Polybenzimidazole fiber
Encyclopedia
Polybenzimidazole fiber
is a synthetic fiber
with a very high melting point
that also does not readily ignite
, because of its exceptional thermal and chemical stability. The U.S. Federal Trade Commission
definition for PBI fiber is "A manufactured fiber in which the fiber-forming substance is a long chain aromatic polymer having recurring imidazole groups as an integral part of the polymer chain". Kermel, a polyamidoimide, is a related "high performance polymer."
PBI is used to fabricate high-performance protective apparel such as firefighter turnout coats and suits, astronaut space suits, high temperature protective gloves, welders' apparel, race driver suits, braided packings, and aircraft wall fabrics.
from 3,3',4,4'-tetraaminobiphenyl and diphenyl isophthalate (an ester of Isophthalic acid
and phenol
). The resulting polymer is processed into a solution using dimethyl acetamide, then fibered via a dry spinning process.
The first U.S. commercial PBI fiber was produced by Celanese
.
([NH-C=CH-C=CH-CH=C-N=C-]2-[C=CH-C=CH-CH=CH-])n OR (C20N4H12)n of Molar mass
308.33608 ± 0.01764 g
/mol
.
!Chemical Resistance
!Grade
|-
||Acids - concentrated
|style="background:#ffdddd;"|Poor
|-
||Acids - dilute
|style="background:#ffdddd;"|Fair-Poor
|-
||Alcohols
|Good
|-
||Alkalis
|
|-
||Aromatic hydrocarbons
|Good
|-
||Greases and Oils
|Good
|-
||Halogenated Hydrocarbons
|Good
|-
||Ketones
|Good
|-
!Chemical Resistance
!Grade
|}>
It is dyeable to dark shades with basic dyes following caustic pretreatment and resistant to most chemicals.
!Electrical
!Properties
|-
||Dielectric constant @ 1 MHz
|3.2
|-
||Dielectric strength
|21 kV·mm−1
|-
||Volume resistivity
|8x1014 Ω·cm
|-
!Electrical
!Properties
|}>
Features low electrical conductivity and low static electricity buildup.
!Mechanical
!Properties
|-
||Coefficient of friction
|0.19-0.27
|-
||Compressive modulus
|6.2 GPa
|-
||Compressive strength
|400 MPa
|-
||Elongation at break
|3%
|-
||Hardness - Rockwell
|K115
|-
||Izod impact strength
|590 J·m−1 unnotched
|-
||Poisson's ratio
|0.34
|-
||Tensile modulus
|5.9 GPa
|-
||Tensile strength
|160 MPa
|-
!Mechanical
!Properties
|}>
Features abrasion resistance.
!Physical
!Properties
|-
||Char
Yield (under pyrolysis
)
|High
|-
||Density
|1.3 g/cm³
|-
||Flammability
|Does not burn
|-
||Limiting oxygen index
|58%
|-
||Radiation resistance
|Good
|-
||Water absorption - over 24 hours
|0.4%
|-
!Physical
!Properties
|}>
Additional features: will not ignite or smolder (burn slowly without flame), mildew
- and age-resistant, resistant to sparks and welding spatter.
!Thermal
!Properties
!Grade
|-
||Coefficient of thermal expansion
|23×10−6·K−1
|Low
|-
||Heat-deflection temperature - 0.45 MPa
|435 °C (815 °F)
|High
|-
||Thermal conductivity
@ 23 °C (73.4 °F)
|0.41 W·m−1·K−1
|Low
|-
||Upper working temperature
|260–400 °C (500–752 F)
|High
|-
!Thermal
!Properties
!Grade
|}>
Other features: continuous temperature: 540 °C (1,004 °F), does not melt but degrades around the temperature: 760 °C (1,400 °F) under pyrolysis, retains fiber integrity and suppleness up to 540 °C (1,004 °F).
Fiber
Fiber is a class of materials that are continuous filaments or are in discrete elongated pieces, similar to lengths of thread.They are very important in the biology of both plants and animals, for holding tissues together....
is a synthetic fiber
Synthetic fiber
Synthetic fibers are the result of extensive research by scientists to improve on naturally occurring animal and plant fibers. In general, synthetic fibers are created by forcing, usually through extrusion, fiber forming materials through holes into the air, forming a thread...
with a very high melting point
Melting point
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
that also does not readily ignite
Ignite
Ignite is a program for gifted and talented young people in South Australia, created in 1998 and formerly known as SHIP . It is administered by the South Australian Department of Education and Children's Services....
, because of its exceptional thermal and chemical stability. The U.S. Federal Trade Commission
Federal Trade Commission
The Federal Trade Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, established in 1914 by the Federal Trade Commission Act...
definition for PBI fiber is "A manufactured fiber in which the fiber-forming substance is a long chain aromatic polymer having recurring imidazole groups as an integral part of the polymer chain". Kermel, a polyamidoimide, is a related "high performance polymer."
PBI is used to fabricate high-performance protective apparel such as firefighter turnout coats and suits, astronaut space suits, high temperature protective gloves, welders' apparel, race driver suits, braided packings, and aircraft wall fabrics.
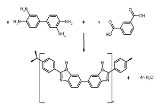
Production
PBI is prepared by step-growth polymerizationStep-growth polymerization
Step-growth polymerization refers to a type of polymerization mechanism in which bi-functional or multifunctional monomers react to form first dimers, then trimers, longer oligomers and eventually long chain polymers. Many naturally occurring and some synthetic polymers are produced by step-growth...
from 3,3',4,4'-tetraaminobiphenyl and diphenyl isophthalate (an ester of Isophthalic acid
Isophthalic acid
Isophthalic acid is an organic compound with the formula C6H42. This colourless solid is an isomer of phthalic acid and terephthalic acid. These aromatic dicarboxylic acids are used as precursors to commercially important polymers, e.g. the fire-resistant material Nomex...
and phenol
Phenol
Phenol, also known as carbolic acid, phenic acid, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid. The molecule consists of a phenyl , bonded to a hydroxyl group. It is produced on a large scale as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds...
). The resulting polymer is processed into a solution using dimethyl acetamide, then fibered via a dry spinning process.
The first U.S. commercial PBI fiber was produced by Celanese
Celanese
Celanese Corporation is a Fortune 500 global technology and specialty materials company with its headquarters in Dallas, Texas. The company is a leading producer of acetyl products, which are intermediate chemicals for nearly all major industries, and is the world's largest producer of vinyl...
.
PBI fiber characteristics
The chemical formula of poly[2,2’-(m-phenylen)-5,5’ bibenzimidazol] (PBI) is believed to be:([NH-C=CH-C=CH-CH=C-N=C-]2-[C=CH-C=CH-CH=CH-])n OR (C20N4H12)n of Molar mass
Molar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
308.33608 ± 0.01764 g
Gram
The gram is a metric system unit of mass....
/mol
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
.
Chemical resistance
!Grade
|-
||Acids - concentrated
|style="background:#ffdddd;"|Poor
|-
||Acids - dilute
|style="background:#ffdddd;"|Fair-Poor
|-
||Alcohols
|Good
|-
||Alkalis
|
|-
||Aromatic hydrocarbons
|Good
|-
||Greases and Oils
|Good
|-
||Halogenated Hydrocarbons
|Good
|-
||Ketones
|Good
|-
!Chemical Resistance
!Grade
|}>
It is dyeable to dark shades with basic dyes following caustic pretreatment and resistant to most chemicals.
Electrical Properties
!Properties
|-
||Dielectric constant @ 1 MHz
|3.2
|-
||Dielectric strength
|21 kV·mm−1
|-
||Volume resistivity
|8x1014 Ω·cm
|-
!Electrical
!Properties
|}>
Features low electrical conductivity and low static electricity buildup.
Mechanical Properties
!Properties
|-
||Coefficient of friction
|0.19-0.27
|-
||Compressive modulus
|6.2 GPa
|-
||Compressive strength
|400 MPa
|-
||Elongation at break
|3%
|-
||Hardness - Rockwell
|K115
|-
||Izod impact strength
|590 J·m−1 unnotched
|-
||Poisson's ratio
|0.34
|-
||Tensile modulus
|5.9 GPa
|-
||Tensile strength
|160 MPa
|-
!Mechanical
!Properties
|}>
Features abrasion resistance.
Physical Properties
!Properties
|-
||Char
Char
Char is the solid material that remains after light gases and tar coal tar have been driven out or released from a carbonaceous material during the initial stage of combustion, which is known as carbonization, charring, devolatilization or pyrolysis.Further stages of efficient combustion are...
Yield (under pyrolysis
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures without the participation of oxygen. It involves the simultaneous change of chemical composition and physical phase, and is irreversible...
)
|High
|-
||Density
|1.3 g/cm³
|-
||Flammability
|Does not burn
|-
||Limiting oxygen index
|58%
|-
||Radiation resistance
|Good
|-
||Water absorption - over 24 hours
|0.4%
|-
!Physical
!Properties
|}>
Additional features: will not ignite or smolder (burn slowly without flame), mildew
Mildew
Mildew refers to certain kinds of molds or fungi.In Old English, it meant honeydew , and later came to mean mildew in the modern sense of mold or fungus....
- and age-resistant, resistant to sparks and welding spatter.
Thermal Properties
!Properties
!Grade
|-
||Coefficient of thermal expansion
|23×10−6·K−1
|Low
|-
||Heat-deflection temperature - 0.45 MPa
|435 °C (815 °F)
|High
|-
||Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
@ 23 °C (73.4 °F)
|0.41 W·m−1·K−1
|Low
|-
||Upper working temperature
|260–400 °C (500–752 F)
|High
|-
!Thermal
!Properties
!Grade
|}>
Other features: continuous temperature: 540 °C (1,004 °F), does not melt but degrades around the temperature: 760 °C (1,400 °F) under pyrolysis, retains fiber integrity and suppleness up to 540 °C (1,004 °F).

