
Polarization-maintaining optical fiber
Encyclopedia
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
in which the polarization of linearly polarized
Linear polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation...
light waves launched into the fiber is maintained during propagation
Wave propagation
Wave propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel.With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves....
, with little or no cross-coupling of optical power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
between the polarization mode
Normal mode
A normal mode of an oscillating system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. The frequencies of the normal modes of a system are known as its natural frequencies or resonant frequencies...
s. Such fiber is used in special applications where preserving polarization is essential.
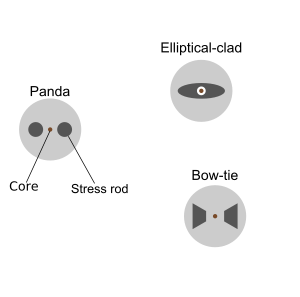
Several different designs of PM fiber are used. Most work by inducing stress
Stress (physics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a measure of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Quantitatively, it is a measure of the average force per unit area of a surface within the body on which internal forces act. These internal forces are a reaction to external forces applied on the body...
in the core via a non-circular cladding
Cladding (fiber optics)
Cladding is one or more layers of material of lower refractive index, in intimate contact with a core material of higher refractive index. The cladding causes light to be confined to the core of the fiber by total internal reflection at the boundary between the two. Light propagation in the...
cross-section
Cross section (geometry)
In geometry, a cross-section is the intersection of a figure in 2-dimensional space with a line, or of a body in 3-dimensional space with a plane, etc...
, or via rods of another material included within the cladding. Several different shapes of rod are used, and the resulting fiber is sold under brand names such as "Panda" and "Bow-tie". The differences in performance between these types of fiber are subtle. Some of the differences are explained in the article "PANDA-style fibers move beyond telecom".
Polarization-maintaining optical fibers are used in special applications, such as in fiber optic sensing, interferometry
Interferometry
Interferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
and quantum key distribution. They are also commonly used in telecommunications for the connection between a source laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
and a modulator, since the modulator requires polarized light as input. They are rarely used for long-distance transmission, because PM fiber is expensive and has higher attenuation than singlemode fiber.
Polarization-maintaining fiber will not polarize light like a polarizer
Polarizer
A polarizer is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular...
does. Rather, PM fiber maintains the existing polarization of linearly polarized light that is launched into the fiber with the correct orientation. If the polarization of the input light is not aligned with the stress direction in the fiber, the output will vary between linear and circular polarization
Circular polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization in which the electric field of the passing wave does not change strength but only changes direction in a rotary type manner....
(and generally will be elliptically polarized
Elliptical polarization
In electrodynamics, elliptical polarization is the polarization of electromagnetic radiation such that the tip of the electric field vector describes an ellipse in any fixed plane intersecting, and normal to, the direction of propagation...
). The exact polarization will then be sensitive to variations in temperature and stress in the fiber.
The output of a PM fiber is typically characterized by its polarization extinction ratio (PER)—the ratio of correctly to incorrectly polarized light, expressed in decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s. The quality of PM patchcords and pigtails can be characterized with a PER meter.
External links
- Fujikura's PANDA Fiber Specs for the most common type of PM fiber

