituted element by element. This technique consists of highlighting elements to pass them off as three-dimensional realities - columns for example, dividing the wall-space into zones - and was a method widely used by the Romans.
It is characterized by use of relative perspective (not precise linear perspective because this style involves mathematical concepts and scientific proportions like that of the Renaissance) to create trompe l'oeil in wall paintings. The picture plane was pushed farther back into the wall by painted architectonic features such as Ionic columns or stage platforms. These wall paintings counteracted the claustrophobic nature of the small, windowless rooms of Roman houses.
Images and landscapes began to be introduced to the first style around 90 BC, and gained ground from 70 BC onwards, along with illusionistic and architectonic motives. Decoration had to give the greatest possible impression of depth. Imitations of images appeared, at first in the higher section, then (after 50 BC) in the background of landscapes which provided a stage for mythological stories, theatrical masks, or decorations.
During the reign of Augustus
Augustus
Augustus ;23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14) is considered the first emperor of the Roman Empire, which he ruled alone from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD.The dates of his rule are contemporary dates; Augustus lived under two calendars, the Roman Republican until 45 BC, and the Julian...
, the style evolved. False architectural elements opened up wide expanses with which to paint artistic compositions. A structure inspired by stage sets developed, whereby one large central tableau is flanked by two smaller ones. In this style, the illusionistic tendency continued, with a 'breaking up' of walls with painted architectural elements or scenes. The landscape elements eventually took over to cover the entire wall, with no framing device, so it looked to the viewer as if he or she was merely looking out of a room onto a real scene. Basically, the more developed Second Style was the antithesis of the First Style. Instead on confining and strengthening the walls, the goal was to break down the wall to show scenes of nature and the outside world. Much of the depth of the mature Second Style comes from the use of aerial (atmospheric) perspective that blurred the appearance of objects further away. Thus, the foreground is rather precise while the background is somewhat indistinctly purple, blue, and gray.
One of the most recognized and unique pieces representing the Second Style is the Dionysiac mystery frieze in the Villa of the Mysteries. This work depicts the Dionysian Cult that was made mostly women. In the scene, however,one boy is depicted.
Fashionable particularly from the 40s BC onwards, it began to wane in the final decades BC.
An example is the architectural painting at the Villa Boscoreale
Villa Boscoreale
Villa Boscoreale is an ancient Roman villa located in the town of Boscoreale, about one and a half kilometers north of Pompeii, southwest of Vesuvius, in Campania, southern Italy. This area was a hunting reserve and also used agriculturally, specializing in wine and olive oil. Evidence in tablets...
at Boscoreale
Boscoreale
Boscoreale is a comune and town in the province of Naples, Campania, located in the Parco Nazionale del Vesuvio under the slopes of Mount Vesuvius, known for the fruit and vineyards of Lacryma Christi del Vesuvio...
(c. 40 BC).
Third Style
The Third style, or ornate style, was popular around 2020 BC
Year 20 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday or Thursday or a leap year starting on Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Tuesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar...
-0 BC] as a reaction to the austerity of the previous period. It leaves room for more figurative and colorful decoration, with an overall more ornamental feeling, and often presents great finesse in execution. This style is typically noted as simplistically elegant.
Its main characteristic was departure from illusionistic devices, although these (along with figural representation) later crept back into this style. It obeyed strict rules of symmetry dictated by the central element, dividing the wall into 3 horizontal and 3-5 vertical zones. The vertical zones would be divided up by geometric motifs or bases, or slender columns of foliage hung around candelabra
Candelabra
"Candelabra" is the traditional term for a set of multiple decorative candlesticks, each of which often holds a candle on each of multiple arms or branches connected to a column or pedestal...
. Delicate motifs of birds or semi-fantastical animals appeared in the background. Plants and characteristically Egyptian animals were often introduced, part of the Egyptomania in Roman art after Augustus's defeat of Cleopatra and annexation of Egypt in 30 BC.
These paintings were decorated with delicate linear fantasies, predominantly monochromatic, that replaced the three-dimensional worlds of the Second Style. An example is the Villa of Livia
Prima Porta
Prima Porta is a suburb of Rome located 12 kilometres north of its center along the Via Flaminia and just a kilometre outside of the Grande Raccordo Anulare highway. It is located on the right bank of the Tiber where the Via Tiberina leads away from the Via Flaminia and another road led off along...
in Prima Porta (c. 30-20 BC). Also included in this style are paintings similar to the one found in Cubiculum 15 of the Villa of Agrippa Postumus
Agrippa Postumus
Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa Postumus , also known as Agrippa Postumus or Postumus Agrippa, was a son of Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa and Julia the Elder. His maternal grandparents were Roman Emperor Augustus and his second wife Scribonia.Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa Postumus was born on June 26, 12 BC, the...
in Boscotrecase
Boscotrecase
Boscotrecase is a comune in the Province of Naples in the Italian region Campania, located about 20 km southeast of Naples...
(ca. 10 BC). These involve a delicate architectural frame over a blank, monochromatic background with only a small scene located in the middle, like a tiny floating landscape.
It was found in Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
until 40
40
Year 40 was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus without colleague...
AD and in the Pompeii area until 60
60
Year 60 was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Afer...
AD.
Fourth Style

Baroque
The Baroque is a period and the style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, literature, dance, and music...
reaction to the Third Style's mannerism, the Fourth Style in Roman wall painting (ca. 60–79 AD) is generally less ornamented than its predecessor. The style was, however, much more complex. It revives large-scale narrative painting and panoramic vistas while retaining the architectural details of the Second and First Styles. In the Julio-Claudian phase (ca. 20–54 AD), a textile like quality dominates and tendrils seem to connect all the elements on the wall. The colors warm up once again, and they are used to advantage in the depiction of scenes drawn from mythology.
The overall feeling of the walls typically formed a mosaic of framed pictures that took up entire walls. The lower zones of these walls tended to be composed of the First Style. Panels were also used with floral designs on the walls. A prime example of the Fourth Style is the Ixion Room in the House of Vetti in Pompeii. One of the largest contributions seen in the Fourth Style is the advancement of still life with intense space and light. Shading was very important in the Roman still life. This style was never truly seen again until 17th and 18th centuries with the Dutch.
Sources
- Metropolitan Museum site on the Styles
- Pompeian 'Style' - a re-examination
- [Gardner's Art Through the Ages]

