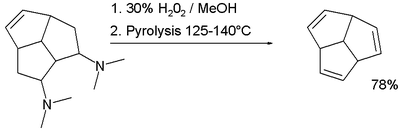
Polyquinane
Encyclopedia
A polyquinane and polyquinene is a saturated or unsaturated
, respectively, polycyclic hydrocarbon
consisting of fused five-membered rings . The simplest member is the bicyclic compound bicyclo[3.3.0]octane. Other members are triquinacene and dodecahedrane
.
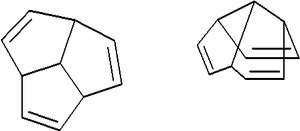 The compound triquinacene (tricyclo[5.2.1.-04,10]deca-2,5,8-triene) is the second member of a family of polyquinenes. It was synthesized in 1964 in the group of R. B. Woodward
The compound triquinacene (tricyclo[5.2.1.-04,10]deca-2,5,8-triene) is the second member of a family of polyquinenes. It was synthesized in 1964 in the group of R. B. Woodward
in connection with its suspected homoaromatic
properties (although it was found to have no such properties), and also as part of a failed attempt to synthesize the then-elusive and much-coveted compound dodecahedrane
. Unlike the related pentacene
, triquinacene is stable, and has a melting point
of 18°C. The final step of its synthesis is a Cope elimination.
Unsaturated compound
In organic chemistry, a saturated compound is a chemical compound that has of a chain of carbon atoms linked together by single bonds and has hydrogen atoms filling all of the other bonding orbitals of the carbon atoms. Alkanes are an example of saturated compounds...
, respectively, polycyclic hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
consisting of fused five-membered rings . The simplest member is the bicyclic compound bicyclo[3.3.0]octane. Other members are triquinacene and dodecahedrane
Dodecahedrane
Dodecahedrane is a chemical compound first synthesised by Leo Paquette of Ohio State University in 1982, primarily for the "aesthetically pleasing symmetry of the dodecahedral framework"....
.
Triquinacene

Robert Burns Woodward
Robert Burns Woodward was an American organic chemist, considered by many to be the preeminent organic chemist of the twentieth century...
in connection with its suspected homoaromatic
Homoaromaticity
Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom...
properties (although it was found to have no such properties), and also as part of a failed attempt to synthesize the then-elusive and much-coveted compound dodecahedrane
Dodecahedrane
Dodecahedrane is a chemical compound first synthesised by Leo Paquette of Ohio State University in 1982, primarily for the "aesthetically pleasing symmetry of the dodecahedral framework"....
. Unlike the related pentacene
Pentacene
Pentacene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of five linearly-fused benzene rings. This highly conjugated compound is an organic semiconductor. The compound generates excitons upon absorption of ultra-violet or visible light; this makes it very sensitive to oxidation...
, triquinacene is stable, and has a melting point
Melting point
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
of 18°C. The final step of its synthesis is a Cope elimination.
See also
- Fused 6 membered rings: the aceneAceneAcenes or polyacenes is a class of organic compounds and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons made up of linearly fused benzene rings. The larger representatives have potential interest in optoelectronic applications and are actively researched in chemistry and electrical engineering...
s - triquinacene is Isomeric with: bullvaleneBullvaleneBullvalene is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C10H10 with the unusual property that the chemical bonds making up the molecule are constantly rearranging as in fluxional molecules...
, diisopropenyldiacetylene